 W
WAshley's Sack is a mid-1800s cloth seed or feed sack featuring an embroidered text that recounts the slave sale of a nine-year-old girl named Ashley and the parting gift of the sack by her mother, Rose. The sack is on display at the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington D.C. Rose filled the sack with a dress, braid of her hair, pecans, and "my love always". The gift was likely passed down to Ashley's granddaughter, Ruth (Jones) Middleton, who embroidered their story on to the sack in 1921.
 W
WThe Axelrod quartet is a set of four Stradivarius instruments collected by Herbert R. Axelrod. The collection consists of the Greffuhle violin, Axelrod viola, Ole Bull violin, and Marylebone cello.
 W
WThe Bat Creek inscription is an inscribed stone collected as part of a Native American burial mound excavation in Loudon County, Tennessee, in 1889 by the Smithsonian Bureau of Ethnology's Mound Survey, directed by entomologist Cyrus Thomas. The inscriptions were initially described as Cherokee, but in 2004, similarities to an inscription that was circulating in a Freemason book were discovered. Hoax expert Kenneth Feder says the peer reviewed work of Mary L. Kwas and Robert Mainfort has "demolished" any claims of the stone's authenticity. Mainfort and Kwas themselves state "The Bat Creek stone is a fraud."
 W
WThe Boeing 367-80, known simply as the Dash 80, is an American quadjet prototype aircraft built by Boeing to demonstrate the advantages of jet propulsion for commercial aviation. It served as basis for the design of the KC-135 tanker and the 707 airliner.
 W
WCrystal skulls are human skull hardstone carvings made of clear or milky white quartz, claimed to be pre-Columbian Mesoamerican artifacts by their alleged finders; however, these claims have been refuted for all of the specimens made available for scientific studies. The results of these studies demonstrated that those examined were manufactured in the mid-19th century or later, almost certainly in Europe, during a time when interest in ancient culture abounded. The skulls appear to have been crafted in Germany, quite likely at workshops in the town of Idar-Oberstein, which was renowned for crafting objects made from imported Brazilian quartz in the late 19th century.
 W
WDumbo the Flying Elephant is an aerial carousel-style ride located in Fantasyland at six Disney parks around the world. It is based on the 1941 film, Dumbo. The original attraction opened at Disneyland on August 16, 1955. The four other versions of the attraction were opening-day attractions at their respective parks. It is the only attraction that can be found at all six Disney castle parks worldwide.
 W
WFallen Astronaut is a 3.5-inch (8.9 cm) aluminum sculpture created by Paul Van Hoeydonck. It is a small stylized figure, meant to depict an astronaut in a spacesuit, intended to commemorate the astronauts and cosmonauts who have died in the advancement of space exploration. It was commissioned and placed on the Moon by the crew of Apollo 15 at Hadley Rille on August 1, 1971, next to a plaque listing the 14 men known who died. The statue lies horizontal on the ground among several footprints.
 W
WThe Goose Lake meteorite is a meteorite that was found at Goose Lake in the United States by two hunters from Oakland, California on October 13, 1938.
 W
WThe Greffuhle Stradivarius is a violin made by Antonio Stradivari of Cremona, Italy, around the year 1709. It derives its name from a French nobleman who once owned it. The Greffuhle is one of the eleven Stradivarius instruments that are decorated.
 W
WThe History of the Indian Tribes of North America is a three-volume collection of Native American biographies and accompanying lithograph portraits, originally published in the United States from 1836 to 1844 by Thomas McKenney and James Hall. The majority of the portraits were first painted in oil by Charles Bird King. McKenney was working as the US Superintendent of Indian Trade and would head the Office of Indian Affairs, both within the War Department. He planned publication of the biographical project to be supported by private subscription, as was typical for publishing of the time.
 W
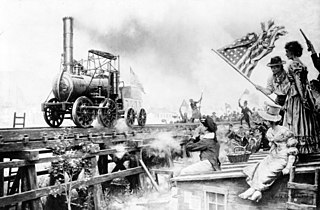
WJohn Bull is a British-built railroad steam locomotive that operated in the United States. It was operated for the first time on September 15, 1831, and it became the oldest operable steam locomotive in the world when the Smithsonian Institution operated it in 1981. Built by Robert Stephenson and Company, the John Bull was initially purchased by and operated for the Camden and Amboy Railroad, the first railroad in New Jersey, which gave John Bull the number 1 and its first name, "Stevens". The C&A used the locomotive heavily from 1833 until 1866, when it was removed from active service and placed in storage.
 W
WJulia Child's kitchen is a historic artifact on display on the ground floor of the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of American History: Kenneth E. Behring Center, located in Washington, D.C., on the National Mall. The kitchen is not a replica, but is the actual kitchen used by noted 20th-century cookbook author and cooking show host Julia Child, appearing as the backdrop to several of her television shows.
 W
WLin Tinggui was a Chinese painter of the Southern Song Dynasty. His artwork was greatly influenced by themes of Chinese Buddhism.
 W
WThe List of space artifacts in the Smithsonian Institution includes space artifacts exhibited in the Smithsonian Institution's National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, and the Paul E. Garber Preservation, Restoration, and Storage Facility. The Smithsonian Institution's collection of space artifacts is the largest on display in the world.
 W
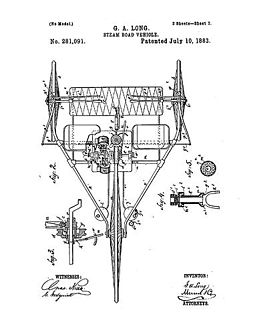
WThe Long steam tricycle appears to be one of the earliest preserved examples of a steam tricycle, built by George A. Long around 1880 and patented in 1883. One example was built, which after some years of use was dismantled and the parts dispersed. In 1946, one John H. Bateman, with assistance from the 96-year-old Long, reassembled the machine, which is now on display at the Smithsonian Institution. The example at the Smithsonian has been noted as the "oldest completely operable self-propelled road vehicle in the museum".
 W
WThe Loreto is a meteorite that was found in Baja California Sur, Mexico. It was found in 1896 and weighed approximately 95 kilograms (209 lb).
 W
WBefore humans went into space in the 1960s, several other animals were launched into space, including numerous other primates, so that scientists could investigate the biological effects of spaceflight. The United States launched flights containing primate passengers primarily between 1948 and 1961 with one flight in 1969 and one in 1985. France launched two monkey-carrying flights in 1967. The Soviet Union and Russia launched monkeys between 1983 and 1996. Most primates were anesthetized before lift-off.
 W
WOld Glory is a nickname for the flag of the United States. The original "Old Glory" was a flag owned by the 19th-century American sea captain William Driver, who flew the flag during his career at sea and later brought it to Nashville, Tennessee, where he settled. Driver greatly prized the flag and ensured its safety from the Confederates, who attempted to seize the flag during the American Civil War. In 1922, Driver's daughter and niece claimed to own the original "Old Glory," which became part of the collection of the Smithsonian Institution, where it remains at the National Museum of American History.
 W
WThe Olomana is a 3 ft narrow gauge 0-4-2 saddle tank locomotive built by Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1883 for the Waimanalo Sugar Company in Hawaii. It is currently in the Railroad Museum of Pennsylvania, on loan from the Smithsonian Institution. It was the third self-propelled vehicle to operate in Hawaii.
 W
WPasargadae was the capital of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great, who ordered its construction and the location of his tomb. Today it is an archaeological site and one of Iran's UNESCO World Heritage Sites, about 90 kilometres (56 mi) to the northeast of the modern city of Shiraz.
 W
WUSS Philadelphia is a gunboat of the Continental Navy. She was constructed from July-August 1776 for service during the American Revolutionary War. Manned by Continental Army soldiers, she was part of a fleet under the command of General Benedict Arnold that fought against the British Royal Navy in the Battle of Valcour Island on Lake Champlain. Philadelphia was sunk during the battle, on 11 October 1776.
 W
WRagamala paintings are a form of Indian miniature painting, a set of illustrative paintings of the Ragamala or "Garland of Ragas", depicting variations of the Indian musical modes called ragas. They stand as a classical example of the amalgamation of art, poetry and classical music in medieval India.
 W
WThe ruby slippers are the magic pair of shoes worn by Dorothy Gale as played by Judy Garland in the 1939 Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer musical film The Wizard of Oz. Because of their iconic stature, the ruby slippers are among the most valuable items of film memorabilia. A number of pairs were made for the film, though the exact number is unknown. Five pairs are known to have survived; one pair was stolen from a museum in 2005 and recovered in 2018.
 W
WThe Santa Cruz Railroad no. 3 is a narrow gauge steam locomotive in Washington D.C.. It is one of three preserved Baldwin Class 8/18 C 4-4-0 locomotives in the United States, the other two being the North Pacific Coast Railroad no. 12, the "Sonoma" displayed at the California State Railroad Museum, and the Eureka and Palisade Railroad no. 4, the "Eureka" which is privately owned, the latter of which it is the only operable example. It was common practice for American railroads of the 19th century to name their engines after Jupiter, "King of Gods", and other mythological figures to attract attention, thus the engine should not be confused with the engine of Golden Spike fame.
 W
WSouthern Railway 1401 is a steam locomotive that is the sole survivor of Southern Railway's Ps-4 class. Today it is on permanent display at the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of American History in Washington, D.C. It has a Pacific-type or 4-6-2 wheel arrangement and was built in 1926 by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) at their Richmond works.
 W
WSpace Shuttle Discovery is one of the orbiters from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the third of five fully operational orbiters to be built. Its first mission, STS-41-D, flew from August 30 to September 5, 1984. Over 27 years of service it launched and landed 39 times, aggregating more spaceflights than any other spacecraft to date. The Space Shuttle launch vehicle has three main components: the Space Shuttle orbiter, a single-use central fuel tank, and two reusable solid rocket boosters. Nearly 25,000 heat-resistant tiles cover the orbiter to protect it from high temperatures on re-entry.
 W
WThe Star-Spangled Banner, or the Great Garrison Flag, was the garrison flag that flew over Fort McHenry in Baltimore Harbor during the naval portion of the Battle of Baltimore during the War of 1812. It is on exhibit at the National Museum of American History, Smithsonian Institution. Seeing the flag flying over Fort McHenry on the morning of September 14, 1814, after the battle ended, Francis Scott Key was inspired to write the poem "Defence of Fort M'Henry". These words were written by Key and set to the tune of "To Anacreon in Heaven" by John Stafford Smith, a popular song at the time. It was not until 1931 that the song became the national anthem of the United States.
 W
WThe Stourbridge Lion was a railroad steam locomotive. It was the first to be operated in the United States, and one of the first locomotives to operate outside Britain. It takes its name from the lion's face painted on the front, and Stourbridge in England, where it was manufactured by the firm Foster, Rastrick and Company in 1829. The locomotive, obtained by the Delaware & Hudson Canal Company, was shipped to New York in May 1829, where it was tested raised on blocks. It was then taken to Honesdale, Pennsylvania for testing on the company's newly built track. The locomotive performed well in its first test in August 1829 but was found to be too heavy for the track and was never used for its intended purpose of hauling coal wagons. During the next few decades a number of parts were removed from the abandoned locomotive until only the boiler and a few other components remained. These were acquired by the Smithsonian Institution in 1890 and are currently on display at the B&O Railroad Museum in Baltimore.
 W
WThe Servais Stradivarius is an antique cello crafted in 1701 by Italian luthier Antonio Stradivari of Cremona (1644–1737). One of only sixty-three extant cellos attributed to Stradivari, it was crafted from exceptional wood reserved by the luthier for large instruments. Its varnish has been described as "unusually rich" and the color a reddish-orange with golden transparency. The cello takes its name from the nineteenth-century Belgian cellist, Adrien Francois Servais (1807–1866), who played this cello.
 W
WThe United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby Jones. Funding for the original expedition was requested by President John Quincy Adams in 1828, however, Congress would not implement funding until eight years later. In May 1836, the oceanic exploration voyage was finally authorized by Congress and created by President Andrew Jackson.
 W
WUSS Enterprise (NCC-1701) is a starship in the Star Trek media franchise. It is the main setting of the original Star Trek television series (1966–1969) and several films, and it has been depicted in spinoffs, films, books, products, and fan-created media. Under the command of Captain James T. Kirk, the Enterprise carries its crew on a mission "to explore strange, new worlds; to seek out new life and new civilizations; to boldly go where no man has gone before". The upcoming series Star Trek: Strange New Worlds will depict the Enterprise led by Kirk's predecessor, Captain Christopher Pike.
 W
WRichard Russell Waldron was a purser "and special agent" in the Wilkes Expedition, together with younger brother Thomas Westbrook Waldron (consul). Several landmarks were named after him or his brother. After the expedition was completed Waldron enjoyed some popularity and influence in Washington, D.C.
 W
WThomas Westbrook Waldron was a captain's clerk on the Wilkes Expedition, and the first United States consul to Hong Kong. His service to the United States consular service was honoured by Secretary of State Hillary Clinton during a ceremony in 2009.