 W
WThe Casa da Índia was a Portuguese state-run commercial organization founded during the Age of Discovery, charged with the regulation of international trade and the administration of the Portuguese Empire's territories, colonies, and factories across India, Africa, and the rest of Asia. Central to the Casa da Índia's objectives was the establishment and protection of a Portuguese mare clausum in the Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Arabian sea, and the Indies. It was founded by King Manuel I of Portugal in 1500 to direct Portugal's monopoly of the spice trade and to manage royal policy for Portuguese India. Following 1503, it absorbed the Casa da Guiné e Mina, an organization founded by Prince Henry the Navigator in 1443, which operated under a similar mandate for Portuguese Africa, thus making the Casa da Índia responsible for the regulation of all Portuguese imperial trade, the administration of Portuguese trade posts and military bases in Asia and Africa, and protection of the Portuguese Crown's commercial interests.
 W
WThe Danish East India Company refers to two separate Danish-Norwegian chartered companies. The first company operated between 1616 and 1650. The second company existed between 1670 and 1729, however, in 1730 it was re-founded as the Asiatic Company.
 W
WDent & Co. or Dent's, was one of the wealthiest British merchant firms, or Hongs, active in China during the 19th century. A direct rival to Jardine, Matheson & Co, together with Russell & Co., these three companies are recognised as the original Canton Hongs active in early Colonial Hong Kong.
 W
WDodwell & Co. or Dodwell's, was one of the leading British merchant firms, or hongs, active in China and Japan during the 19th and 20th century. It was a direct rival to Jardine, Matheson & Co.
 W
WE.D. Sassoon & Co., Ltd. was a trading company operating in the second half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century predominantly in India, China and Japan.
 W
WThe East India Company (EIC), also known as the Honourable East India Company (HEIC), East India Trading Company (EITC), the English East India Company or the British East India Company, and informally known as John Company, Company Bahadur, or simply The Company was an English and later British joint-stock company founded in 1600. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies, and later with Qing China. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong after the First Opium War, and maintained trading posts and colonies in the Persian Gulf Residencies.
 W
WGibb, Livingston & Co., known in Chinese as Jinkee or Renji, was one of the most important and best-known foreign trading firms in China in the late 19th and the first half of the 20th century.
 W
WThe Grill family are noted for their contribution to the Swedish iron industry and for exports of iron and copper during the 18th century. Starting as silversmiths and experts on noble metals the Grills became engaged in a wide range of businesses. After 1700 the family began its rise to prominence. They owned ironworks, while operating wharfs, and importing material related to shipbuilding. The Grills benefited from mercantilist policy. With a positive balance on their account the Grills became engaged in banking, also in the Dutch Republic; around 1720 in the market for government liabilities and then mediating large credits and clearing international bills of exchange. The Grills had significant influence with the Swedish East India Company (SOIC); three members became directors of the SOIC and the Grill firm traded as members of the SOIC and privately.
 W
WThe Hongkong Canton & Macao Steamboat Company was a British merchant shipping and maritime trading company founded in 1865 in the Crown colony of Hong Kong.
 W
WHudson River Trading (HRT) is a multi-asset class quantitative trading firm, and more specifically a high-frequency trading (HFT) firm, based in New York City and founded in 2002. According to the Wall Street Journal, it is responsible for about 5% of all stock trading in the United States.
 W
W'MMTC Ltd., Metals and Minerals Trading Corporation of India, is one of the two highest earners of foreign exchange for India and India's largest public sector trading body. Not only handling the export and import of primary products such as coal, iron ore, agro and industrial products, MMTC also exports and imports important commodities such as ferrous and nonferrous metals for industry, and agricultural fertilizers. MMTC's diverse trade activities cover Third Country Trade, Joint Ventures and Link Deals and all modern forms of international trading. The company has a vast international trade network, spanning almost in all countries in Asia, Europe, Africa, Oceania, America and also includes a wholly owned international subsidiary in Singapore, MTPL. It is one of the Miniratnas companies.
 W
WKunst and Albers or Kunst & Albers was a German trading company in Russia. Founded by Gustav Kunst, a merchant, and Gustav Albers, a sailor, it operated the first department store in Vladivostok. At its height, it was a vast business empire and the largest trading company in the Russian Far East.
 W
WPlus500 is a British international financial firm providing online trading services in contracts for difference (CFDs), across more than 2,000 securities and multiple asset classes. The company is headquartered in Israel and has subsidiaries in UK, Cyprus, Australia, Singapore, and Bulgaria.
 W
WThe Portuguese East India Company was a short-lived ill-fated attempt by Philip III of Portugal to create a national chartered company to ensure the security of Portuguese interests in India in the face of increasing influence by the Dutch and English following the personal union of the Portuguese and Spanish Crowns.
 W
WThe Hon. John Richardson,, M.P., J.P., was a Scots-Quebecer and arguably Montreal's leading businessman in his time. In trade, he was in partnership with his first cousin, John Forsyth. A member of the Beaver Club, he established the XY Company and co-founded the Bank of Montreal. A staunch Conservative and Royalist, he represented Montreal East in the 1st Parliament of Lower Canada; assuming the role of the voice of the merchants and appointed an honorary member of the Executive Council of Lower Canada. An intellectual, he was President of the Natural History Society of Montreal and well read in modern and ancient history, law, economics, and British poetry. He was a generous patron to both the Presbyterian and the Anglican Churches, and the first President of the Montreal General Hospital, where the west wing was named for him.
 W
WThe Royal Greenland Trading Department was a Danish state enterprise charged with administering the realm's settlements and trade in Greenland. The company managed the government of Greenland from 1774 to 1908 through its Board of Managers in Copenhagen and a series of Royal Inspectors and Governors in Godthaab and Godhavn on Greenland. The company was headquartered at Grønlandske Handels Plads at Christianshavn.
 W
WSalt Trading Corporation (STC) is a Nepalese company founded in 1963 for the purpose of regularising the distribution primarily of salt but also sugar, wheat, oil, rice, other grains, tea, LP gas, paper, coal and tyres for vehicles.
 W
WShewan, Tomes & Co. was one of the leading trading companies in Hong Kong and China during the late 19th and early 20th century.
 W
WThe Society of Suriname was a Dutch private company, modelled on the ideas of Jean-Baptiste Colbert and set up on 21 May 1683 to profit from the management and defense of the Dutch Republic's colony of Suriname. It had three participants, with equal shares in the costs and benefits of the society; the city of Amsterdam, the family Van Aerssen van Sommelsdijck, and the Dutch West India Company. Only through mutual consent could these shareholders withdraw from the society.
 W
WThe Gesellschaft Süd-Kamerun was a private trading corporation formed in 1898, facilitated by governor Jesko von Puttkamer, to run the rubber and ivory trade in the southeast of the German colony of Kamerun.
 W
WThe Swedish East India Company was founded in Gothenburg, Sweden, in 1731 for the purpose of conducting trade with China and the Far East. The venture was inspired by the success of the Dutch East India Company and the British East India Company. This made Gothenburg a European center of trade in eastern products. The main goods were silk, tea, furniture, porcelain, precious stones and other distinctive luxury items. Trade with China saw the arrival of some new customs in Sweden. The Chinese cultural influence increased, and tea, rice, arrack and new root vegetables started appearing in Swedish homes.
 W
WThe Swedish West India Company was a Swedish chartered company which was based in the West Indies. It was the main operator in the Swedish slave trade during its existence.
 W
WThe Veerse Compagnie was a pre-company from the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands that was founded by Balthazar de Moucheron, a ship owner from Antwerp in the Southern Netherlands. After the fall of Antwerp he moved his business to Zeeland. The fleet of the Veerse Compagnie was made up of two ships; 'Leeuw' (Lion) and 'Leeuwin' (Lioness) and was headed by Cornelis Houtman. Its fleet left from Veere on 28 March 1598 and returned to the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands in 1600.
 W
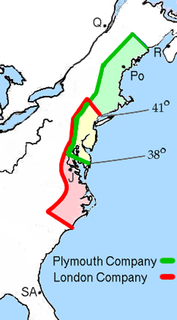
WThe Virginia Company refers collectively to two joint-stock companies chartered under James I on April 10, 1606 with the goal of establishing settlements on the coast of North America. The two companies are referred to as the "Virginia Company of London" and the "Virginia Company of Plymouth", and they operated with identical charters in different territories. The charters established an area of overlapping territory in North America as a buffer zone, and the two companies were not permitted to establish colonies within 100 miles of each other. The Plymouth Company never fulfilled its charter, but its territory was claimed by England and became New England.
 W
WA voorcompagnie (pre-company) is the naming given to the trading companies from the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands that traded in Asia between 1594 and 1602, before they all merged to form the Dutch East India Company (VOC). The pre-companies were financed by merchants from the Northern Netherlands and rich immigrants from the Southern Netherlands. Because of the deadly competition, the government forced the smaller trading companies to unite and form the (United) East India Company, that on its turn received the exclusive rights for the trade with Asia for the following 21 years.