 W
WAnimal cognition encompasses the mental capacities of non-human animals. The study of animal conditioning and learning used in this field was developed from comparative psychology. It has also been strongly influenced by research in ethology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary psychology; the alternative name cognitive ethology is sometimes used. Many behaviors associated with the term animal intelligence are also subsumed within animal cognition.
 W
WAnimal Cognition is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Springer Science+Business Media. It covers research in ethology, behavioral ecology, animal behavior, cognitive sciences, and all aspects of human and animal cognition. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2017 impact factor of 2.805.
 W
WBrain-to-body mass ratio, also known as the brain-to-body weight ratio, is the ratio of brain mass to body mass, which is hypothesized to be a rough estimate of the intelligence of an animal, although fairly inaccurate in many cases. A more complex measurement, encephalization quotient, takes into account allometric effects of widely divergent body sizes across several taxa. The raw brain-to-body mass ratio is however simpler to come by, and is still a useful tool for comparing encephalization within species or between fairly closely related species.
 W
WCollective animal behavior is a form of social behavior involving the coordinated behavior of large groups of similar animals as well as emergent properties of these groups. This can include the costs and benefits of group membership, the transfer of information across the group, the group decision-making process, and group locomotion and synchronization. Studying the principles of collective animal behavior has relevance to human engineering problems through the philosophy of biomimetics. For instance, determining the rules by which an individual animal navigates relative to its neighbors in a group can lead to advances in the deployment and control of groups of swimming or flying micro-robots such as UAVs.
 W
WAnimal consciousness, or animal awareness, is the quality or state of self-awareness within a non-human animal, or of being aware of an external object or something within itself. In humans, consciousness has been defined as: sentience, awareness, subjectivity, qualia, the ability to experience or to feel, wakefulness, having a sense of selfhood, and the executive control system of the mind. Despite the difficulty in definition, many philosophers believe there is a broadly shared underlying intuition about what consciousness is.
 W
WConsumer demand tests for animals are studies designed to measure the relative strength of an animal's motivation to obtain resources such as different food items. Such demand tests quantify the strength of motivation animals have for resources whilst avoiding anthropomorphism and anthropocentrism.
 W
WThe cooperative pulling paradigm is an experimental design in which two or more animals pull rewards toward themselves via an apparatus that they cannot successfully operate alone. Researchers use cooperative pulling experiments to try to understand how cooperation works and how and when it may have evolved.
 W
WDistraction displays, also known as diversionary displays, or paratrepsis are anti-predator behaviors used to attract the attention of an enemy away from something, typically the nest or young, that is being protected by a parent. Distraction displays are sometimes classified more generically under "nest protection behaviors" along with aggressive displays such as mobbing. These displays have been studied most extensively in bird species, but also have been documented in populations of stickleback fish and in some mammal species.
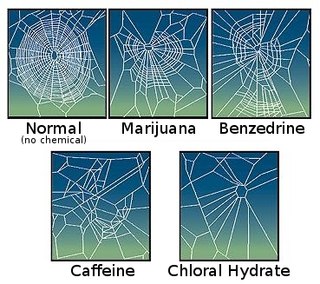 W
WPsychoactive drugs, such as caffeine, amphetamine, mescaline, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana, chloral hydrate, theophylline, IBMX and others, can have strong effects on certain animals. It is believed that plants developed caffeine as a chemical defense against insects.
 W
WThe elevated plus maze (EPM) is a test measuring anxiety in laboratory animals that usually uses rodents as a screening test for putative anxiolytic or anxiogenic compounds and as a general research tool in neurobiological anxiety research such as PTSD and TBI. The model is based on the test animal's aversion to open spaces and tendency to be thigmotaxic. In the EPM, this anxiety is expressed by the animal spending more time in the enclosed arms.
 W
WInsect cognition describes the mental capacities and study of those capacities in insects. The field developed from comparative psychology where early studies focused more on animal behavior. Researchers have examined insect cognition in bees, fruit flies, and wasps.
 W
WInstinct or innate behaviour is the inherent inclination of a living organism towards a particular complex behaviour. The simplest example of an instinctive behavior is a fixed action pattern (FAP), in which a very short to medium length sequence of actions, without variation, are carried out in response to a corresponding clearly defined stimulus.
 W
WAn interspecies friendship is a nonsexual bond that is formed between animals of different species. Numerous cases of interspecies friendships among wild and domesticated animals have been reported and documented with photography and video. Domestication of animals has led to interspecies friendships between species that would never naturally exist together. In many cases of interspecies friendship, the pair of animals include those not known to get along, and sometimes, one is of a species that ordinarily preys upon the other in nature.
 W
WAnimal navigation is the ability of many animals to find their way accurately without maps or instruments. Birds such as the Arctic tern, insects such as the monarch butterfly and fish such as the salmon regularly migrate thousands of miles to and from their breeding grounds, and many other species navigate effectively over shorter distances.
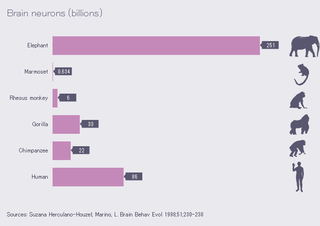 W
WThe following are two lists of animals ordered by the size of their nervous system. The first list shows number of neurons in their entire nervous system, indicating their overall neural complexity. The second list shows the number of neurons in the structure that has been found to be representative of animal intelligence. The human brain contains 86 billion neurons, with 16 billion neurons in the cerebral cortex.
 W
WA preference test is an experiment in which animals are allowed free access to multiple environments which differ in one or more ways. Various aspects of the animal's behaviour can be measured with respect to the alternative environments, such as latency and frequency of entry, duration of time spent, range of activities observed, or relative consumption of a goal object in the environment. These measures can be recorded either by the experimenter or by motion detecting software. Strength of preference can be inferred by the magnitude of the difference in the response, but see "Advantages and disadvantages" below. Statistical testing is used to determine whether observed differences in such measures support the conclusion that preference or aversion has occurred. Prior to testing, the animals are usually given the opportunity to explore the environments to habituate and reduce the effects of novelty.
 W
WTheory of mind in animals is an extension to non-human animals of the philosophical and psychological concept of theory of mind (ToM), sometimes known as mentalisation or mind-reading. It involves an inquiry into whether animals have the ability to attribute mental states to themselves and others, including recognition that others have mental states that are different from their own. To investigate this issue experimentally, researchers place animals in situations where their resulting behavior can be interpreted as supporting ToM or not.