 W
WThe Cave of Nicanor is an ancient burial cave located on Mount Scopus in Jerusalem, Israel. Among the ossuaries discovered in the cave is one with an inscription referring to "Nicanor the door maker". The cave is located in the National Botanic Garden of Israel on the grounds of the Mount Scopus campus of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
 W
WThe Cave of the Minor Sanhedrin is a burial cave located next to the Tomb of Simeon the Just in the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood of Jerusalem. It contains 26 burial niches, in which the 26 members of the Minor Sanhedrin are said to be buried. There are also other burial caves in the complex.
 W
WThe Cave of the Patriarchs or Tomb of the Patriarchs, known to Jews as the Cave of Machpelah and to Muslims as the Sanctuary of Abraham, is a series of caves located in the heart of the Old City of Hebron in the southern West Bank. According to the Abrahamic religions, the cave and adjoining field were purchased by Abraham as a burial plot.
 W
WEzra's Tomb or the Tomb of Ezra is a Shi'ite Islam and Jewish shrine, located in the settlement of Al-ʻUzair, in the Qalat Saleh district, in the Maysan Province of Iraq; on the western shore of the Tigris that was popularly believed to be the burial place of the biblical figure Ezra.
 W
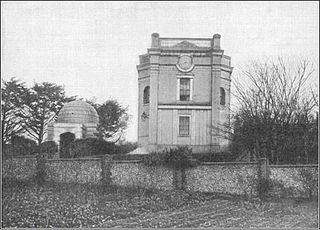
WJason's Tomb is a rock-cut tomb dating to the first century BCE in the Hasmonean period, discovered in the Rehavia neighborhood in Jerusalem, Israel. It has been identified as the burial site of a certain Jason, possibly a naval commander, based on the charcoal drawing of two warships discovered in the cave.
 W
WThe Montefiore Synagogue is the former private synagogue of Sir Moses Montefiore. It is an 1833, Grade II* listed building in Ramsgate, Kent, England. The synagogue and mausoleum are cared for and maintained by the Montefiore Endowment. The endowment also maintains the nearby Ramsgate Jewish Cemetery.
 W
WIn the Chabad-Lubavitch Jewish movement, the Ohel is an ohel in New York City at which the two Jewish messiah claimants the Rebbe, Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson, and his father-in-law, Rabbi Yosef Yitzchok Schneersohn, are buried. The Ohel is visited by thousands of Jews and non-Jews each year. Approximately 50,000 people make a pilgrimage each year on the anniversary of Schneerson's death.
 W
WOhel is a structure built around a Jewish grave as a sign of prominence of the deceased. Ohelim cover the graves of some Hasidic Rebbes, important rabbis, tzadikim, prominent Jewish community leaders, and biblical figures. Typically a small masonry building, an ohel may include room for visitors to pray, meditate, and light candles in honor of the deceased.
 W
WRachel's Tomb is the site revered as the burial place of the matriarch Rachel. The tomb is considered holy to Jews, Christians, and Muslims. The site is also referred to as the Bilal bin Rabah mosque
 W
WRock-cut tombs are a form of burial and interment chamber used in ancient Israel. Cut into the landscapes surrounding ancient Judean cities, their design ranges from single chambered, with simple square or rectangular layouts, to multi-chambered with more complex designs. Almost all burial chambers contain a platform for primary burial and an ossuary or other receptacle for secondary burial. There is debate on if these tombs were originally intended for secondary burials, or if that practice arose later. The use of rock-cut cave tombs in the region began in the early Canaanite period, from 3100–2900 BCE. The custom lapsed a millennium, however, before reemerging in the earliest Israelite tombs, dating to the 9th century BCE in Jerusalem. The use of rock-cut tombs reached its peak in the 7th and 8th centuries BCE, before rapidly declining and eventually falling out of use in the 6th century BCE in some regions. Use of the tombs has been recorded as recently as the Late Roman Period around the 3rd century CE. The use of such tombs was generally reserved for the middle- and upper-classes, and each typically belonged to a single nuclear or extended family.
 W
WThe Sassoon Mausoleum is the former grave of Sir Albert Sassoon and other members of his family, including Sir Edward Sassoon, 2nd Baronet, of Kensington Gore. It stands at 83 St. George's Road in Brighton, England. The single-storey building, which is Grade II listed, has since served as a furniture depository and an air-raid shelter, and since being purchased by a brewery in 1949 has remained a pub or bar.
 W
WTomb of Absalom, also called Absalom's Pillar, is an ancient monumental rock-cut tomb with a conical roof located in the Kidron Valley in Jerusalem, a few metres from the Tomb of Zechariah and the Tomb of Benei Hezir. Although traditionally ascribed to Absalom, the rebellious son of King David of Israel, recent scholarship has dated it to the 1st century AD.
 W
WThe Tomb of Benei Hezir, previously known as the Tomb of Saint James, is the oldest of four monumental rock-cut tombs that stand in the Kidron Valley, adjacent to the Tomb of Zechariah and a few meters from the Tomb of Absalom. It dates to the period of the Second Temple. It is a complex of burial caves. The tomb was originally accessed from a single rock-cut stairwell which descends to the tomb from the north. At a later period an additional entrance was created by quarrying a tunnel from the courtyard of the monument known as "the Tomb of Zechariah". This is also the contemporary entrance to the burial complex.
 W
WThe Tomb of Daniel is the traditional burial place of the Judeo-Islamic prophet Daniel. Various locations have been named for the site, but the tomb in Susa, Iran (Persia), is the most widely accepted, it being first mentioned by Benjamin of Tudela, who visited Asia between 1160 and 1163.
 W
WThe Tomb of Esther and Mordechai is located in Hamadan, Iran. Iranian Jews believe it houses the remains of the biblical Queen Esther and her cousin Mordechai, and is the most important pilgrimage site for Jews in Iran, and was declared a World Heritage Site by the Iranian government in 2008. There is no mention of it in either the Bavli or the Jerusalem Talmud and the Iranian Jewish tradition has not been supported by Jews beyond Iran.
 W
WThe Tomb of Zechariah is an ancient stone monument adjacent to the Tomb of Benei Hezir that is considered in Jewish tradition to be the tomb of Zechariah ben Jehoiada. It is a few meters from the Tomb of Absalom and adjacent to the Tomb of Benei Hezir.
 W
WTombs of the Sanhedrin, also Tombs of the Judges, is an underground complex of 63 rock-cut tombs located in a public park in the northern Jerusalem neighborhood of Sanhedria. Built in the 1st century CE, the tombs are noted for their elaborate design and symmetry. They have been a site for Jewish pilgrimage since the medieval period. The popular name of the complex, which has the most magnificently carved pediment of ancient Jerusalem, is due to the fact that the number of burial niches it contains is somewhat close to that of the members of the ancient Jewish supreme court, the Great Sanhedrin, namely 71.