 W
WThe ankh or key of life is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol that was most commonly used in writing and in Egyptian art to represent the word for "life" and, by extension, as a symbol of life itself.
 W
WAn Apotropaic mark or witch mark is a symbol or pattern scratched into the fabric of a building to keep witches out. It should not be confused with a witches' mark, which is a mark made by a witch.
 W
WBaphomet was a deity that the Knights Templar were accused of worshipping, and that subsequently was incorporated into occult and mystical traditions. The name Baphomet appeared in trial transcripts for the Inquisition of the Knights Templar starting in 1307. It first came into popular English usage in the 19th century during debate and speculation on the reasons for the suppression of the Templars.
 W
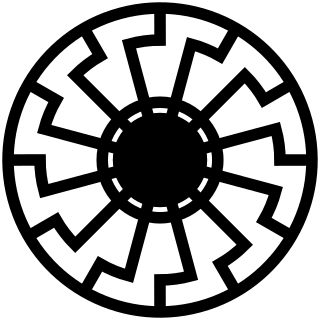
WThe Black Sun is a Nazi symbol, a type of sun wheel employed in a post–Nazi Germany context by neo-Nazis and in some strains of Satanism.
 W
WThe Symbol of Chaos originates from Michael Moorcock's Eternal Champion stories and its dichotomy of Law and Chaos. In them, the Symbol of Chaos comprises eight arrows in a radial pattern. In contrast, the symbol of Law is a single upright arrow. It is also called the Arms of Chaos, the Arrows of Chaos, the Chaos Star, the Chaos Cross, the Chaosphere, or the Symbol of Eight.
 W
WThe circled dot, circumpunct, or circle with a point at its centre is an ancient symbol. It can represent:Solar systemSolar symbol used to represent the Sun The sun / Gold The sun / Ra The sun / a day Religion and philosophyKeter (Kabbalah) Spirit (Ojibwa) MonismLanguage and linguistics
 W
WAccording to Rudolf Koch, the Dragon's Eye is an ancient Germanic symbol. The Dragon's Eye is an isosceles or equilateral triangle pointing downward, with a "Y" in the middle connecting the three points of the triangle together. According to Carl G. Liungman's Dictionary of Symbols, it combines the triangle meaning "threat" and the "Y" meaning a choice between good and evil.
 W
WThe Eye of Horus, also known as wadjet, wedjat or udjat, is an ancient Egyptian symbol of protection, royal power, and good health. The Eye of Horus is similar to the Eye of Ra, which belongs to a different god, Ra, but represents many of the same concepts.
 W
WThe Helm of Awe or Helm of Terror is an object in Norse mythology and subsequently the name of an Icelandic magical stave. The symbol used for the reference in the sagas came from the Huld manuscript written and collected in 1847. The symbol has no historical evidence prior to this. Was used as a part of a christian magic ritual that "may" have had some movements rooted in icelandic culture; but was very common ritualistic practice across christiandom.
 W
WHex signs are a form of Pennsylvania Dutch folk art, related to fraktur, found in the Fancy Dutch tradition in Pennsylvania Dutch Country. Barn paintings, usually in the form of "stars in circles", began to appear on the landscape in the early 19th century and became widespread decades later when commercial ready-mixed paint became readily available. By the 1950s commercialized hex signs, aimed at the tourist market, became popular and these often include stars, compass roses, stylized birds known as distelfinks, hearts, tulips, or a tree of life. Two schools of thought exist on the meaning of hex signs. One school ascribes a talismanic nature to the signs; the other sees them as purely decorative. Both schools recognize that there are sometimes superstitions associated with certain hex sign themes and neither ascribes strong magical power to them. The Amish do not use hex signs.
 W
WThe Indalo is a prehistoric magical symbol found in the cave of "Los Letreros" in Sierra de María-Los Vélez Natural Park in Vélez Blanco, Almería, Andalusia, Spain. It has been customary to paint the Indalo symbol on the front of houses and businesses to protect them from evil and is considered to be a god totem. The indalo has an origin in the Levante, Spain and dates back to 2500 BC. The pictograph was named in memory of Saint Indaletius, and means Indal eccius in the Iberian language.
 W
WThe Kagome crest or Kagome mon is a star-shaped crest related to the kagome lattice design. The Kagome crest can be depicted as, either, a six-pointed star and as an eight-pointed star :The six-pointed star version is composed of two interlocking equilateral triangles, similar to/interchangeable with the Hindu Shatkona, which represents the represents the union between opposites, similar to Yin and yang) and to the Jewish Star of David. The eight-pointed star version is composed of two interlocking squares, similar to/interchangeable with the Hindu Star of Lakshmi.
 W
WA magic circle is a circle of space marked out by practitioners of some branches of ritual magic, which they generally believe will contain energy and form a sacred space, or will provide them a form of magical protection, or both. It may be marked physically, drawn in a material like salt or chalk, or merely visualised.
 W
WIn recreational mathematics, a square array of numbers, usually positive integers, is called a magic square if the sums of the numbers in each row, each column, and both main diagonals are the same. The order of the magic square is the number of integers along one side (n), and the constant sum is called the magic constant. If the array includes just the positive integers , the magic square is said to be normal. Some authors take magic square to mean normal magic square.
 W
WThe Monas Hieroglyphica is an esoteric symbol invented and designed by John Dee, the Elizabethan Magus and Court Astrologer of Elizabeth I of England. It is also the title of the 1564 book in which Dee expounds the meaning of his symbol.
 W
WA nazar is an eye-shaped amulet believed to protect against the evil eye. Hindi, Urdu, Pashto, Bengali, Kurdish, Persian, Punjabi, Turkish and other languages use the term as well. In Turkey, it is known by the name nazar boncuğu, in Greece is known as mati. In Persian and Afghan folklore, it is called a cheshm nazar or nazar qurbāni. In India and Pakistan, the Hindi-Urdu slogan Chashm-e-Baddoor is used to ward off the evil eye. In the Indian subcontinent, the phrase "Nazar lag gai" is used to indicate that one has been affected by the evil eye.
 W
WThe ouroboros or uroboros is an ancient symbol depicting a serpent or dragon eating its own tail. Originating in ancient Egyptian iconography, the ouroboros entered western tradition via Greek magical tradition and was adopted as a symbol in Gnosticism and Hermeticism and most notably in alchemy. The term derives from Ancient Greek οὐροβόρος, from οὐρά oura 'tail' plus -βορός -boros '-eating'. The ouroboros is often interpreted as a symbol for eternal cyclic renewal or a cycle of life, death, and rebirth. The skin-sloughing process of snakes symbolizes the transmigration of souls, the snake biting its own tail is a fertility symbol in some religions, and the tail of the snake is a phallic symbol, the mouth is a yonic or womb-like symbol.
 W
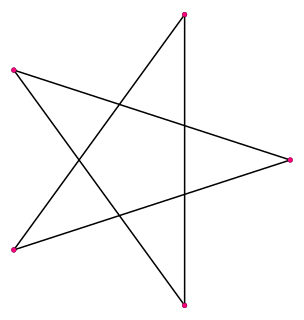
WA pentagram is the shape of a five-pointed star polygon.
 W
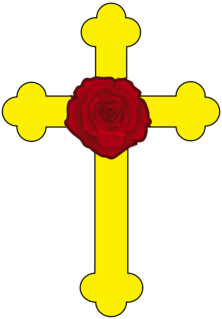
WThe Rose Cross is a symbol largely associated with the semi-mythical Christian Rosenkreuz: Qabbalist, alchemist, and founder of the Rosicrucian Order. The Rose Cross is a cross with a red, golden or white rose at its centre and symbolizes the teachings of a western esoteric tradition formed within the Christian tenets, albeit a Christianity not yet conspicuously in evidence:"What think you, loving people, and how seem you affected, seeing that you now understand and know, that we acknowledge ourselves truly and sincerely to profess Christ, condemn the Pope, addict ourselves to the true Philosophy, lead a Christian life, and daily call, entreat and invite many more unto our Fraternity, unto whom the same Light of God likewise appeareth?" --Confessio Fraternitatis, the second Rosicrucian Manifesto, printed in 1615
 W
WRunes are the letters in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets, which were used to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialised purposes thereafter. The Scandinavian variants are also known as futhark or fuþark ; the Anglo-Saxon variant is futhorc or fuþorc.
 W
WThe Sator Square is a two-dimensional word square containing a five-word Latin palindrome. It features in early Christian as well as in magical contexts. The earliest example of the square dates from the ruins of Pompeii, which some scholars attribute to pre-Christian origins, such as Jewish or Mithraic.
 W
WThe Seal of Solomon is the signet ring attributed to King Solomon in medieval Arabic tradition, from which it developed in Islamic and Jewish mysticism and in Western occultism. It is the predecessor of the Star of David, which became the symbol of the Jewish people in modern times.
 W
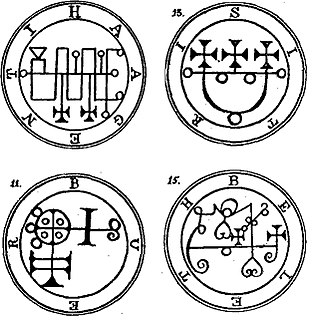
WA sigil is a type of symbol used in ritual magic. The term has usually referred to a type of pictorial signature of a Jinn or other entity. In modern usage, especially in the context of chaos magic, sigil refers to a symbolic representation of the practitioner's desired outcome.
 W
WThe Sigil of Baphomet is the official insignia of the Church of Satan. It first appeared on the cover of The Satanic Mass LP in 1968 and later on the cover of The Satanic Bible in 1969. The sigil has been called a "material pentagram" representational of carnality and earthy principles. The Church describes the symbol as the "...preeminent visual distillation of the iconoclastic philosophy of Satanism."
 W
WThe Sigillum Dei is a magical diagram, composed of two circles, a pentagram, two heptagons, and one heptagram, and is labeled with the name of God and his angels. It was an amulet (amuletum) with the magical function that, according to one of the oldest sources, allowed the initiated magician to have power over all creatures except Archangels, but usually only reserved for those who can achieve the blessed vision of God and angels.
 W
WSriramachakra is a mystic diagram or a yantra given in Tamil almanacs as an instrument of astrology for predicting one's future. The geometrical diagram consists of a square divided into smaller squares by equal numbers of lines parallel to the sides of the square. Certain integers in well defined patterns are written in the various smaller squares. In some almanacs, for example, in the Panchangam published by the Sringeri Sharada Peetham or the Pnachangam published by Srirangam Temple, the diagram takes the form of a magic square of order 4 with certain special properties. This magic square belongs to a certain class of magic squares called strongly magic squares which has been so named and studied by T V Padmakumar, an amateur mathematician from Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. In some almanacs, for example, in the Pambu Panchangam, the diagram consists of an arrangement of 36 small squares in 6 rows and 6 columns in which the digits 1, 2, ..., 9 are written in that order from left to right starting from the top-left corner, repeating the digits in the same direction once the digit 9 is reached.
 W
WA sun cross, solar cross, or wheel cross is a solar symbol consisting of an equilateral cross inside a circle.
 W
WThe swastika symbol, 卐 or 卍, is an ancient religious icon in the cultures of Eurasia. It is used as a symbol of divinity and spirituality in Indian religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.
 W
WThe swastika design is known from artefacts of various cultures since the Neolithic, and it recurs with some frequency on artefacts dated to the Germanic Iron Age, i.e. the Migration period to Viking Age period in Scandinavia, including the Vendel era in Sweden, attested from as early as the 3rd century in Elder Futhark inscriptions and as late as the 9th century on Viking Age image stones.
 W
WTaper burn marks are deep flame shaped scorch marks often found on the timber beams of early modern houses. They were originally thought to have been accidental, but research suggests that most marks may have been made deliberately, as there is clear patterning of the activity. They are theorised to have been made as part of a folk superstition, then thought to protect the building from fire and lightning.
 W
WThe tarot is a pack of playing cards, used from the mid-15th century in various parts of Europe to play games such as Italian tarocchini, French tarot and Austrian Königrufen, many of which are still played today. In the late 18th century, some tarot decks began to be used for divination via tarot card reading and cartomancy leading to custom decks developed for such occult purposes.
 W
WThe tree of life is a diagram used in various mystical traditions. It usually consists of 10 nodes symbolizing different archetypes and 22 lines connecting the nodes. The nodes are often arranged into three columns to represent that they belong to a common category.
 W
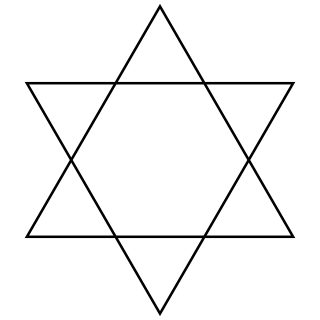
WThe unicursal hexagram is a hexagram or six-pointed star that can be traced or drawn unicursally, in one continuous line rather than by two overlaid triangles. The hexagram can also be depicted inside a circle with the points touching it. It is often depicted in an interlaced form with the lines of the hexagram passing over and under one another to form a knot. It is a specific instance of the far more general shape discussed in Blaise Pascal's 1639 Hexagrammum Mysticum Theorem.
 W
WThe valknut is a symbol consisting of three interlocked triangles. It appears on a variety of objects from the archaeological record of the ancient Germanic peoples. The term valknut is derived from the modern era, and the term or terms used to refer to the symbol during its historical employment is unknown.
 W
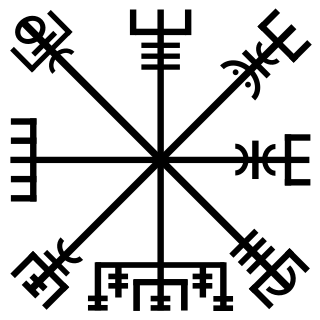
WA vegvísir is an Icelandic magical stave intended to help the bearer find their way through rough weather. The symbol is attested in the Huld Manuscript, collected in Iceland by Geir Vigfusson in 1880.
 W
WA veve is a religious symbol commonly used in different branches of Vodun throughout the African diaspora, such as Haitian Vodou. Veves should not be confused with the patipembas used in Palo, nor the pontos riscados used in Umbanda and Quimbanda since these are separate African religions. The veve acts as a "beacon" for the Loa, and will serve as a loa's representation during rituals.