 W
WFood security is a measure of the availability of food and individuals' ability to access it. According the United Nations’ Committee on World Food Security, food security is defined as the means that all people, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food that meets their food preferences and dietary needs for an active and healthy life. The availability of food irrespective of class, gender or region is another one. There is evidence of food security being a concern many thousands of years ago, with central authorities in ancient China and ancient Egypt being known to release food from storage in times of famine. At the 1974 World Food Conference the term "food security" was defined with an emphasis on supply; food security is defined as the "availability at all times of adequate, nourishing, diverse, balanced and moderate world food supplies of basic foodstuffs to sustain a steady expansion of food consumption and to offset fluctuations in production and prices". Later definitions added demand and access issues to the definition. The final report of the 1996 World Food Summit states that food security "exists when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life."
 W
WThe 100-Mile Diet: A Year of Local Eating is a non-fiction book written by Canadian writers Alisa Smith and J.B. MacKinnon. In the book, the authors recount their experiences, including motivations and challenges, on restricting their diet, for one year, to include only foods grown within 100 miles of their residence. Beginning in March 2005, with little preparation the urban couple began only purchasing foods with ingredients they knew were all from within 100 miles. Finding little in grocery stores, they relied on farmers' markets and visits to local farms. Staples in their diet included seafood, chicken, root vegetable, berries, and corn. They lacked cooking oils, rice, and sugar. They preserved foods for use in the winter but ended with extra supplies.
 W
WAquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the farming of fish, crustaceans, mollusks, aquatic plants, algae, and other organisms. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater and saltwater populations under controlled conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture commonly known as marine farming refers to aquaculture practiced in marine environments and in underwater habitats, opposed to in freshwater.
 W
WCarbon sequestration or carbon dioxide removal (CDR) is the long-term removal, capture or sequestration of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to slow or reverse atmospheric CO2 pollution and to mitigate or reverse global warming.
 W
WCellular Agriculture Society is an international 501c3 nonprofit organization based in Miami, created in 2017 to research, fund and advance cellular agriculture.
 W
WCommunity-supported agriculture or cropsharing is a system that connects the producer and consumers within the food system more closely by allowing the consumer to subscribe to the harvest of a certain farm or group of farms. It is an alternative socioeconomic model of agriculture and food distribution that allows the producer and consumer to share the risks of farming. The model is a subcategory of civic agriculture that has an overarching goal of strengthening a sense of community through local markets.
 W
WCompost is made by decomposing organic materials into simpler organic and inorganic compounds in a process called composting. This process recycles various organic materials otherwise regarded as waste products. A good compost is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms.
 W
WConservation agriculture (CA) can be defined by a statement given by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations as "A farming system that promotes minimum soil disturbance, maintenance of a permanent soil cover, and diversification of plant species. It enhances Biodiversity and natural biological processes above and below the ground surface, which contribute to increased water and nutrient use efficiency and to improved and sustained crop production."
 W
WCultured meat is meat produced by in vitro cell culture of animal cells, instead of from slaughtered animals. It is a form of cellular agriculture.
 W
WEdible tableware is tableware, such as plates, drinkware and glasses, utensils and cutlery, that is edible. Edible tableware can be homemade and has also been mass-produced by some companies, and can be prepared using many various foods.
 W
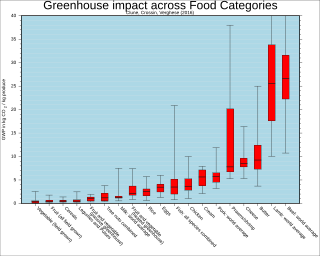
WEnvironmental vegetarianism is the practice of vegetarianism when motivated by the desire to create a sustainable diet that avoids the negative environmental impact of meat production. Livestock as a whole is estimated to be responsible for around 18% of global greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, significant reduction in meat consumption has been advocated by, among others, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in their 2019 special report and as part of the 2017 World Scientists' Warning to Humanity.
 W
WFarm-to-table is a social movement which promotes serving local food at restaurants and school cafeterias, preferably through direct acquisition from the producer. This might be accomplished by a direct sales relationship, a community-supported agriculture arrangement, a farmer's market, a local distributor or by the restaurant or school raising its own food. Farm-to-table often incorporates a form of food traceability where the origin of the food is identified to consumers. Often restaurants cannot source all the food they need for dishes locally, so only some dishes or only some ingredients are labelled as local.
 W
WFood miles is the distance food is transported from the time of its making until it reaches the consumer. Food miles are one factor used when testing the environmental impact of food, such as the carbon footprint of the food.
 W
WFood rescue, also called food recovery or food salvage, is the practice of gleaning edible food that would otherwise go to waste from places such as restaurants, grocery stores, produce markets, or dining facilities and distributing it to local emergency food programs.
 W
Wfoodsharing.de is an online platform that saves and distributes surplus food in Germany and Austria. It is managed by the Foodsharing association and was founded on December 12, 2012. On foodsharing.de individuals, retailers and producers can offer or collect food that would otherwise be thrown away. This service is completely free, and functions thanks to volunteer work. The project's goal is to fight everyday food waste and to raise awareness about this problem in society.
 W
WMasanobu Fukuoka was a Japanese farmer and philosopher celebrated for his natural farming and re-vegetation of desertified lands. He was a proponent of no-till, herbicide and pesticide free cultivation methods from which he created a particular method of agriculture, commonly referred to as "natural farming" or "do-nothing farming".
 W
WHolistic Management in agriculture is an approach to managing resources that was originally developed by Allan Savory. Holistic Management is a registered trademark of Holistic Management International.
 W
WA keyhole garden is a two-meter-wide circular raised garden with a keyhole-shaped indentation on one side. The indentation allows gardeners to add uncooked vegetable scraps, greywater, and manure into a composting basket that sits in the center of the bed. In this way, composting materials can be added to the basket throughout the growing season to provide nutrients for the plants. The upper layer of soil is hilled up against the center basket so the soil slopes gently down from the center to the sides. Most keyhole gardens rise about one meter above the ground and have walls made of stone. The stone wall not only gives the garden its form, but helps trap moisture within the bed. Keyhole gardens originated in Lesotho and are well adapted to dry arid lands and deserts. In Africa, they are positioned close to the kitchen and used to raise leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and spinach; herbs; and root crops such as onions, garlic, carrots, and beets. Keyhole gardens are ideal for intensive planting, a technique in which plants are placed close together to maximize production. Plants with wide-reaching root systems such as tomatoes and zucchini may not perform well in a keyhole garden.
 W
WThe Land Institute is a non-profit research, education, and policy organization dedicated to sustainable agriculture based in Salina, Kansas, United States. Their goal is to develop an agricultural system based on perennial crops that "has the ecological stability of the prairie and a grain yield comparable to that from annual crops".
 W
WLivestock's Long Shadow: Environmental Issues and Options is a United Nations report, released by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations on 29 November 2006, that "aims to assess the full impact of the livestock sector on environmental problems, along with potential technical and policy approaches to mitigation". It stated that livestock accounts for 18% of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, a figure which FAO changed to 14.5% in its 2013 study Tackling climate change through livestock.
 W
WLocal food is food that is produced within a short distance of where it is consumed, often accompanied by a social structure and supply chain different from the large-scale supermarket system.
 W
WThe Mediterranean diet is a diet inspired by the eating habits of Greece, Italy, and Spain in the 1960s. The principal aspects of this diet include proportionally high consumption of olive oil, legumes, unrefined cereals, fruits, and vegetables, moderate to high consumption of fish, moderate consumption of dairy products, moderate wine consumption, and low consumption of non-fish meat products. Olive oil has been studied as a potential health factor for reducing all-cause mortality and the risk of chronic diseases.
 W
WMote Marine Laboratory is an independent, nonprofit, marine research organization based on City Island in Sarasota, Florida, with additional campuses in eastern Sarasota County, Boca Grande, Florida, and the Florida Keys. Founded in 1955 by Dr. Eugenie Clark in Placida, Florida, it was known as the Cape Haze Marine Laboratory until 1967. The laboratory aims to advance marine science and education, supporting conservation and sustainable use of marine resources. A public aquarium and associated education program interpret its research for the public.
 W
WOrganic farming is an agricultural system which originated early in the 20th century in reaction to rapidly changing farming practices. Certified organic agriculture accounts for 70 million hectares globally, with over half of that total in Australia. Organic farming continues to be developed by various organizations today. It is defined by the use of fertilizers of organic origin such as compost manure, green manure, and bone meal and places emphasis on techniques such as crop rotation and companion planting. Biological pest control, mixed cropping and the fostering of insect predators are encouraged. Organic standards are designed to allow the use of naturally occurring substances while prohibiting or strictly limiting synthetic substances. For instance, naturally occurring pesticides such as pyrethrin and rotenone are permitted, while synthetic fertilizers and pesticides are generally prohibited. Synthetic substances that are allowed include, for example, copper sulfate, elemental sulfur and Ivermectin. Genetically modified organisms, nanomaterials, human sewage sludge, plant growth regulators, hormones, and antibiotic use in livestock husbandry are prohibited. Organic farming advocates claim advantages in sustainability, openness, self-sufficiency, autonomy/independence, health, food security, and food safety.
 W
WPermaculture is an approach to land management and philosophy that adopts arrangements observed in flourishing natural ecosystems. It includes a set of design principles derived using whole systems thinking. It uses these principles in fields such as regenerative agriculture, rewilding, and community resilience. Permaculture was originally a portmanteau of "permanent agriculture", but was later adjusted to "permanent culture", to incorporate necessary social aspects as inspired by Masanobu Fukuoka's natural farming. The term was coined by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren in 1978, who formulated the concept in opposition to Western industrialized methods and in congruence with Indigenous or traditional knowledge.
 W
WPescetarianism is the practice of using seafood as the only source of meat in a diet that is otherwise vegetarian.
 W
WThe planetary health diet is a flexitarian diet created by the EAT-Lancet commission as part of a report released in The Lancet on 16 January 2019. The aim of the report and the diet it developed is to create dietary paradigms that have the following aims:To feed a world's population of 10 billion people in 2050 To greatly reduce the worldwide number of deaths caused by poor diet To be environmentally sustainable as to prevent the collapse of the natural world
 W
WSeafood Watch is one of the best known sustainable seafood advisory lists, and has influenced similar programs around the world. It is best known for developing science-based seafood recommendations that consumers, chefs, and business professionals use to inform their seafood purchasing decisions.
 W
WSeaweed farming or kelp farming is the practice of cultivating and harvesting seaweed. In its simplest form, it consists of the management of naturally found batches. In its most advanced form, it consists of fully controlling the life cycle of the algae.
 W
WUrban agriculture, urban farming, or urban gardening is the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. Urban agriculture is also the term used for animal husbandry, aquaculture, urban beekeeping, and horticulture. These activities occur in peri-urban areas as well. Peri-urban agriculture may have different characteristics.
 W
WUrban beekeeping is the practice of keeping bee colonies in urban areas. It may also be referred to as hobby beekeeping or backyard beekeeping. Bees from city apiaries are said to be "healthier and more productive than their country cousins". Their presence also provides cities with environmental and economic benefits.
 W
WThe United States Food Sovereignty Alliance is a group of food producers and labor, environmental, faith-based, social justice and anti-hunger advocacy organizations, including the Applied Research Center, Family Farm Defenders, the Indigenous Environmental Network, and the National Family Farm Coalition. The USFA advocates food sovereignty, which is the right to sufficient and culturally appropriate food to all people and communities, and aims to reestablish better relations between food producers and consumers, placing the needs of local farmers, fishers, indigenous peoples and landless workers most impacted by global hunger, poverty, and unbalanced food distribution above agribusiness and larger corporations. The USFA is organized into four Alliance Teams: Land & Resource Grabs, Immigrant Rights & Trade, Defense of Mother Earth, and Racism & Leadership.
 W
WVeganism is the practice of abstaining from the use of animal products, particularly in diet, and an associated philosophy that rejects the commodity status of animals. An individual who follows the diet or philosophy is known as a vegan. Distinctions may be made between several categories of veganism. Dietary vegans, also known as "strict vegetarians", refrain from consuming meat, eggs, dairy products, and any other animal-derived substances. An ethical vegan, also known as a "moral vegetarian", is someone who not only follows a vegan diet but extends the philosophy into other areas of their lives, and opposes the use of animals for any purpose. Another term is "environmental veganism", which refers to the avoidance of animal products on the premise that the industrial farming of animals is environmentally damaging and unsustainable.
 W
WVertical farming is the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers. It often incorporates controlled-environment agriculture, which aims to optimize plant growth, and soilless farming techniques such as hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics. Some common choices of structures to house vertical farming systems include buildings, shipping containers, tunnels, and abandoned mine shafts. As of 2020, there is the equivalent of about 30 ha of operational vertical farmland in the world. The modern concept of vertical farming was proposed in 1999 by Dickson Despommier, professor of Public and Environmental Health at Columbia University. Despommier and his students came up with a design of a skyscraper farm that could feed 50,000 people. Although the design has not yet been built, it successfully popularized the idea of vertical farming. Current applications of vertical farmings coupled with other state-of-the-art technologies, such as specialized LED lights, have resulted in over 10 times the crop yield than would receive through traditional farming methods.