 W
WThe digital divide refers to the gap between those able to benefit from the digital age and those who are not. The concern is that people without access to the Internet and other information and communication technologies will be disadvantaged, as they are unable or less able to obtain digital information, shop online, participate democratically, or learn skills and offer skills. This resulted in programs to give computers and related services to people without access.
 W
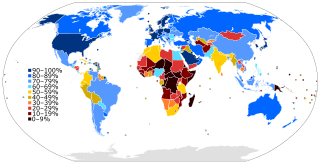
WThe global digital divide describes global disparities, primarily between developed and developing countries, in regards to access to computing and information resources such as the Internet and the opportunities derived from such access. As with a smaller unit of analysis, this gap describes an inequality that exists, referencing a global scale.
 W
WThe Center for Digital inclusion (CDI) is a nonprofit organization that uses technology to fight poverty and stimulate entrepreneurship. CDI and partners create community centers in low-income, rural, indigenous communities, hospitals, prisons, and psychiatric clinics. These centers work to strengthen low-income communities by providing access to information and communication technologies.
 W
WCode Club is a voluntary initiative, founded in 2012. The initiative aims to provide opportunities for children aged 9 to 13 to develop coding skills through free after-school clubs. As of November 2015, over 3,800 schools and other public venues established a Code Club, regularly attended by an estimated 44,000 young people across the UK. The organization also expanded internationally, and there are now over 13,000 Code Club operating worldwide. Volunteer programmers and software developers give their time to run Code Club sessions, passing on their programming skills and mentoring the young students. Children create their own computer games, animations and websites, learning how to use technology creatively.
 W
WA digital citizen is a person using information technology (IT) in order to engage in society, politics, and government. As defined by Karen Mossberger, one of the authors of Digital Citizenship: The Internet, Society, and Participation, digital citizens are "those who use the internet regularly and effectively." They also have a comprehensive understanding of digital citizenship, which is the appropriate and responsible behavior when using technology. Since digital citizenship evaluates the quality of an individual's response to membership in a digital community, it often requires the participation of all community members, both visible and those who are less visible. A large part in being a responsible digital citizen encompasses digital literacy, etiquette, online safety, and an acknowledgement of private versus public information.
 W
WThe term digital native describes a young person who has grown up in the digital age, in close contact with computers, the Internet, and video game consoles, and later mobile phones, social media, and tablets. The term is often used to refer to millennials, Generation Z, and Generation Alpha; the latter two are sometimes described as distinct "neo-digital natives", "true" digital natives, or "digital integrators".
 W
WThe Digital Writing and Research Lab (DWRL) is a research lab at The University of Texas at Austin, United States, dedicated to the identification and promotion of twenty-first-century literacies. These literacies range from navigating online newsfeeds and participating in social networking sites to composing multimedia texts that require producing, sampling, and/or remixing media content.
 W
WGeekcorps is a non-profit organization that sends people with technical skills to developing countries to assist in computer infrastructure development.
 W
WThe International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for all matters related to information and communication technologies. Established in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union it is one of the oldest international organizations in operation.
 W
WNational Digital Inclusion Alliance (NDIA) is a US nonprofit organization that brings together over 300 non-profit organizations, policy-makers, and academics to advocate for national access to broadband and to put an end to the multiple digital divides. NDIA has provided community-vetted definitions of digital equity and digital inclusion, puts on an annual conference called Net Inclusion, and sponsors a Digital Inclusion Week. NDIA argues that the US government needs "an organized federal strategy" to get broadband to rural and other underserved areas and have worked to support the expansion of the Federal Communications Commission's Lifeline program to expand to include broadband subsidies.
 W
WNo Child Left Unplugged (NOCU) was a San Francisco based non-profit organization founded by Corey Linehan with the purpose of teaching technology skills at economically challenged schools as well as providing computers for such schools.
 W
WOne Laptop per Child (OLPC) was a non-profit initiative established with the goal of transforming education for children around the world; this goal was to be achieved by creating and distributing educational devices for the developing world, and by creating software and content for those devices.
 W
WSimon Rogerson is lifetime Professor Emeritus in Computer Ethics at the Centre for Computing and Social Responsibility (CCSR), De Montfort University. He was the founder and is the current editor of the Journal of Information, Communication and Ethics in Society. He has had two careers; first as a technical software developer and then in academia as reformer. He was the founding Director of CCSR, launching it in 1995 at the first ETHICOMP conference which he conceived and co-directed until 2013. He became Europe's first Professor in Computer Ethics in 1998. His most important research focuses on providing rigorously grounded practical tools and guidance to computing practitioners. For his leadership and research achievements in the computer and information ethics interdisciplinary field he was awarded the fifth IFIP-WG9.2 Namur Award in 2000 and the SIGCAS Making a Difference Award in 2005.
 W
WStemettes is a social enterprise which encourages girls aged 5–22 to pursue careers in Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths. Stemettes runs panel events, hackathons, the Student to Stemette mentoring programme supported by Deutsche Bank, Outbox Incubator and an app, OtotheB, an online platform for girls interested in STEM and entrepreneurship.
 W
WA telecentre is a public place where people can access computers, the Internet, and other digital technologies that enable them to gather information, create, learn, and communicate with others while they develop essential digital skills. Telecentres exist in almost every country, although they sometimes go by a different names including public internet access center (PIAP), village knowledge center, infocenter, Telecottage, Electronic Village Hall, community technology center (CTC), community multimedia center (CMC), multipurpose community telecentre (MCT), Common/Citizen Service Centre (CSC) and school-based telecentre. While each telecentre is different, their common focus is on the use of digital technologies to support community, economic, educational, and social development—reducing isolation, bridging the digital divide, promoting health issues, creating economic opportunities, and reaching out to youth for example.
 W
WThe United Nations Information and Communication Technologies Task Force was a multi-stakeholder initiative associated with the United Nations which is "intended to lend a truly global dimension to the multitude of efforts to bridge the global digital divide, foster digital opportunity and thus firmly put ICT at the service of development for all".
 W
WThe World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) was a two-phase United Nations-sponsored summit on information, communication and, in broad terms, the information society that took place in 2003 in Geneva and in 2005 in Tunis. One of its chief aims was to bridge the global digital divide separating rich countries from poor countries by increasing internet accessibility in the developing world. The conferences established 17 May as World Information Society Day.
 W
WYoung Rewired State was an organisation based in the United Kingdom, which ran events and schemes for technically gifted young people aged 18 and under. It brought together young developers, designers, and those with other technical skills to build projects to attempt to solve real world problems. Many developers who participated in Young Rewired State events learned coding skills outside the traditional school curriculum.