 W
WMichel Aflaq was a Syrian philosopher, sociologist and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement; he is considered by several Ba'athists to be the principal founder of Ba'athist thought. He published various books during his lifetime, the most notable being The Battle for One Destiny (1958) and The Struggle Against Distorting the Movement of Arab Revolution (1975).
 W
WGeorge Habib Antonius, CBE (hon.) was a Lebanese-Egyptian author and diplomat, settled in Jerusalem, one of the first historians of Arab nationalism. Born in Deir al Qamar in a Lebanese Eastern Orthodox Christian family, he served as a civil servant in the British Mandate of Palestine. His 1938 book The Arab Awakening generated an ongoing debate over such issues as the origins of Arab nationalism, the significance of the Arab Revolt of 1916, and the machinations behind the post-World War I political settlement in the Middle East.
 W
WMohammed Yasser Abdel Rahman Abdel Raouf Arafat al-Qudwa al-Husseini, popularly known as Yasser Arafat or by his kunya Abu Ammar, was a Palestinian political leader. He was Chairman of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) from 1969 to 2004 and President of the Palestinian National Authority (PNA) from 1994 to 2004. Ideologically an Arab nationalist, he was a founding member of the Fatah political party, which he led from 1959 until 2004.
 W
WZakī al-Arsūzī was a Syrian philosopher, philologist, sociologist, historian, and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement. He published several books during his lifetime, most notably The Genius of Arabic in its Tongue (1943).
 W
WAhmed Ben Bella was an Algerian politician, socialist soldier and revolutionary who served as the first President of Algeria from 1963 to 1965.
 W
WSalah al-Din al-Bitar was a Syrian politician who co-founded the Arab Ba'ath Party with Michel Aflaq in the early 1940s. As students in Paris in the early 1930s, the two formulated a doctrine that combined aspects of nationalism and socialism. Bitar later served as prime minister in several early Ba'athist governments in Syria but became alienated from the party as it grew more radical. In 1966 he fled the country, lived mostly in Europe and remained politically active until he was assassinated in 1980.
 W
WMuammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi, commonly known as Colonel Gaddafi, was a Libyan revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He governed Libya as Revolutionary Chairman of the Libyan Arab Republic from 1969 to 1977 and then as the "Brotherly Leader" of the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya from 1977 to 2011. He was initially ideologically committed to Arab nationalism and Arab socialism but later ruled according to his own Third International Theory.
 W
WRashid Ali al-Gaylani was an Iraqi politician who served as Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Iraq on three occasions: from March to November 1933, from March 1940 to February 1941 and from April to May 1941. He is chiefly remembered as an ardent Arab nationalist who attempted to remove the British influence from Iraq by starting a coup against the government in 1941. During his brief tenures as Prime Minister in 1940 and 1941, he attempted to negotiate settlements with the Axis powers during World War II in order to counter British influence in Iraq.
 W
WGeorge Habash, also known by his laqab "al-Hakim" was a Palestinian Christian politician who founded the left-wing secular nationalist Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP). Habash served as Secretary-General of the PFLP until 2000, when ill health forced him to resign.
 W
WSāṭi` al-Ḥuṣrī was an Ottoman, Syrian and Iraqi writer, educationalist and an influential Arab nationalist thinker in the 20th century.
 W
W'Abd al-Rahman al-Kawakibi was a Syrian author and Pan-Arab solidarity supporter. He was one of the most prominent intellectuals of his time; however, his thoughts and writings continue to be relevant to the issues of Islamic identity and Pan-Arabism. His criticisms of the Ottoman Empire eventually led to Arabs calling for the sovereignty of the Arab Nations, setting the basis for Pan-Arab nationalism. Al-Kawakibi articulated his ideas in two influential books, Tabai al-Istibdad wa-Masari al-Isti’bad and Umm Al-Qura. He died in 1902 of “mysterious” causes. His family alleged that he was poisoned by Turkish agents.
 W
WKhazʽal bin Jabir bin Merdaw al-Kaʽbi, Muaz us-Sultana, and Sardar-e-Aqdas, was the Ruler of Arabistan, the Sheikh of Mohammerah from the Kasebite clan of the Banu Ka'b, of which he was the Sheikh of Sheikhs, the Overlord of the Mehaisan tribal confederation and the Ruler of the Shatt al-Arab. He was the fifth and youngest son of Haji Jabir Khan Ibn Merdaw, and his mother, Sheikha Noura, was the daughter of Talal Bin Alwan, the Sheikh of the powerful Bawi tribe. He was born on 18 August 1863, in the village Qout Al Zain in the district of Abu Khasib in Basra and he ascended to the throne on 2 June 1897 upon the death of his brother and predecessor, Sheikh Miz'al Khan ibn Haji Jabir Khan.
 W
WGamal Abdel Nasser Hussein was an Egyptian politician who served as the second President of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the 1952 overthrow of the monarchy and introduced far-reaching land reforms the following year. Following a 1954 attempt on his life by a Muslim Brotherhood member, he cracked down on the organization, put President Mohamed Naguib under house arrest and assumed executive office. He was formally elected president in June 1956.
 W
WAmeen Rihani (Amīn Fāris Anṭūn ar-Rīḥānī), was a Lebanese American writer, intellectual and political activist. He was also a major figure in the mahjar literary movement developed by Arab emigrants in North America, and an early theorist of Arab nationalism. He became an American citizen in 1901.
 W
WSaddam Hussein Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti was an Iraqi politician who served as the fifth President of Iraq from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003. A leading member of the revolutionary Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, and later, the Baghdad-based Ba'ath Party and its regional organization, the Iraqi Ba'ath Party—which espoused Ba'athism, a mix of Arab nationalism and Arab socialism—Saddam played a key role in the 1968 coup that brought the party to power in Iraq.
 W
WJurji Zaydan was a prolific Lebanese novelist, journalist, editor and teacher, most noted for his creation of the magazine Al-Hilal, which he used to serialize his 23 historical novels.
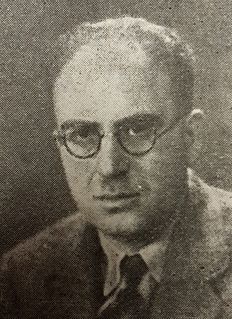 W
WConstantin K. Zurayk was a prominent and influential Syrian Arab intellectual who was one of the first to pioneer and express the importance of Arab nationalism. He stressed the urgent need to transform stagnant Arab society by means of rational thought and radical modification of the methods of thinking and acting. He developed some ideas, such as the "Arab mission" and "national philosophy", which were to become key concepts for Arab nationalist thinkers, and in more recent years was a strong proponent of an intellectual reformation of Arab society, emphasizing the need for rationalism and an ethical revolution.