 W
WMUSA was an early prototype of Speech Synthesis machine started in 1975.
 W
WArticulatory synthesis refers to computational techniques for synthesizing speech based on models of the human vocal tract and the articulation processes occurring there. The shape of the vocal tract can be controlled in a number of ways which usually involves modifying the position of the speech articulators, such as the tongue, jaw, and lips. Speech is created by digitally simulating the flow of air through the representation of the vocal tract.
 W
WCereProc is a speech synthesis company based in Edinburgh, Scotland, founded in 2005. The company specialises in creating natural and expressive-sounding text to speech voices, synthesis voices with regional accents, and in voice cloning.
 W
WDECtalk was a speech synthesizer and text-to-speech technology developed by Digital Equipment Corporation in 1984, based largely on the work of Dennis Klatt at MIT, whose source-filter algorithm was variously known as KlattTalk or MITalk.
 W
WSpeech-generating devices (SGDs), also known as voice output communication aids, are electronic augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems used to supplement or replace speech or writing for individuals with severe speech impairments, enabling them to verbally communicate. SGDs are important for people who have limited means of interacting verbally, as they allow individuals to become active participants in communication interactions. They are particularly helpful for patients suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) but recently have been used for children with predicted speech deficiencies.
 W
WThe Ebert test gauges whether a computer-based synthesized voice can tell a joke with sufficient skill to cause people to laugh. It was proposed by film critic Roger Ebert at the 2011 TED conference as a challenge to software developers to have a computerized voice master the inflections, delivery, timing, and intonations of a speaking human. The test is similar to the Turing test proposed by Alan Turing in 1950 as a way to gauge a computer's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior by generating performance indistinguishable from a human being.If the computer can successfully tell a joke, and do the timing and delivery as well as Henny Youngman, then that's the voice I want.
 W
WThe Echo II was a plug-in expansion card, speech synthesizer card for the Apple II and Apple IIe personal computers that allowed applications to use speech synthesis. The Echo II used the TMS5220 speech synthesis chip to synthesize speech. The Echo II software could synthesize either unlimited text-to-speech using stitched phonemes, or play back raw LPC data for specific words, with resulting higher speech quality.
 W
WThe Euphonia was a talking machine created in the early to mid-nineteenth century by the Austrian inventor Joseph Faber and exhibited in 1845 in Philadelphia and in 1846 in London's Egyptian Hall. An earlier version of the invention had been destroyed in 1844 by Faber.
 W
WGI-SPO256 refers to a family of closely related NMOS LSI chips manufactured by General Instrument in the early 1980s, able to model the human vocal tract by a software programmable digital filter, creating a digital output converted into an analog signal through an external low pass filter. The SPO256 includes 2 KB of mask ROM. The various versions of SPO256 differ primarily in the voice data programmed into their mask ROMs.
 W
WHaskins Laboratories, Inc. is an independent 501(c) non-profit corporation, founded in 1935 and located in New Haven, Connecticut, since 1970. Upon moving to New Haven, Haskins entered in to formal affiliation agreements with both Yale University and the University of Connecticut; it remains fully independent, administratively and financially, of both Yale and UConn. Haskins is a multidisciplinary and international community of researchers which conducts basic research on spoken and written language. A guiding perspective of their research is to view speech and language as emerging from biological processes, including those of adaptation, response to stimuli, and conspecific interaction. The Laboratories has a long history of technological and theoretical innovation, from creating systems of rules for speech synthesis and development of an early working prototype of a reading machine for the blind to developing the landmark concept of phonemic awareness as the critical preparation for learning to read an alphabetic writing system.
 W
WThe Mockingboard is a sound card for the Apple II series of microcomputers built by Sweet Micro Systems, which improve on the Apple II's limited sound capabilities.
 W
WNETtalk is an artificial neural network. It is the result of research carried out in the mid-1980s by Terrence Sejnowski and Charles Rosenberg. The intent behind NETtalk was to construct simplified models that might shed light on the complexity of learning human level cognitive tasks, and their implementation as a connectionist model that could also learn to perform a comparable task.
 W
WPhasor is a stereo music, sound and speech synthesizer created by Applied Engineering for the Apple II family of computers. Consisting of a sound card and a set of related software, the Phasor system was designed to be compatible with most software written for other contemporary Apple II cards, including the Sweet Micro Systems Mockingboard, ALF's Apple Music Synthesizer, Echo+ and Applied Engineering's earlier card Super Music Synthesizer.
 W
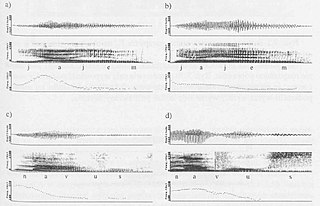
WPSOLA is a digital signal processing technique used for speech processing and more specifically speech synthesis. It can be used to modify the pitch and duration of a speech signal. It was invented around 1986.
 W
WSensory, Inc. is an American company which develops and makes speech technologies on both hardware and software platforms for consumer products, offering IC and software-only solutions for speech recognition, speech synthesis, speaker verification, music synthesis. It is based in Santa Clara, California.
 W
WThe Texas Instruments LPC Speech Chips are a series of speech synthesizer digital signal processor integrated circuits created by Texas Instruments beginning in 1978. They continued to be developed and marketed for many years, though the speech department moved around several times within TI until finally dissolving in late 2001. The rights to the speech-specific subset of the MSP line, the last remaining line of TI speech products as of 2001, were sold to Sensory, Inc. in October 2001.
 W
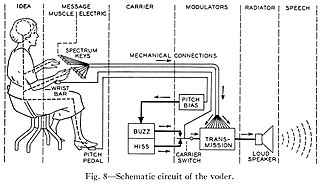
WThe Bell Telephone Laboratory's Voder was the first attempt to electronically synthesize human speech by breaking it down into its acoustic components. It was invented by Homer Dudley in 1937–1938 and developed on his earlier work on the vocoder. The quality of the speech was limited; however, it demonstrated the synthesis of the human voice, which became one component of the vocoder used in voice communications for security and to save bandwidth.
 W
WVoiceroid is a speech synthesizer application developed by AH-Software and is designed for speech. It is only available in the Japanese language. Its name comes from the singing software Vocaloid, for which AH-Software also develops voicebanks. Both AH-Software's first Vocaloids and Voiceroids went on sale on December 4, 2009.
 W
WWaveNet is a deep neural network for generating raw audio. It was created by researchers at London-based artificial intelligence firm DeepMind. The technique, outlined in a paper in September 2016, is able to generate relatively realistic-sounding human-like voices by directly modelling waveforms using a neural network method trained with recordings of real speech. Tests with US English and Mandarin reportedly showed that the system outperforms Google's best existing text-to-speech (TTS) systems, although as of 2016 its text-to-speech synthesis still was less convincing than actual human speech. WaveNet's ability to generate raw waveforms means that it can model any kind of audio, including music.
 W
WWolfgang von Kempelen's speaking machine is a manually operated speech synthesizer that began development in 1769, by Austro-Hungarian author and inventor Wolfgang von Kempelen. It was in this same year that he completed his far more infamous contribution to history: The Turk, a chess-playing automaton, later revealed to be a very far-reaching and elaborate hoax due to the chess-playing human-being occupying its innards.[4] But while the Turk's construction was completed in six months, Kempelen's speaking machine occupied the next twenty years of his life.[2] After two conceptual "dead ends" over the first five years of research, Kempelen's third direction ultimately led him to the design he felt comfortable deeming "final": a functional representational model of the human vocal tract.[3]
 W
WWordQ® is assistive technology software developed by Quillsoft Ltd. and Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital, represented by goQSoftware and distributed in the United States by ST4Learning and in Canada by Quillsoft Ltd. WordQ's main purpose is helping individuals who struggle with writing. WordQ uses word prediction to suggest words that the user is typing into documents and emails, helping with spelling. It also uses high-quality Acapela text-to-speech voices to read back text that the user has entered, allowing for proofreading and editing. WordQ is sold alongside a companion product, SpeakQ®, which combines speech recognition with the features of WordQ to allow users to switch between speaking and typing while writing. The combined program works with Windows. WordQ also works with Mac OS X.