 W
WThe Bion satellites, also named Biocosmos, is a series of Soviet biosatellites focused on space medicine. They are part of the Kosmos satellites.
 W
WBion-M No.1 (Бион-М) is a Russian robotic space mission, part of the Bion series focused on space medicine.
 W
WKosmos 690, or Bion 2, was a Bion satellite launched by the Soviet Union.
 W
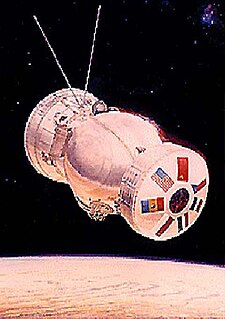
WKosmos 782 was a Bion satellite. It carried 14 experiments prepared by seven countries in all, with participation from scientists in France, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Poland, Romania, United States and the Soviet Union.
 W
WKosmos 936 or Bion 4 was a Bion satellite. The mission involved nine countries in a series of biomedical research experiments. The experiments were primarily follow-ups to the Bion 3 flight. Scientists from the Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, France, Hungary, Poland, Romania, the United States and the Soviet Union conducted experiments in physics and biology on the mission.
 W
WBion 5, or also Kosmos 1129 was a Bion satellite. It was a biomedical research mission involving scientists from nine countries. Among the experiments was the first attempt to breed mammals in space, which proved unsuccessful. The mission ended after 18.5 days, on 14 October 1979. The mission had the cooperation of the Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, France, Hungary, Poland, Romania, the United States and the Soviet Union.
 W
WKosmos 1514 or Bion 6 was a biomedical spaceflight research mission that was launched on 12 December 1983. It was part of the Bion satellite program.
 W
WKosmos 1667, or Bion 7 was a biomedical research mission satellite involving scientists from nine countries. It was part of the Bion program. This mission was the scientific participation of nine countries.
 W
WBion 8 or Kosmos 1887 was a Bion satellite.
 W
WKosmos 2044, or Bion 9 was a biomedical research mission involving in nine countries plus ESA: United Kingdom, Hungarian People's Republic, East Germany, Polish People's Republic, Czechoslovakia, United States, Canada, Australia, Soviet Union and European Space Agency (ESA). It was part of the Bion program.
 W
WKosmos 2229, or Bion 10 was a biomedical research mission involving in ten countries plus ESA. A Russian spacecraft, was launched by a Soyuz-U launch vehicle from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome. It was part of the Bion program.