 W
WFood safety is used as a scientific discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent food-borne illness. The occurrence of two or more cases of a similar illnesses resulting from the ingestion of a common food is known as a food-borne disease outbreak. This includes a number of routines that should be followed to avoid potential health hazards. In this way food safety often overlaps with food defense to prevent harm to consumers. The tracks within this line of thought are safety between industry and the market and then between the market and the consumer. In considering industry to market practices, food safety considerations include the origins of food including the practices relating to food labeling, food hygiene, food additives and pesticide residues, as well as policies on biotechnology and food and guidelines for the management of governmental import and export inspection and certification systems for foods. In considering market to consumer practices, the usual thought is that food ought to be safe in the market and the concern is safe delivery and preparation of the food for the consumer.
 W
WIn 1900, more than 6,000 people in England were poisoned by arsenic-tainted beer, with more than 70 of the afflicted dying as a result. The food safety crisis was caused by arsenic entering the supply chain through impure sugar which had been made with contaminated sulphuric acid. The illness was prevalent across the Midlands and North West England, with Manchester being the most heavily affected.
 W
WAn adulterant is a substance found within other substances such as food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, fuel or other chemicals that compromises the safety or effectiveness of said substance.
 W
WThe Codex Alimentarius is a collection of internationally recognized standards, codes of practice, guidelines, and other recommendations relating to food, food production, food labeling, and food safety.
 W
WThe Codex Alimentarius Austriacus is a collection of standards, guidelines and product descriptions for a variety of foods. It was originally established by the Austrian-Hungarian Empire in 1891 and is still in use today. The Codex Alimentarius Austriacus standards are primarily the product of a voluntary effort of experts in the food industry and universities. While the standards laid out in the codex were not legally enforceable, they were nonetheless used by the courts to determine the identity and quality of a variety of food products.
 W
WA cold chain is a temperature-controlled supply chain. An unbroken cold chain is an uninterrupted series of refrigerated production, storage and distribution activities, along with associated equipment and logistics, which maintain quality via a desired low-temperature range. It is used to preserve and to extend and ensure the shelf life of products, such as fresh agricultural produce, seafood, frozen food, photographic film, chemicals, and pharmaceutical products. Such products, during transport and when in transient storage, are sometimes called cool cargo. Unlike other goods or merchandise, cold chain goods are perishable and always en route towards end use or destination, even when held temporarily in cold stores and hence commonly referred to as "cargo" during its entire logistics cycle.
 W
WA colony picker is an instrument used to automatically identify microbial colonies growing on a solid media, pick them and duplicate them either onto solid or liquid media. It is used in research laboratories as well as in industrial environments such as food testing and in microbiological cultures.
 W
WCritical Control Point (CCP) is the point where the failure of Standard Operation Procedure (SOP) could cause harm to customers and to the business, or even loss of the business itself. It is a point, step or procedure at which controls can be applied and a food safety hazard can be prevented, eliminated or reduced to acceptable (critical) levels. The most common CCP is cooking, where food safety managers designate critical limits. CCP identification is also an important step in risk and reliability analysis for water treatment processes.
 W
WThe danger zone is the temperature range in which food-borne bacteria can grow. Food safety agencies, such as the United States' Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSiIS), define the danger zone as roughly 40 to 140 °F. The FSIS stipulates that potentially hazardous food should not be stored at temperatures in this range in order to prevent foodborne illness, and that food that remains in this zone for more than two hours should not be consumed. Foodborne microorganisms grow much faster in the middle of the zone, at temperatures between 21 and 47 °C.
 W
WIn excitotoxicity, nerve cells suffer damage or death when the levels of otherwise necessary and safe neurotransmitters such as glutamate, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA), or N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) become pathologically high resulting in excessive stimulation of receptors. For example, when glutamate receptors such as the NMDA receptor or AMPA receptor encounter excessive levels of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate significant neuronal damage might ensue. Excess glutamate allows high levels of calcium ions (Ca2+) to enter the cell. Ca2+ influx into cells activates a number of enzymes, including phospholipases, endonucleases, and proteases such as calpain. These enzymes go on to damage cell structures such as components of the cytoskeleton, membrane, and DNA. In evolved, complex adaptive systems such as biologic life it must be understood that mechanisms are rarely, if ever, simplistically direct. For example, NMDA in subtoxic amounts induces neuronal survival to otherwise toxic levels of glutamate.
 W
WFAT TOM is a mnemonic device used in the food service industry to describe the six favorable conditions required for the growth of foodborne pathogens. It is an acronym for food, acidity, time, temperature, oxygen and moisture.
 W
WThe five-second rule, sometimes also the ten-second rule, is a food hygiene myth that states a defined window where it is safe to pick up food after it has been dropped and thus exposed to contamination.
 W
WFood contact materials are materials that are intended to be in contact with food. These can be things that are quite obvious like a glass or a can for soft drinks as well as machinery in a food factory or a coffee machine.
 W
WFood contamination refers to the presence of harmful chemicals and microorganisms in food, which can cause consumer illness. This article addresses the chemical contamination of foods, as opposed to microbiological contamination, which can be found under foodborne illness.
 W
WFood microbiology is the study of the microorganisms that inhibit, create, or contaminate food. This includes the study of microorganisms causing food spoilage; pathogens that may cause disease ; microbes used to produce fermented foods such as cheese, yogurt, bread, beer, and wine; and microbes with other useful roles, such as producing probiotics.
 W
WFood sampling is a process used to check that a food is safe and that it does not contain harmful contaminants, or that it contains only permitted additives at acceptable levels, or that it contains the right levels of key ingredients and its label declarations are correct, or to know the levels of nutrients present.
 W
WFood spoilage is the process where a food product becomes unsuitable to ingest by the consumer. The cause of such a process is due to many outside factors as a side-effect of the type of product it is, as well as how the product is packaged and stored. Due to food spoilage, one-third of the world's food produced for the consumption of humans is lost every year. Bacteria and various fungi are the cause of spoilage and can create serious consequences for the consumers, but there are preventive measures that can be taken.
 W
WFoodborne illness is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food, pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food, as well as prions, and toxins such as aflatoxins in peanuts, poisonous mushrooms, and various species of beans that have not been boiled for at least 10 minutes.
 W
WGenerally recognized as safe (GRAS) is a United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) designation that a chemical or substance added to food is considered safe by experts. An ingredient with a GRAS designation is exempted from the usual Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) food additive tolerance requirements. The concept of food additives being "generally recognized as safe" was first described in the Food Additives Amendment of 1958, and all additives introduced after this time had to be evaluated by new standards. The FDA list of GRAS notices is updated approximately each month, as of 2021.
 W
WGood manufacturing practices (GMP) are the practices required in order to conform to the guidelines recommended by agencies that control the authorization and licensing of the manufacture and sale of food and beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceutical products, dietary supplements, and medical devices. These guidelines provide minimum requirements that a manufacturer must meet to assure that their products are consistently high in quality, from batch to batch, for their intended use. The rules that govern each industry may differ significantly; however, the main purpose of GMP is always to prevent harm from occurring to the end user. Additional tenets include ensuring the end product is free from contamination, that it is consistent in its manufacture, that its manufacture has been well documented, that personnel are well trained, and that the product has been checked for quality more than just at the end phase. GMP is typically ensured through the effective use of a quality management system (QMS).
 W
WHazard analysis and critical control points, or HACCP, is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, physical hazards and more recently radiological hazards in production processes that can cause the finished product to be unsafe and designs measures to reduce these risks to a safe level. In this manner, HACCP attempts to avoid hazards rather than attempting to inspect finished products for the effects of those hazards. The HACCP system can be used at all stages of a food chain, from food production and preparation processes including packaging, distribution, etc. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) require mandatory HACCP programs for juice and meat as an effective approach to food safety and protecting public health. Meat HACCP systems are regulated by the USDA, while seafood and juice are regulated by the FDA. All other food companies in the United States that are required to register with the FDA under the Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002, as well as firms outside the US that export food to the US, are transitioning to mandatory hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls (HARPC) plans.
 W
WHazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls or HARPC is a successor to the Hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) food safety system, mandated in the United States by the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) of 2010.
 W
WHeterocyclic amines are a group of chemical compounds, many of which can be formed during cooking. They are found in meats that are cooked to the "well done" stage, in pan drippings and in meat surfaces that show a brown or black crust. Epidemiological studies show associations between intakes of heterocyclic amines and cancers of the colon, rectum, breast, prostate, pancreas, lung, stomach/esophagus and animal feeding experiments support a causal relationship. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service labeled several heterocyclic amines as likely carcinogens in its 13th Report on Carcinogens. Changes in cooking techniques reduce the level of heterocyclic amines.
 W
WRoxarsone is an organoarsenic compound that has been used in poultry production as a feed additive to increase weight gain and improve feed efficiency, and as a coccidiostat. As of June 2011, it was approved for chicken feed in the United States, Canada, Australia, and 12 other countries. The drug was also approved in the United States and elsewhere for use in pigs.
 W
WFoodborne illness is any illness resulting from the food spoilage of contaminated food, pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food. Infant food safety is the identification of risky food handling practices and the prevention of illness in infants. Fooddborne illness is a serious health issue, especially for babies and children. Infants and young children are particularly vulnerable to foodborne illness because their immune systems are not developed enough to fight off foodborne bacterial infections. In fact, 800,000 illnesses affect children under the age of 10 in the U.S. each year. Therefore, extra care should be taken when handling and preparing their food.
 W
WThe National Organic Program (NOP) is the federal regulatory framework in the United States of America governing organic food. It is also the name of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) program responsible for administering and enforcing the regulatory framework. The core mission of the NOP is to protect the integrity of the USDA organic seal. The seal is used for products adhering to USDA standards that contain at least 95% organic ingredients.
 W
WOlive oil regulation and adulteration are complex issues overseen and studied by various governmental bodies, non-governmental organizations, and private researchers across the world.
 W
WOsteoblast milk protein is the name used by Mengniu, a Chinese dairy company, for a milk protein used as a food additive in their Milk Deluxe since 2005. It is supposed to help the absorption of calcium and promote bone growth in the osteoblasts and prevent osteoporosis.
 W
WThe Circle of Poison (COP) refers to the export of domestically banned pesticides for use on foods elsewhere, some of which returns by way of import. The "circle" is complete when the toxic chemicals that were exported are then used to grow fruit, meat, and produce that are imported and available for domestic consumption. This circle was first identified relative to the United States but the relationship also exists between other nations of the Global North and South.
 W
WA pot-in-pot refrigerator, clay pot cooler or zeer is an evaporative cooling refrigeration device which does not use electricity. It uses a porous outer clay pot containing an inner pot within which the food is placed. The evaporation of the outer liquid draws heat from the inner pot. The device can cool any substance, and requires only a flow of relatively dry air and a source of water.
 W
WQuaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure NR+4, R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule.
 W
WRactopamine is an animal feed additive used to promote leanness and increase food conversion efficiency in livestock in some countries, but banned in others. Pharmacologically, it is a phenol-based TAAR1 agonist and β adrenoreceptor agonist that stimulates β1 and β2 adrenergic receptors. It is most commonly administered to animals for meat production as ractopamine hydrochloride. It is the active ingredient in products marketed in the US as Paylean for swine, Optaflexx for cattle, and Topmax for turkeys. It was developed by Elanco Animal Health, a division of Eli Lilly and Company.
 W
WShelf life is the length of time that a commodity may be stored without becoming unfit for use, consumption, or sale. In other words, it might refer to whether a commodity should no longer be on a pantry shelf, or just no longer on a supermarket shelf. It applies to cosmetics, foods and beverages, medical devices, medicines, explosives, pharmaceutical drugs, chemicals, tyres, batteries, and many other perishable items. In some regions, an advisory best before, mandatory use by or freshness date is required on packaged perishable foods. The concept of expiration date is related but legally distinct in some jurisdictions.
 W
WA spiral plater is an instrument used to dispense a liquid sample onto a Petri dish in a spiral pattern. Commonly used as part of a CFU count procedure for the purpose of determining the number of microbes in the sample. In this setting, after spiral plating, the Petri dish is incubated for several hours after which the number of colony forming microbes (CFU) is determined. Spiral platers are also used for research, clinical diagnostics and as a method for covering a Petri dish with bacteria before placing antibiotic discs for AST.
 W
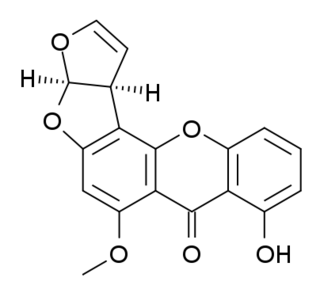
WSterigmatocystin is a polyketide mycotoxin produced by certain species of Aspergillus. The toxin is naturally found in some cheeses.
 W
WT-2 Mycotoxin is a trichothecene mycotoxin. It is a naturally occurring mold byproduct of Fusarium spp. fungus which is toxic to humans and animals. The clinical condition it causes is alimentary toxic aleukia and a host of symptoms related to organs as diverse as the skin, airway, and stomach. Ingestion may come from consumption of moldy whole grains. T-2 can be absorbed through human skin. Although no significant systemic effects are expected after dermal contact in normal agricultural or residential environments, local skin effects can not be excluded. Hence, skin contact with T-2 should be limited.
 W
WWater activity (aw) is the partial vapor pressure of water in a solution divided by the standard state partial vapor pressure of water. In the field of food science, the standard state is most often defined as the partial vapor pressure of pure water at the same temperature. Using this particular definition, pure distilled water has a water activity of exactly one. As temperature increases, aw typically increases, except in some products with crystalline salt or sugar.
 W
WYellow stickers are a method of alerting shoppers to food which has been reduced in price because it is approaching its sell by date.