 W
WFascism is a form of far-right, authoritarian ultranationalism characterized by dictatorial power, forcible suppression of opposition and strong regimentation of society and of the economy which came to prominence in early 20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements emerged in Italy during World War I, before spreading to other European countries. Opposed to liberalism, democracy, Marxism, and anarchism, fascism is placed on the far right within the traditional left–right spectrum.
 W
WActual idealism was a form of idealism, developed by Giovanni Gentile, that grew into a 'grounded' idealism, contrasting the transcendental idealism of Immanuel Kant, and the absolute idealism of G. W. F. Hegel. To Gentile, who considered himself the "philosopher of fascism," actualism was the sole remedy to philosophically preserving free agency, by making the act of thinking self-creative and, therefore, without any contingency and not in the potency of any other fact.
 W
WThe Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis was a military coalition that fought in World War II against the Allies. The Axis powers agreed on their opposition to the Allies, but did not completely coordinate their activity.
 W
WCorporatism is a political ideology which advocates the organization of society by corporate groups, such as agricultural, labour, military, scientific, or guild associations, on the basis of their common interests. The term is derived from the Latin corpus, or "human body". The hypothesis that society will reach a peak of harmonious functioning when each of its divisions efficiently performs its designated function, such as a body's organs individually contributing its general health and functionality, lies at the center of corporatist theory.
 W
WFascism is a form of far-right, authoritarian ultranationalism characterized by dictatorial power, forcible suppression of opposition and strong regimentation of society and of the economy which came to prominence in early 20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements emerged in Italy during World War I, before spreading to other European countries. Opposed to liberalism, democracy, Marxism, and anarchism, fascism is placed on the far right within the traditional left–right spectrum.
 W
WFalangism was the political ideology of two political parties in Spain that were known as the Falange, namely first the Falange Española de las Juntas de Ofensiva Nacional Sindicalista and afterwards the Falange Española Tradicionalista y de las Juntas de Ofensiva Nacional Sindicalista. Falangism has a disputed relationship with fascism as some historians consider the Falange to be a fascist movement based on its fascist leanings during the early years, while others focus on its transformation into an authoritarian conservative movement in Francoist Spain.
 W
WThe history of fascist ideology is long and draws on many sources. Fascists took inspiration from sources as ancient as the Spartans for their focus on racial purity and their emphasis on rule by an elite minority. Fascism has also been connected to the ideals of Plato, though there are key differences between the two. Fascism styled itself as the ideological successor to Rome, particularly the Roman Empire. The concept of a "high and noble" Aryan culture as opposed to a "parasitic" Semitic culture was core to Nazi racial views. From the same era, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel's view on the absolute authority of the state also strongly influenced Fascist thinking. The French Revolution was a major influence insofar as the Nazis saw themselves as fighting back against many of the ideas which it brought to prominence, especially liberalism, liberal democracy and racial equality, whereas on the other hand Fascism drew heavily on the revolutionary ideal of nationalism. Common themes among fascist movements include: nationalism, hierarchy and elitism, militarism, quasi-religion, masculinity and philosophy. Other aspects of fascism such as its "myth of decadence", anti‐egalitarianism and totalitarianism can be seen to originate from these ideas. These fundamental aspects however, can be attributed to a concept known as "Palingenetic ultranationalism", a theory proposed by Roger Griffin, that fascism is a synthesis of totalitarianism and ultranationalism sacralized through myth of national rebirth and regeneration.
 W
WFascist has been used as a pejorative epithet against a wide range of individuals, political movements, governments, public and private institutions since the emergence of fascism in Europe in the 1920s. The widespread use of this term as an insult was noted as early as 1944, when British writer George Orwell commented that "the word 'Fascism' is almost entirely meaningless" and that "almost any English person would accept 'bully' as a synonym for 'Fascist'".
 W
WFascism is a form of far-right, authoritarian ultranationalism characterized by dictatorial power, forcible suppression of opposition and strong regimentation of society and of the economy which came to prominence in early 20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements emerged in Italy during World War I, before spreading to other European countries. Opposed to liberalism, democracy, Marxism, and anarchism, fascism is placed on the far right within the traditional left–right spectrum.
 W
WFascism is a form of far-right, authoritarian ultranationalism characterized by dictatorial power, forcible suppression of opposition and strong regimentation of society and of the economy which came to prominence in early 20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements emerged in Italy during World War I, before spreading to other European countries. Opposed to liberalism, democracy, Marxism, and anarchism, fascism is placed on the far right within the traditional left–right spectrum.
 W
WItalian Fascism, also known as Classical Fascism or simply Fascism, is the original fascist ideology as developed in Italy by Giovanni Gentile and Benito Mussolini. The ideology is associated with a series of two political parties led by Benito Mussolini; the National Fascist Party (PNF), which ruled the Kingdom of Italy from 1922 until 1943, and the Republican Fascist Party that ruled the Italian Social Republic from 1943 to 1945. Italian Fascism is also associated with the post-war Italian Social Movement and subsequent Italian neo-fascist movements.
 W
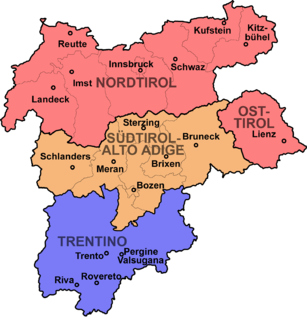
WIn 1919, at the time of its annexation, the middle part of the County of Tyrol which is today called South Tyrol was inhabited by almost 90% German speakers. Under the 1939 South Tyrol Option Agreement, Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini determined the status of the German and Ladin (Rhaeto-Romanic) ethnic groups living in the region. They could emigrate to Germany, or stay in Italy and accept their complete Italianization. As a consequence of this, the society of South Tyrol was deeply riven. Those who wanted to stay, the so-called Dableiber, were condemned as traitors while those who left (Optanten) were defamed as Nazis. Because of the outbreak of World War II, this agreement was never fully implemented. Illegal Katakombenschulen were set up to teach children the German language.
 W
WThe March of the Iron Will was an Italian Fascist propaganda event staged from 26 April to 5 May 1936, during the final days of the Second Italo-Ethiopian War. The goal of the march was to capture the Ethiopian capital in a show of force. An Italian mechanized column under the command of Pietro Badoglio, Marshal of Italy, advanced from the town of Dessie to take Addis Ababa. The march covered a distance of approximately 200 miles (320 km).
 W
WMetaxism is a totalitarian nationalist ideology associated with Greek dictator Ioannis Metaxas. It called for the regeneration of the Greek nation and the establishment of a modern, culturally homogenous Greece. Metaxism disparaged liberalism, and held individual interests to be subordinate to those of the nation, seeking to mobilize the Greek people as a disciplined mass in service to the creation of a "new Greece."
 W
WNational syndicalism is an adaptation of syndicalism to suit the social agenda of integral nationalism. National syndicalism developed in France, and then spread to Italy, Spain, and Portugal.
 W
WThe Nazi salute, Hitler salute, or Sieg Heil salute, is a gesture that was used as a greeting in Nazi Germany. The salute is performed by extending the right arm from the neck into the air with a straightened hand. Usually, the person offering the salute would say 'Heil Hitler!', lit. Hail Hitler!,, "Heil, mein Führer!", or "Sieg Heil!". It was adopted in the 1930s by the Nazi Party to signal obedience to the party's leader, Adolf Hitler, and to glorify the German nation. The salute was mandatory for civilians but mostly optional for military personnel, who retained the traditional military salute until the failed assassination attempt on Hitler on 20 July 1944.
 W
WProto-fascism refers to the direct predecessor ideologies and cultural movements that influenced and formed the basis of fascism. A prominent proto-fascist figure is Gabriele D'Annunzio, the Italian nationalist whose politics influenced Benito Mussolini and Italian Fascism. Proto-fascist political movements include the Italian Nationalist Association, the German National Association of Commercial Employees and the German National People's Party.
 W
WSyndicalism is a current in the labor movement to establish local, worker-based organizations and advance the demands and rights of workers through strikes. Most active in the early 20th century, syndicalism was predominant in the revolutionary left in the decade which preceded the outbreak of World War I because orthodox Marxism was mostly reformist at that time, according to the Marxist historian Eric Hobsbawm.
 W
WThe white genocide, white extinction, or white replacement conspiracy theory is a white supremacist belief that there is a deliberate plot, often blamed on Jews, to promote miscegenation, interracial marriage, mass non-white immigration, racial integration, low fertility rates, abortion, governmental land-confiscation from whites, organised violence, and eliminationism in white-founded countries in order to cause the extinction of whites through forced assimilation and violent genocide. Less frequently, black people, Hispanics, and Muslims are blamed, but merely as more fertile immigrants, invaders, or violent aggressors, rather than the masterminds of a secret plot.