 W
WPan-Arabism is an ideology that espouses the unification of the countries of North Africa and Western Asia from the Atlantic Ocean to the Arabian Sea, which is referred to as the Arab world. It is closely connected to Arab nationalism, which asserts the view that the Arabs constitute a single nation. Its popularity reached its height during the 1950s and 1960s. Advocates of pan-Arabism have often espoused socialist principles and strongly opposed Western political involvement in the Arab world. It also sought to empower Arab states against outside forces by forming alliances and, to a lesser extent, economic co-operation.
 W
WThe Arab Islamic Republic was a proposed unification of Tunisia and Libya in 1974, agreed upon by Libyan head of state Muammar Gaddafi and Tunisian President Habib Bourguiba. Additional countries—Morocco and Algeria—were later included in the proposal, which was never implemented.
 W
WThe Pan-Arab colors are black, white, green, and red. Individually, each of the four Pan-Arab colours were intended to represent a certain historical Arab dynasty, or era. The black was the Abbasid dynastic colour; white was the Umayyad dynastic colour; green was the Fatimid dynastic colour; and red was the Hashemite dynastic colour. The four colours also derived their potency from a verse by 14th century Iraqi poet Safi al-Din al-Hilli: "White are our acts, black our battles, green our fields, and red our swords".
 W
WThe Hashemite Arab Federation was a short-lived country that was formed in 1958 from the union of Iraq and Jordan. Although the name implies a federal structure, it was de facto a confederation.
 W
WThe Federation of Arab Republics was an attempt by Muammar Gaddafi to merge Libya, Egypt and Syria in order to create a unified Arab state. Although approved by a referendum in each country on 1 September 1971, the three countries disagreed on the specific terms of the merger. The federation lasted from 1 January 1972 to 19 November 1977.
 W
WThe Fertile Crescent Plan was an Iraqi Hashemite proposal for the union of the Kingdom of Iraq with Mandatory Syria, Mandatory Palestine, and Transjordan. Nuri as-Said, prime minister of Iraq, presented the plan to British officials during World War II, when it appeared that France had become too weak to hold on to Syria.
 W
WThe Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, originally known as the Gulf Cooperation Council, is a regional intergovernmental political and economic union consisting of all Arab states of the Persian Gulf - Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates - except for Iraq. The Charter of the GCC was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution.
 W
WAl-Hadaf, is a Palestinian weekly political and cultural magazine published in Lebanon.
 W
WThe Arab League, formally the League of Arab States, is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Africa and Western Asia. The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 initially with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined as a member on 5 May 1945. Currently, the League has 22 members, but Syria's participation has been suspended since November 2011.
 W
WAs-Safir, meaning The Ambassador, was a leading Arabic-language daily newspaper in Lebanon. The headquarters of the daily is in Beirut. It has been in circulation from March 1974 until December 2016. The last issue of the paper was published on 31 December 2016. The online version was also closed on the same date.
 W
WThe Unification of Saudi Arabia was a military and political campaign in which the various tribes, sheikhdoms, city-states, emirates, and kingdoms of most of the Arabian Peninsula were conquered by the House of Saud, or Al Saud. Unification started in 1902 and continued until 1932, when the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was proclaimed under the leadership of King Abdulaziz, creating what is sometimes referred to as the Third Saudi State, to differentiate it from the Emirate of Diriyah, the First Saudi State and the Emirate of Nejd, the Second Saudi State, also House of Saud states.
 W
WA Unified Political Command, also translated as Joint Political Command or Unified Political Leadership, was agreed in 1964 between the presidents of Egypt and Iraq as well as between the presidents of Egypt and North Yemen. Both projects were parallel but not linked with each other. The Unified Political Command was meant as a kind of transitional government which should prepare the gradual merger of Iraq with Egypt and North Yemen with Egypt in a new United Arab Republic.
 W
WThe Union of Arab National Olympic Committees is an international organization that unites the 22 National Olympic Committees (NOCs) of the Arab world. It is headquartered in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
 W
WThe United Arab Republic was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 to 1971. It was initially a political union between Egypt and Syria from 1958 until Syria seceded from the union after the 1961 Syrian coup d'état — leaving a rump state. Egypt continued to be known officially as the United Arab Republic until 1971.
 W
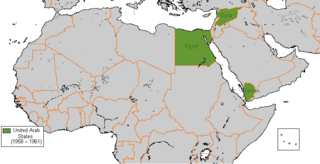
WThe United Arab States was a short-lived confederation of the United Arab Republic and North Yemen from 1958 to 1961.