 W
WHuman physical appearance is the outward phenotype or look of human beings.
 W
WAestheticism was an art movement, both practical and theoretical, of the late 19th century supporting an emphasis on aesthetic value and effects— in preference to the socio-political themes and positions— of literature, fine art, music and other arts. This meant that the art of the movement was produced with a view toward being beautiful first and foremost, rather than serving a moral, allegorical, doctrinal or other such purpose — "art for art's sake". It was particularly prominent in England during the late 19th century, supported by notable writers such as Walter Pater and Oscar Wilde, having started in a small way in the 1860s in the studios and houses of a radical group of artists and designers, including William Morris and Dante Gabriel Rossetti, reformers who explored new ways of living in defiance of the design standards of the age as revealed in the 1851 Great Exhibition at Hyde Park, London. Flourishing in the 1870s and 1880s, critic Walter Hamilton was the first writer to name the movement, publishing The Aesthetic Movement in England in 1882.
 W
WAlternative modeling is a branch of the modeling industry that features models who do not conform to mainstream ideals of beauty. Alternative models are often niche-specific, with a personal style that represents subcultures like goth, steampunk, and fetishism. An alternative model may, for example, be tattooed, pierced, or have other body modifications, have distinctively subcultural hair such as being shaved, dyed a distinctively unnatural color, or styled into a mohawk or dreadlocks. Alternative modeling can be clothed or unclothed.
 W
WBarefoot is the most common term for the state of not wearing any footwear.
 W
W"Big Beautiful Woman" is a euphemism for an overweight woman.
 W
WBody dysmorphic disorder (BDD), occasionally still called dysmorphophobia, is a mental disorder characterized by the obsessive idea that some aspect of one's own body part or appearance is severely flawed and therefore warrants exceptional measures to hide or fix it. In BDD's delusional variant, the flaw is imagined. If the flaw is actual, its importance is severely exaggerated. Either way, thoughts about it are pervasive and intrusive, and may occupy several hours a day, causing severe distress and impairing one’s otherwise normal activities. BDD is classified as a somatoform disorder, and the DSM-5 categorizes BDD in the obsessive–compulsive spectrum, and distinguishes it from anorexia nervosa.
 W
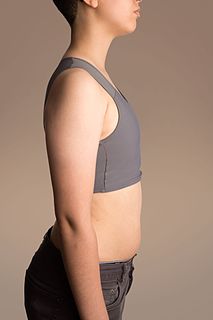
WBreast binding is the act of flattening breasts by the use of constrictive materials. The term also refers to the material used in this act. Common binding materials include cloth strips, purpose-built undergarments, often using spandex or other synthetic fiber, and shirts layered from tight to loose. The act of breast binding is common for trans men, but is also done by androgynous and non-binary people, as well as crossdressers, cosplayers, and performers. In a general sense, women may also use binders as alternatives to bras or as a practice of propriety.
 W
WButtock cleavage is minor exposure of the buttocks and the intergluteal cleft between them, often because of low-rise pants. The crena is a formal term for the cleft between the buttocks, and the medical term is posterior rugae.
 W
WCardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder.
 W
WCleavage is the narrow depression or hollow between human breasts. The superior portion of cleavage may be accentuated by clothing such as a low-cut neckline that exposes the division. Joseph Breen, head of the U.S. film industry's Production Code Administration, coined the term in its current meaning when evaluating the 1943 film The Outlaw, starring Jane Russell. The term was explained in Time magazine on August 5, 1946. It is most commonly used in the parlance of Western female fashion to refer to necklines that reveal or emphasize décolletage.
 W
WThe intermammary cleft or intermammary sulcus or sulcus intermammarius is a surface feature of males and females that marks the division of the two breasts with the sternum (breastbone) in the middle. The International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) uses the terms "sulcus intermammarius" or "intermammary cleft" when referring to the area between the breasts.
 W
WA comb over or combover is a hairstyle commonly worn by balding men in which the hair is grown long and combed over the bald area to minimize the appearance of baldness. Sometimes the parting is lowered so that more hair can be used to cover the balding area.
 W
WA dandy, historically, is a man who places particular importance upon physical appearance, refined language, and leisurely hobbies, pursued with the appearance of nonchalance in a cult of self. A dandy could be a self-made man who strove to imitate an aristocratic lifestyle despite coming from a middle-class background, especially in late 18th- and early 19th-century Britain.
 W
WA deformity, dysmorphism, or dysmorphic feature is a major abnormality in the shape of a body part or organ compared to the normal shape of that part.
 W
WThe dimples of Venus are sagittally symmetrical indentations sometimes visible on the human lower back, just superior to the gluteal cleft. They are directly superficial to the two sacroiliac joints, the sites where the sacrum attaches to the ilium of the pelvis. An imaginary line joining both dimples of Venus passes over the spinous process of the second sacral vertebra.
 W
WThe Honest Body Project is a collection of photographic portraits and stories from women aimed to empower and encourage self-love. The project was created by photographer Natalie McCain from Rockledge, FL. The collection contains hundreds of portraits and stories on various topics of womanhood, photographed in black and white and without manipulation to alter the appearance of the women. The women are often accompanied by their children. There have been many series taken from the project.
 W
WJewellery or jewelry consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a western perspective, the term is restricted to durable ornaments, excluding flowers for example. For many centuries metal such as gold used in different carats from 21, 18, 12, 9 or even lower, often combined with gemstones, has been the normal material for jewellery, but other materials such as shells and other plant materials may be used.
 W
WA macaroni in mid-18th-century England was a fashionable fellow who dressed and even spoke in an outlandishly affected and epicene manner. The term pejoratively referred to a man who "exceeded the ordinary bounds of fashion" in terms of clothes, fastidious eating, and gambling. He mixed Continental affectations with his English nature, like a practitioner of macaronic verse, laying himself open to satire:There is indeed a kind of animal, neither male nor female, a thing of the neuter gender, lately [1770] started up among us. It is called a macaroni. It talks without meaning, it smiles without pleasantry, it eats without appetite, it rides without exercise, it wenches without passion.
 W
WMacrocephaly-capillary malformation (M-CM) is a multiple malformation syndrome causing abnormal body and head overgrowth and cutaneous, vascular, neurologic, and limb abnormalities. Though not every patient has all features, commonly found signs include macrocephaly, congenital macrosomia, extensive cutaneous capillary malformation, body asymmetry, polydactyly or syndactyly of the hands and feet, lax joints, doughy skin, variable developmental delay and other neurologic problems such as seizures and low muscle tone.
 W
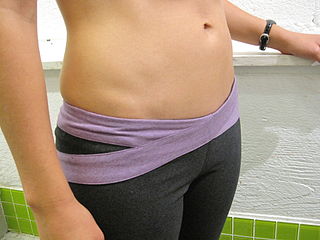
WIn fashion, the midriff is the human abdomen. The midriff is exposed when wearing a crop top or some forms of swimwear. Cholis worn by Indian women expose a section of midriff, usually 4 to 5 inches.
 W
WA model is a person with a role either to promote, display or advertise commercial products or to serve as a visual aid for people who are creating works of art or to pose for photography. Though models are predominantly female, there are also male models, especially to model clothing. Models may work professionally or casually.
 W
WSexual selection in humans concerns the concept of sexual selection, introduced by Charles Darwin as an element of his theory of natural selection, as it affects humans. Sexual selection is a biological way one sex chooses a mate for the best reproductive success. Most compete with others of the same sex for the best mate to contribute their genome for future generations. This has shaped our evolution for many years, but reasons why humans choose their mates are hardly understood. Sexual selection is quite different in non-human animals than humans as they feel more of the evolutionary pressures to reproduce and can easily reject a mate. The role of sexual selection in human evolution has not been firmly established although neoteny has been cited as being caused by human sexual selection. It has been suggested that sexual selection played a part in the evolution of the anatomically modern human brain, i.e. the structures responsible for social intelligence underwent positive selection as a sexual ornamentation to be used in courtship rather than for survival itself, and that it has developed in ways outlined by Ronald Fisher in the Fisherian runaway model. Fisher also stated that the development of sexual selection was "more favourable" in humans.
 W
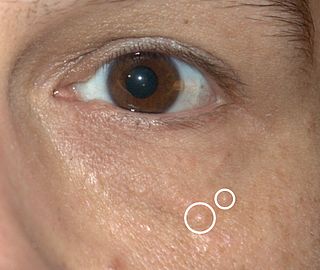
WSyringomas are benign eccrine sweat duct tumors, typically found clustered on eyelids, although they may also be found in the armpits, abdomen, chest, neck, scalp or groin area including genitals in a symmetric pattern. They are skin-colored or yellowish firm, rounded bumps, 1–3 mm in diameter, and may be confused with xanthoma, milia, hidrocystoma, trichoepithelioma, and xanthelasma. They are more common in women and are most commonly found in middle-aged Asian women. While they can present at any time in life, they typically present during adolescence. They are usually not associated with any other symptoms although can sometimes cause itchiness or irritation.
 W
WA toupée is a hairpiece or partial wig of natural or synthetic hair worn to cover partial baldness or for theatrical purposes. While toupées and hairpieces are typically associated with male wearers, some women also use hairpieces to lengthen existing hair, or cover a partially exposed scalp.
 W
WTucking is a technique whereby an individual hides the crotch bulge of the penis and testicles so that they are not conspicuous through clothing.
 W
WXanthelasma is a sharply demarcated yellowish deposit of cholesterol underneath the skin. It usually occurs on or around the eyelids. While they are neither harmful to the skin nor painful, these minor growths may be disfiguring and can be removed. There is a growing body of evidence for the association between xanthelasma deposits and blood low-density lipoprotein levels and increased risk of atherosclerosis.