 W
WThe Atlas languages are a subgroup of the Northern Berber languages of the Afro-Asiatic language family spoken in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. By mutual intelligibility, they are a single language spoken by perhaps 14 million people; however, they are distinct sociolinguistically and are considered separate languages by the Royal institute of the Amazigh culture. They are:Central Atlas Tamazight, spoken in the central Atlas Mountains Shilha, spoken in southern Morocco Senhaja de Srair, spoken in the southern part of the Rif Ghomara, spoken in the western part of the Rif
 W
WThe Berber Arabic alphabet is an Arabic-based alphabet that was used to write various Berber languages in the Middle Ages. Nowadays users have largely reverted to either the Tifinagh alphabet in Morocco, or Berber Latin alphabet in Algeria.
 W
WThe East Zenati languages or Tunisian and Zuwara are a group of the Zenati Berber dialects spoken in Tunisia and Libya.
 W
WThe Eastern Berber languages are a group of Berber languages spoken in Libya and Egypt. They include Awjila, Sokna and Fezzan (El-Fogaha), Siwi and Ghadamès, though it is not clear that they form a valid genealogical group.
 W
WEastern Middle Atlas Berber is a cluster of Berber dialects spoken in the eastern and north-eastern parts of the Middle Atlas, in Morocco. These dialects are those of the tribes of Aït Seghrushen, Aït Waraïn, Marmusha, Aït Alaham, Aït Yub and Aït Morghi.
 W
WEastern Morocco Zenati dialects are a group of Berber dialects spoken in Morocco from Jerada Province to Berkane Province.
 W
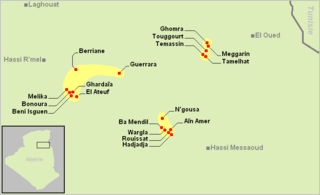
WGurara (Gourara) is a Zenati Berber language spoken in the Gourara (Tigurarin) region, an archipelago of oases surrounding the town of Timimoun in southwestern Algeria. Ethnologue gives it the generic name Taznatit ("Zenati"), along with Tuwat spoken to its south; however, Blench (2006) classifies Gurara as a dialect of Mzab–Wargla and Tuwat as a dialect of the Riff languages.
 W
WThe Institute of Coptic Studies was founded in 1954 by the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria. It is based in Cairo.
 W
WIznasen Berber is a Berber dialect of the Zenati languages. It is spoken in the extreme northeast of Morocco, in the Iznasen region in a speech area between Riffian language and the Berber languages of western Algeria.
 W
WChelha, or Djerbi, is a Zenati Berber language spoken in Djerba, Tunisia.
 W
WKaro is a South Omotic language spoken in the Debub (South) Omo Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People's Region in Ethiopia. Karo is described as being closely related to its neighbor, Hamer-Banna, with a lexical similarity of 81%, and is considered a dialect of Hamer by Blench (2006), but as a separate language belonging to the Hamer-Karo subfamily in Glottolog. The Karo people, who live close to the lower Omo River, use colorful bodywork, complex headdresses and body scars to express beauty and importance within the community. 2,400 speakers are using the Karo language.
 W
WMatmata Berber is a Zenati Berber dialect spoken around the town of Matmâta in southern Tunisia, and in the villages of Taoujjout, Tamezret and Zrawa. According to Ben Mamou's lexicon, its speakers call it Tmaziɣṯ or Eddwi nna, meaning "our speech", while it is called Shelha or Jbali (جبالي) in local Tunisian Arabic dialects. The total population speaking this variety was estimated at 3,726 in 1975.
 W
WMozabite, or Tumẓabt, is a Zenati Berber language spoken by the Mozabites, an Ibadi Berber group inhabiting the seven cities of the M'zab natural region in the northern Saharan Algeria. It is also spoken by small numbers of Mozabite emigrants in other local cities and elsewhere. Mozabite is one of the Mzab–Wargla languages, a dialect cluster of the Zenati languages. It is very closely related to the nearby Berber languages of Ouargla and Oued Righ as well as the more distant Gourara.
 W
WThe Mzab–Wargla languages or Northern Saharan oasis dialects are a dialect cluster of the Zenati languages, within the Northern Berber subbranch. They are spoken in scattered oases of Algeria and Morocco.
 W
WIn some classifications, the Riff (Rif) languages are a branch of the Zenati Berber languages, of the Rif area of Morocco, that includes Riffian, one of the major Berber languages.
 W
WThe Sakuye are a semi-nomadic People, Cousins of Somali people living in Marsabit and Isiolo Counties, Northern Frontier District Region, now Northern Kenya.
 W
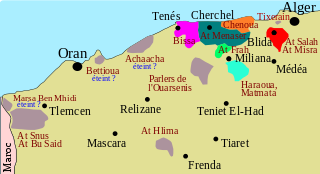
WSenhaja de Srair is a Northern Berber language. It is spoken by the Sanhaja Berbers inhabiting the southern part of the Moroccan Rif. It is spoken in the Ketama area west of Tarifit in the Taza-Al Hoceima-Taounate region
 W
WSened is an extinct East Zenati Berber language that was spoken in the nearby towns of Sened and Majoura in southern Tunisia until the mid-20th century. In 1911, the whole town of Sened spoke Berber; by 1968, only the elderly did.
 W
WTawellemmet (Tawəlləmmət) is the largest of the Tuareg languages in the Berber branch of the Afroasiatic family. It is usually one of two languages classed within a language called Tamajaq, the other language being Aïr Tamajeq. Tawellemmet is the language of the Iwellemmeden Tuareg. It is spoken in Mali, Niger and parts of northern Nigeria by approximately 801,000 people.
 W
WTugurt, also known as Oued Righ Berber and Temacine Tamazight, is a Zenati Berber variety spoken in some of the oases of the northeastern Oued Righ region around Touggourt in Algeria. As of 1893, its main speech area was in Temacine, Blidet-Amor, Meggarine and Ghomra. It is closely related to the nearby Tumzabt (Mozabite) and Teggargrent (Ouargli) languages.
 W
WThe Western Algerian Zenatic dialects are a diffuse set of Zenati Berber dialects spoken in north-western Algeria, west of the capital Algiers.
 W
WZuwara Berber or Twillult language (also: Zuara, Zwara, is a Berber dialect, one of the Berber Zenati languages. It is spoken in Zuwara city, located on the coast of western Tripolitania in northwestern Libya.