 W
WA calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single, specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills.
 W
WAn Advent calendar is a special calendar used to count the days of Advent in anticipation of Christmas. Since the date of the First Sunday of Advent varies, falling between November 27 and December 3 inclusive, many Advent calendars, especially those that are reusable, often begin on December 1, although those that are produced for a specific year often include the last few days of November that are part of the liturgical season. The Advent calendar was first used by German Lutherans in the 19th and 20th centuries.
 W
WAnalemmatic sundials are a type of horizontal sundial that has a vertical gnomon and hour markers positioned in an elliptical pattern. The gnomon is not fixed and must change position daily to accurately indicate time of day. Hence there are no hour lines on the dial and the time of day is read only on the ellipse. As with most sundials, analemmatic sundials mark solar time rather than clock time. An analemmatic sundial is completely defined byThe size of its ellipse. The latitude of its location. The declination of the sun.
 W
WAnywhere on Earth (AoE) is a calendar designation which indicates that a period expires when the date passes everywhere on Earth. The last place on Earth where any date exists is on Howland and Baker Islands, in the IDLW time zone, and so is the last spot on the globe for any day to exist. Therefore, the day ends AoE when it ends on Howland Island.
 W
WThe Association of Mouth and Foot Painting Artists of the World (AMFPA) is a for-profit international organization facilitating the sale of artwork produced by mouth and foot painting artists associated with the organization. None of the artists have proper use of their hands as a pre-condition to joining the association. It represents around 820 artists located in 76 countries, of whom 143 are full members, and receive a monthly fee from the organization from the date of their admission until their death. The other artists are students, who receive a monthly scholarship until such time as they are promoted.
 W
WA blue moon is an additional full moon that appears in a subdivision of a year: either the third of four full moons in a season, or a second full moon in a month of the common calendar.
 W
WThe Calendar Act 1750 (24 Geo. II c.23), "An act for regulating the commencement of the year; and for correcting the calendar now in use", also known as Chesterfield's Act or the British Calendar Act of 1751, is an act of the Parliament of Great Britain. Its purpose was for Great Britain and the British Empire to adopt the Gregorian calendar. The Act also rectified other dating anomalies, such as changing the start of the legal year from 25 March to 1 January.
 W
WA calendar is used to display dates and related information, usually in a table format. Calendars are used to plan future events and keep track of appointments, and so a typical calendar will include days of the week, week numbering, months, public holidays and clock changes. Printed calendars also often contain additional information relevant for specific groups – for instance, a Christian liturgical calendar will show holy days and liturgical colours, while a calendar for amateur astronomers will highlight phases of the moon, conjunctions and eclipses. Alongside their practical uses, calendars have taken on a decorative purpose, offering an easy way to introduce regularly changing artwork to a space, and have even influenced art and sexuality by popularizing the pin-up style.
 W
WThe civil calendar is the calendar, or possibly one of several calendars, used within a country for civil, official, or administrative purposes. The civil calendar is almost always used for general purposes by people and private organizations.
 W
WA computus clock is a clock equipped with a mechanism that automatically calculates and displays, or helps determine, the date of Easter. A computus watch carries out the same function.
 W
WThe tables below list equivalent dates in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Years are given in astronomical year numbering.
 W
WThe December solstice, also known as the southern solstice, is the solstice that occurs each December – typically on 21 December, but may vary by one day in either direction according to the Gregorian calendar. In the Northern Hemisphere, the December solstice is the winter solstice, whilst in the Southern Hemisphere it is the summer solstice.
 W
WA golden number is a number assigned to each year in sequence which is used to indicate the dates of all the calendric new moons for each year in a 19-year Metonic cycle. They are used in computus and also in Runic calendars. The golden number of any Julian or Gregorian calendar year can be calculated by dividing the year by 19, taking the remainder, and adding 1.
 W
WTheodorus van Hoytema, or Hoijtema was a Dutch lithographer, illustrator and graphic designer, known for his book covers and calendars; especially those depicting birds.
 W
W1972 was proclaimed International Book Year by the United Nations and made effective by UNESCO.
 W
WThe June solstice is the solstice on the Earth that occurs each year falling on 20–22 June according to the Gregorian calendar. In the Northern Hemisphere, the June solstice is the summer solstice, whilst in the Southern Hemisphere it is the winter solstice. It is also known as the northern solstice.
 W
WThe knuckle mnemonic is a mnemonic device for remembering the number of days in the months of the Julian and Gregorian calendars.
 W
WA national or international awareness day or observance is a date usually set by a major organisation or government to commemorate a public health or ethical cause of importance on a national or international level.
 W
WThe Marcus Bains line is a line that shows the current time in many calendar applications and PIM suites. Usually, it is a red horizontal line showing at the location of the current time in the "day" or "week" views of a calendar, sometimes complemented with the current time.
 W
WThe Metonic cycle or enneadecaeteris is a period of approximately 19 years after which the phases of the moon recur at the same time of the year. The recurrence is not perfect, and by precise observation the Metonic cycle defined as 235 synodic lunar months is just 1 hour, 27 minutes and 33 seconds longer than 19 tropical years. Meton of Athens, in the 5th century BC, judged the cycle to be a whole number of days, 6,940. Using these whole numbers facilitates the construction of a luni-solar calendar.
 W
WNepal Sambat is the lunar calendar used by the Nepalese-speaking people native to the Indian subcontinent of Nepalese nationality and ethnic Nepalis. The Calendar era began on 20 October 879 AD, with 1141 in Nepal Sambat corresponding to the year 2020–2021 AD. Nepal Sambat appeared on coins, stone and copper plate inscriptions, royal decrees, chronicles, Hindu and Buddhist manuscripts, legal documents and correspondence. Though Nepal Sambat is declared a national calendar and is used widely in Nepal, it is mostly used by the Newar community whereas Bikram Sambat (B.S) remains the dominant calendar throughout the country. All the major festivals are based on Bikram Sambat along with official purposes.
 W
WThe new calendarists are people who have adopted a new calendar, thus replacing the previous one, and also people who are advocating such a change within some group. Historically, most changes of calendar have been marked by debates between those who wanted to adopt some new calendar and those who opposed such change.
 W
WNew Year is the time or day at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count increments by one. Many cultures celebrate the event in some manner. In the Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system today, New Year occurs on January 1. This was also the first day of the year in the original Julian calendar and the Roman calendar.
 W
WThe Democratic People's Republic of Korea calendar, DPRK calendar, or Juche calendar, named after the Juche ideology, is the system of year-numbering used in North Korea.
 W
WNychthemeron, occasionally nycthemeron or nuchthemeron, is a period of 24 consecutive hours. It is sometimes used, especially in technical literature, to avoid the ambiguity inherent in the term day.
 W
WAn Old Calendarist is any Eastern Orthodox Christian who uses the Julian calendar -- also called the "Old Style Calendar", "Church Calendar" or "Old Calendar" -- and whose church body is not in communion with the Eastern Orthodox churches that use the Revised Julian calendar, the New Calendar, which aligns with the Gregorian calendar.
 W
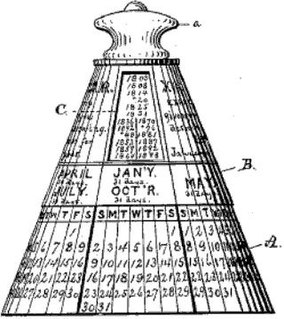
WA perpetual calendar is a calendar valid for many years, usually designed to look up the day of the week for a given date in the future.
Pin-ups For Vets is a non-profit charitable organization dedicated to helping injured and ill American Soldiers, Marines, Airmen, National Guard members, Coast Guard members and Sailors—and current active-duty personnel. The project is the work of Gina Elise who sells and distributes the Pin-ups For Vets Calendar, which hearkens back to 1940s and 1950-style vintage pretty-girl images. The calendars are considered very tasteful by today's standards; they contain no frontal nudity, or nudity of any kind. Elise appears in various types of period costume and lingerie. Several other women are involved in the project as models besides Elise. Some of these women have served in the U.S. Armed Forces themselves. To date, the organization has donated over $50,000 to veterans hospitals.
 W
WA pollen calendar is used to show the peak pollen times for different types of plant pollen, which causes allergic reactions in certain people.
 W
WThe Remaining Signs of Past Centuries by Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī, is a comparative study of calendars of different cultures and civilizations, interlaced with mathematical, astronomical, and historical information, exploring the customs and religions of different peoples.
 W
WThe Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman kingdom and republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the dictator Julius Caesar and emperor Augustus in the late 1st century BC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones, and ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year.
 W
WA season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of Earth's orbit around the Sun and Earth's axial tilt relative to the ecliptic plane. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical cultures whose number of seasons vary.
 W
WIn Thailand, two main calendar systems are used alongside each other: the Thai solar calendar, based on the Gregorian calendar and is used for official and most day-to-day purposes, and the Thai lunar calendar, used for traditional events and Buddhist religious practices.
 W
WA two-cube calendar is a desk calendar consisting of two cubes with faces marked by digits 0 through 9. Each face of each cube is marked with a single digit, and it is possible to arrange the cubes so that any chosen day of the month is visible on the two front faces.
 W
WWinter counts are pictorial calendars or histories in which tribal records and events were recorded by Native Americans in North America. The Blackfeet, Mandan, Kiowa, Lakota, and other Plains tribes used winter counts extensively. There are approximately one hundred winter counts in existence, but many of these are duplicates.
 W
WWorld Oceans Day is an international day that takes place annually on 8 June. The concept was originally proposed in 1992 by Canada's International Centre for Ocean Development (ICOD) and the Ocean Institute of Canada (OIC) at the Earth Summit – UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. "World Oceans Day" was officially recognised by the United Nations in 2008. The international day supports the implementation of worldwide Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and fosters public interest in the protection of the ocean and the sustainable management of its resources.
 W
WThe Year 2000 problem, also known as the Y2K problem, the Millennium bug, Y2K bug, the Y2K glitch, or Y2K, refers to events related to the formatting and storage of calendar data for dates beginning in the year 2000. Problems were anticipated, and arose, because many programs represented four-digit years with only the final two digits – making the year 2000 indistinguishable from 1900, and two-digit years from '01 through '31 also being mistaken for days, and '01–'12 mistaken for months in varying date formats. The assumption of a twentieth-century date in such programs could cause various errors, such as the incorrect display of dates and the inaccurate ordering of automated dated records or real-time events.