 W
WThis is a glossary list of opera genres, giving alternative names.
 W
WThe ballad opera is a genre of English stage entertainment that originated in the early 18th century, and continued to develop over the following century and later. Like the earlier comédie en vaudeville and the later Singspiel, its distinguishing characteristic is the use of tunes in a popular style with spoken dialogue. These English plays were 'operas' mainly insofar as they satirized the conventions of the imported opera seria. Music critic Peter Gammond describes the ballad opera as "an important step in the emancipation of both the musical stage and the popular song."
 W
WA breeches role is one in which an actress appears in male clothing. Breeches, tight-fitting knee-length pants, were the standard male garment at the time these roles were introduced. The theatrical term travesti covers both this sort of cross-dressing and also that of male actors dressing as female characters. Both are part of the long history of cross-dressing in music and opera and later in film and television.
 W
WA claque is an organized body of professional applauders in French theatres and opera houses. Members of a claque are called claqueurs.
 W
WComic opera is a sung dramatic work of a light or comic nature, usually with a happy ending and often including spoken dialogue.
 W
WA concert performance or concert version is a performance of a musical theater or opera in concert form, without set design or costumes, and mostly without theatrical interaction between singers.
 W
WA Gesamtkunstwerk is a work of art that makes use of all or many art forms or strives to do so. The term is a German loanword which has come to be accepted in English as a core term in aesthetics.
 W
WGrand opera is a genre of 19th-century opera generally in four or five acts, characterized by large-scale casts and orchestras, and lavish and spectacular design and stage effects, normally with plots based on or around dramatic historic events. The term is particularly applied to certain productions of the Paris Opéra from the late 1820s to around 1850; 'grand opéra' has sometimes been used to denote the Paris Opéra itself.
 W
WAn insertion aria is an aria sung in an opera for which it was not composed. It was a practice that began in the seventeenth century and continued actively through the late 19th century and sporadically through the 20th century. The insertion aria could replace an existing aria, or might be added to an opera. All insertions were planned in advance. They might be composed by the same composer of the opera, or might have been written by a different composer, with or without the knowledge of the opera's composer. Most insertions were of arias; infrequently non-operatic songs were inserted. Insertions could consist of arias, duets, ensembles, even entire scenes. Although men and women singers used insertion, women are the ones most remembered for the practice. The years 1800–1840 represent the apex of influence that women singers exerted over the operatic stage, influencing most aspects of opera performances, including insertions.
 W
WThe masque was a form of festive courtly entertainment that flourished in 16th- and early 17th-century Europe, though it was developed earlier in Italy, in forms including the intermedio. A masque involved music and dancing, singing and acting, within an elaborate stage design, in which the architectural framing and costumes might be designed by a renowned architect, to present a deferential allegory flattering to the patron. Professional actors and musicians were hired for the speaking and singing parts. Often the masquers, who did not speak or sing, were courtiers: the English queen Anne of Denmark frequently danced with her ladies in masques between 1603 and 1611, and Henry VIII and Charles I of England performed in the masques at their courts. In the tradition of masque, Louis XIV of France danced in ballets at Versailles with music by Jean-Baptiste Lully.
 W
WIn modern usage, a melodrama is a dramatic work wherein the plot, which is typically sensational and designed to appeal strongly to the emotions, takes precedence over detailed characterization. Melodramas typically concentrate on dialogue, which is often bombastic or excessively sentimental, rather than action. Characters are often drawn and may appear stereotyped. Melodramas are typically set in the private sphere of the home, focusing on morality and family issues, love, and marriage, often with challenges from an outside source, such as a "temptress", a scoundrel, or an aristocratic villain. A melodrama on stage, filmed, or on television is usually accompanied by dramatic and suggestive music that offers cues to the audience of the drama being presented.
 W
WAn opera house is a theatre building used for performances of opera. It usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, and backstage facilities for costumes and building sets.
 W
WPastorale héroïque was a type of ballet héroïque, a form of the opéra-ballet genre of French Baroque opera. The first work to bear the name was Jean-Baptiste Lully's final completed opera Acis et Galatée (1686), although musical works on pastoral themes had already appeared on the French stage. The pastorale héroïque usually drew on classical subject matter associated with pastoral poetry. Like the tragédie en musique, it had an allegorical prologue; however, its structure consisted of three acts, rather than the five of the tragédie en musique. Later examples were written by Jean-Philippe Rameau; these include Zaïs (1748) and Naïs (1749), and Acante et Céphise (1751).
 W
WRecitative is a style of delivery in which a singer is allowed to adopt the rhythms and delivery of ordinary speech. Recitative does not repeat lines as formally composed songs do. It resembles sung ordinary speech more than a formal musical composition.
 W
WRescue opera was a genre of opera in the late 18th and early 19th centuries in France and Germany. Generally, rescue operas deal with the rescue of a main character from danger and end with a happy dramatic resolution in which lofty humanistic ideals triumph over base motives. Operas with this kind of subject matter became popular in France around the time of the French Revolution; a number of such operas dealt with the rescue of a political prisoner. Stylistically and thematically, rescue opera was an outgrowth of the French bourgeois opéra comique; musically, it began a new tradition that would influence German Romantic opera and French grand opera. The most famous rescue opera is Ludwig van Beethoven's Fidelio.
 W
WA Singspiel is a form of German-language music drama, now regarded as a genre of opera. It is characterized by spoken dialogue, which is alternated with ensembles, songs, ballads, and arias which were often strophic, or folk-like. Singspiel plots are generally comic or romantic in nature, and frequently include elements of magic, fantastical creatures, and comically exaggerated characterizations of good and evil.
 W
WSurtitles, also known as supertitles, SurCaps, OpTrans, are translated or transcribed lyrics/dialogue projected above a stage or displayed on a screen, commonly used in opera, theatre or other musical performances. The word "surtitle" comes from the French language "sur", meaning "over" or "on", and the English language word "title", formed in a similar way to the related subtitle. The word Surtitle is a trademark of the Canadian Opera Company.
 W
WIn music, timbre, also known as tone color or tone quality, is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish different instruments in the same category.
 W
WTravesti is a theatrical term referring to the portrayal of a character in an opera, play, or ballet by a performer of the opposite sex.
 W
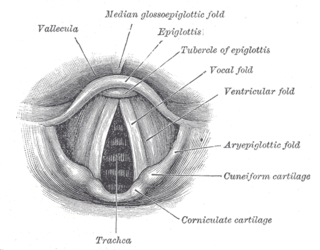
WIn humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal chords, vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of tissue in the throat that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, the folds are controlled via the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve. They are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx. They vibrate, modulating the flow of air being expelled from the lungs during phonation.
 W
WVocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of voice instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how proper singing technique is accomplished.
 W
WA vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice, vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register. Registers originate in laryngeal function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches and produces certain characteristic sounds.
 W
WThe Wagner tuba is an infrequently-used brass instrument that combines tonal elements of both the French horn and the trombone. Wagner tubas are also referred to as Wagner horns or Bayreuth tubas in English and as Bayreuth-Tuben or simply Tuben in German. The term Wagner tuba has been used in English since the 19th century and is standard today. Wagner's published scores usually refer to these instruments in the plural, Tuben, but sometimes in the singular, Tuba.
 W
WZarzuela is a Spanish lyric-dramatic genre that alternates between spoken and sung scenes, the latter incorporating operatic and popular songs, as well as dance. The etymology of the name is uncertain, but some propose it may derive from the name of a royal hunting lodge, the Palace of Zarzuela, near Madrid, where that type of entertainment was allegedly first presented to the court. The palace in turn was named after brambles, which grew there, and so the festivities held within the walls became known as "Zarzuelas".