 W
WThe eusko is a local currency released by the "Eusko Moneta erakundea", and it is one of a number of currencies that are active in the Basque Country. It is mainly used in the Northern Basque Country, France. The currency was created on the 31st of January 2013.
 W
WThe Artsakh dram is a monetary unit of the de facto independent Republic of Artsakh. Although it is legal tender, it is not as widely used as the Armenian dram.
 W
WBerkShares is a local currency that circulates in The Berkshires region of Massachusetts. It was launched on September 29, 2006 by BerkShares Inc., with research and development assistance from the Schumacher Center for a New Economics. The BerkShares website lists around 400 businesses in Berkshire County that accept the currency. Since launch, over 10 million BerkShares have been issued from participating branch offices of local banks. The bills were designed by John Isaacs and were printed by Excelsior Printing on special paper with incorporated security features from Crane & Co.. BerkShares are pegged with an exchange rate to the US dollar, but the Schumacher Center has discussed the possibility of pegging its value to a basket of local goods in order to insulate the local economy against volatility in the US economy.
 W
WCalifornia gold coinage is a broad category of privately-issued coin-like items that were used in place of official currency in the United States territory of California during the gold rush of 1849. Since the federal government reserves the right to issue legal tender coins, California gold coinage is a misnomer and actually references coin-like ingots with a stated tender value, tokens with a stated tender value (denominated), and tokens without a stated tender value (non-denominated). These items are only classified as an ingot if the value of the metal was close to the tender value marked on the piece. In spite of the misnomer, it is common practice among numismatists to label coin-like ingots and denominated tokens as 'coins' while labeling the non-denominated tokens as 'tokens'. Also, the small California Gold coins and tokens have been made in many locations other than California, often with a claim of being from California on the piece and these items are generally labeled as California Gold Coins or Tokens.
 W
WChiemgauer is a regional local currency started in 2003 in Prien am Chiemsee, Bavaria, Germany. Named after the Chiemgau, a region around the Chiemsee lake, it is intended to increase local employment, supporting local culture, and make the local food supply more resilient. The Chiemgauer operates with a fixed exchange rate, tied to the value of the euro: 1 Chiemgauer = €1.
 W
WConder tokens, also known as 18th-century provincial tokens, were a form of privately minted token coinage struck and used during the latter part of the 18th century and the early part of the 19th century in England, Anglesey and Wales, Scotland, and Ireland.
 W
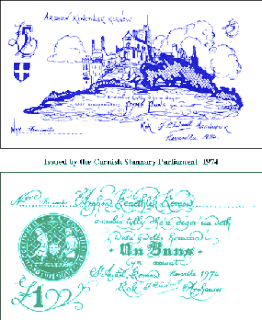
WCurrency, in the form of coins, has been issued in Cornwall periodically since at least the 10th century AD, while banknotes were issued into the 19th century.
 W
WDetroit Community Scrip, also called Detroit Cheers, is a local currency used in Detroit, Michigan, first issued in April 2009. Modeled upon the local scrip that were used during the Great Depression, it is being used to restore local financial confidence following decades of economic decline. The Cheers are backed by U.S. currency and are fully exchangeable for an equal amount of U.S. dollars, backed by several Detroit-based businesses. There are currently $4,500 worth of cheers in circulation. Businesses can sign up to be issuers and print scrip after depositing a matching amount in U.S. dollars and then be entitled to print Cheers. More than 25 businesses have signed up to accept Cheers, but many others informally accept them.
 W
WFindhorn Ecovillage is an experimental architectural community project based at The Park, in Moray, Scotland, near the village of Findhorn. The project's main aim is to demonstrate a sustainable development in environmental, social, and economic terms. Work began in the early 1980s under the auspices of the Findhorn Foundation but now includes a wide diversity of organisations and activities. Numerous different ecological techniques are in use, and the project has won a variety of awards, including the UN-Habitat Best Practice Designation in 1998.
 W
WAs part of the theory of Freiwirtschaft, Freigeld is a monetary unit proposed by Silvio Gesell.
 W
WThe Global Country of World Peace (GCWP) is a non-profit organization that claims to promote Transcendental Meditation, education, and the construction of "buildings for peace" in the world's major cities. Inaugurated by Maharishi Mahesh Yogi, the founder of Transcendental Meditation, on October 7, 2000, the GCWP was originally conceived as "a country without borders for peace-loving people everywhere." It has issued a currency called the "Raam," and its leader is neurologist Tony Nader.
 W
WLabor notes are an alternative currency based on exchange of hours of labor. Two early attempts at implementing labor notes were made by social reformers Josiah Warren and Robert Owen following their experiences attempting to establish a utopian community at New Harmony, Indiana in which currency was prohibited.
 W
WThe Ora is the local currency of Orania, an Afrikaner enclave in South Africa first issued in April 2004. It is pegged at par with the South African rand. The name, recalling that of the town where it circulates, derives from Latin aurum, meaning "gold". The currency is not sanctioned by the South African Reserve Bank.
 W
WReal de alerce or real de madera was a local currency consisting in Fitzroya wood that was used during colonial times in Chiloé Archipelago. It was the Jesuits, established in Chiloé since the 17th century that established Fitzroya as a major export product towards the Viceroyalty of Peru. Real de alerce was also used by some encomenderos to pay their taxes.
 W
WThe Ural franc was a scrip issued in Sverdlovsk (Yekaterinburg) in Russia in 1991 by a team of businessmen and politicians headed by Anton Bakov.
 W
WThe WIR Bank, formerly the Swiss Economic Circle, or WIR, is an independent complementary currency system in Switzerland that serves businesses in hospitality, construction, manufacturing, retail and professional services. WIR issues and manages a private currency, called the WIR Franc, which is used in combination with the Swiss Franc to generate dual-currency transactions.