 W
WThe following table is a list of Mars orbiters, consisting of space probes which were launched from Earth and are currently orbiting Mars. As of February 2021, there have been 18 spacecraft missions operating in Mars' orbit, 8 of which are currently active.
 W
WAkatsuki , also known as the Venus Climate Orbiter (VCO) and Planet-C, is a Japanese (JAXA) space probe tasked to study the atmosphere of Venus. It was launched aboard an H-IIA 202 rocket on 20 May 2010, and failed to enter orbit around Venus on 6 December 2010. After the craft orbited the Sun for five years, engineers successfully placed it into an alternative Venusian elliptic orbit on 7 December 2015 by firing its attitude control thrusters for 20 minutes and made it the first Asian satellite orbiting Venus.
 W
WBepiColombo is a joint mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to the planet Mercury. The mission comprises two satellites launched together: the Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and Mio. The mission will perform a comprehensive study of Mercury, including characterization of its magnetic field, magnetosphere, and both interior and surface structure. It was launched on an Ariane 5 rocket on 20 October 2018 at 01:45 UTC, with an arrival at Mercury planned for on 5 December 2025, after a flyby of Earth, two flybys of Venus, and six flybys of Mercury. The mission was approved in November 2009, after years in proposal and planning as part of the European Space Agency's Horizon 2000+ programme; it is the last mission of the programme to be launched.
 W
WThe Cassini–Huygens space-research mission, commonly called Cassini, involved a collaboration among NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, including its rings and natural satellites. The Flagship-class robotic spacecraft comprised both NASA's Cassini space probe and ESA's Huygens lander, which landed on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Cassini was the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter its orbit. The two craft took their names from the astronomers Giovanni Cassini and Christiaan Huygens.
 W
WDawn is a retired space probe that was launched by NASA in September 2007 with the mission of studying two of the three known protoplanets of the asteroid belt: Vesta and Ceres. In the fulfillment of that mission—the ninth in NASA's Discovery Program—Dawn entered orbit around Vesta on July 16, 2011, and completed a 14-month survey mission before leaving for Ceres in late 2012. It entered orbit around Ceres on March 6, 2015. In 2017, NASA announced that the planned nine-year mission would be extended until the probe's hydrazine fuel supply was depleted. On November 1, 2018, NASA announced that Dawn had depleted its hydrazine, and the mission was ended. The spacecraft is currently in a derelict, but stable, orbit around Ceres.
 W
WEnVision is a proposed orbital mission to Venus that would perform high-resolution radar mapping and atmospheric studies. The mission would help scientists understand the relationships between its geological activity and the atmosphere, and it would investigate why Venus and Earth took such different evolutionary paths. The mission is studied by ESA in collaboration with NASA, with the potential sharing of responsibilities currently under assessment.
 W
WEuropa Clipper is an interplanetary mission in development by NASA comprising an orbiter. Set for a launch in October 2024, the spacecraft is being developed to study the Galilean moon Europa through a series of flybys while in orbit around Jupiter.
 W
WThe Europa Orbiter was a planned NASA mission to Jupiter's Moon Europa, that was cancelled in 2002. Its main objectives included determining the presence or absence of a subsurface ocean and identifying candidate sites for future lander missions. Europa Orbiter received pre-project funding in 1998, and resulted from NASA's Fire and Ice project.
 W
WJuno is a NASA space probe orbiting the planet Jupiter. It was built by Lockheed Martin and is operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The spacecraft was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on 5 August 2011 UTC, as part of the New Frontiers program. Juno entered a polar orbit of Jupiter on 5 July 2016 UTC, to begin a scientific investigation of the planet. After completing its mission, Juno will be intentionally deorbited into Jupiter's atmosphere.
 W
WThe Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) is an interplanetary spacecraft in development by the European Space Agency (ESA) with Airbus Defence and Space as the main contractor. The mission will study three of Jupiter's Galilean moons: Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa all of which are thought to have significant bodies of liquid water beneath their surfaces, making them potentially habitable environments.
 W
WThe Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter (JIMO) was a proposed NASA spacecraft designed to explore the icy moons of Jupiter. The main target was Europa, where an ocean of liquid water may harbor alien life. Ganymede and Callisto, which are now thought to have liquid, salty oceans beneath their icy surfaces, were also targets of interest for the probe.
 W
WThe Magellan spacecraft was a 1,035-kilogram (2,282 lb) robotic space probe launched by NASA of the United States, on May 4, 1989, to map the surface of Venus by using synthetic-aperture radar and to measure the planetary gravitational field.
 W
WMESSENGER was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging", and a reference to the messenger god Mercury from Roman mythology.
 W
WA Uranus orbiter and probe is a mission concept for study of the planet Uranus. It was first recommended to NASA in 2011 by its Planetary Science Decadal Survey 2013–2022.
 W
WNear Earth Asteroid Rendezvous – Shoemaker, renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA to study the near-Earth asteroid Eros from close orbit over a period of a year. The mission succeeded in closing in with the asteroid and orbited it several times, finally terminating by touching down on the asteroid on February 12, 2001.
 W
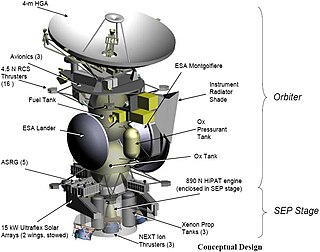
WNeptune Orbiter is an unselected proposal to NASA for an unmanned spacecraft to explore the planet Neptune. It was envisioned that it would be launched sometime around 2016 and take 8 to 12 years to reach the planet; however, NASA's website no longer lists any possible launch date. The Neptune Orbiter concept would have answered many questions about the nature of the planet.
 W
WODINUS is a space mission concept proposed to the European Space Agency's Cosmic Vision programme. The ODINUS mission concept proposes to expand the Uranus orbiter and probe mission to two twin orbiters— dubbed Freyr and Freyja, the twin gods of the Norse pantheon. Their primary mission would be to study Neptune and Uranus with one orbiter each. If selected, ODINUS would launch in 2034.
 W
WRosetta was a space probe built by the European Space Agency launched on 2 March 2004. Along with Philae, its lander module, Rosetta performed a detailed study of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P). During its journey to the comet, the spacecraft performed flybys of Earth, Mars, and the asteroids 21 Lutetia and 2867 Šteins. It was launched as the third cornerstone mission of the ESA's Horizon 2000 programme, after SOHO / Cluster and XMM-Newton.
 W
WTitan Saturn System Mission (TSSM) was a joint NASA–ESA proposal for an exploration of Saturn and its moons Titan and Enceladus, where many complex phenomena were revealed by Cassini. With an estimated NASA cost of $2.5 billion (FY07), TSSM was proposed to launch in 2020, get gravity assists from Earth and Venus, and arrive at the Saturn system in 2029. The 4-year prime mission would include a two-year Saturn tour, a 2-month Titan aero-sampling phase, and a 20-month Titan orbit phase.
 W
WUranus Pathfinder was a mission concept for the Uranian system evaluated in the 2010s by the European Space Agency. In 2011, scientists from the Mullard Space Science Laboratory in the United Kingdom proposed the joint NASA–ESA Uranus Pathfinder mission to Uranus. It would be a medium-class (M-class) mission to be launched in 2022, and was submitted to the ESA in December 2010 with the signatures of 120 scientists from around the globe. ESA caps the cost of M-class missions at €470 million. Uranus Pathfinder was proposed in support of ESA's Cosmic Vision 2015–2025. The mission study including a number of possible combinations of launch dates, trajectories, and flybys, including flybys of Earth, Venus, and of the planet Saturn. Indeed, the study noted the velocity change requirements are only marginally higher than for typical missions to Saturn of this period.
 W
WVenus Express (VEX) was the first Venus exploration mission of the European Space Agency (ESA). Launched in November 2005, it arrived at Venus in April 2006 and began continuously sending back science data from its polar orbit around Venus. Equipped with seven scientific instruments, the main objective of the mission was the long term observation of the Venusian atmosphere. The observation over such long periods of time had never been done in previous missions to Venus, and was key to a better understanding of the atmospheric dynamics. It was hoped that such studies can contribute to an understanding of atmospheric dynamics in general, while also contributing to an understanding of climate change on Earth. ESA concluded the mission in December 2014.