 W
WA biosatellite is an artificial satellite designed to carry plants or animals in outer space. They are used to research the effects of space on biological matter while in orbit around a celestial body. The first satellite carrying an animal was Soviet Sputnik 2 on November 3, 1957. On August 20, 1960 Soviet Sputnik 5 launched and recovered dogs from orbit Earth orbit.
 W
WA communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. As of 1 August 2020, there are 2,787 artificial satellites in Earth's orbit, with 1,364 of these being communications satellites, used by both private and government organizations. Most communications satellites are in geostationary orbit 22,236 miles (35,785 km) above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite.
 W
WA CubeSat is a type of miniaturized satellite for space research that is made up of multiple cubic modules of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm size. CubeSats have a mass of no more than 1.33 kilograms (2.9 lb) per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are commonly put in orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. As of 1 January 2021, more than 1350 CubeSats have been launched. More than 1200 have been successfully deployed in orbit and more than 90 have been destroyed in launch failures.
 W
WA DemoSat is a boilerplate spacecraft used to test a carrier rocket without risking a real satellite on the launch. They are most commonly flown on the maiden flights of rockets, but have also been flown on return-to-flight missions after launch failures. Defunct satellites from cancelled programmes may be flown as DemoSats, for example the maiden flight of the Soyuz-2 rocket placed an obsolete Zenit-8 satellite onto a sub-orbital trajectory in order to test the rocket's performance.
 W
WAn Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others. The most common type are Earth imaging satellites, that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs; some EO satellites may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation.
 W
WA geosynchronous satellite is a satellite in geosynchronous orbit, with an orbital period the same as the Earth's rotation period. Such a satellite returns to the same position in the sky after each sidereal day, and over the course of a day traces out a path in the sky that is typically some form of analemma. A special case of geosynchronous satellite is the geostationary satellite, which has a geostationary orbit – a circular geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator. Another type of geosynchronous orbit used by satellites is the Tundra elliptical orbit.
 W
WA military satellite is an artificial satellite used for a military purpose. The most common missions are intelligence gathering, navigation and military communications.
 W
WList of passive satellites is a listing of inert or mostly inert satellites, mainly of the Earth. This includes typically various reflector type satellites used for geodesy and atmospheric measurements.
 W
WPseudolite is a contraction of the term "pseudo-satellite," used to refer to something that is not a satellite which performs a function commonly in the domain of satellites. Pseudolites are most often small transceivers that are used to create a local, ground-based Global Positioning System (GPS) alternative. The range of each transceiver's signal is dependent on the power available to the unit.
 W
WThe shuttle pallet satellite was a satellite bus designed to be deployed and then retrieved for return to Earth on NASA's Space Shuttle. It carried a variety of payloads both scientific and military in nature.
 W
WA small satellite, miniaturized satellite, or smallsat is a satellite of low mass and size, usually under 500 kg (1,100 lb). While all such satellites can be referred to as "small", different classifications are used to categorize them based on mass. Satellites can be built small to reduce the large economic cost of launch vehicles and the costs associated with construction. Miniature satellites, especially in large numbers, may be more useful than fewer, larger ones for some purposes – for example, gathering of scientific data and radio relay. Technical challenges in the construction of small satellites may include the lack of sufficient power storage or of room for a propulsion system.
 W
WA reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications.
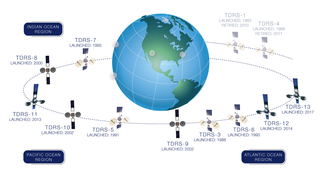 W
WA tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft, the International Space Station, and remote bases like the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station. This system was designed to replace an existing worldwide network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions and uncrewed satellites in low-Earth orbits. The primary system design goal was to increase the amount of time that these spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. These TDRSS satellites are all designed and built to be launched to and function in geosynchronous orbit, 35,786 km (22,236 mi) above the surface of the Earth.