 W
WThe 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 (MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 (MDCCC). The term is often used to refer to the 1700s, the century between January 1, 1700 and December 31, 1799. During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded on a global scale. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported the slave trade.
 W
W1659 (MDCLIX) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 1659th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 659th year of the 2nd millennium, the 59th year of the 17th century, and the 10th and last year of the 1650s decade. As of the start of 1659, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.
 W
WThe 1910s was a decade of the Gregorian calendar that began on January 1, 1910, and ended on December 31, 1919.
 W
WThe Asian Century is the projected 21st-century dominance of Asian politics and culture, assuming certain demographic and economic trends persist. The concept of Asian Century parallels the characterisation of the 19th century as Britain's Imperial Century, and the 20th century as the American Century.
 W
WThe blessing of same-sex marriages and same-sex unions is an issue about which Christian churches are in ongoing disagreement. Traditionally Christianity teaches that homosexual acts are gravely sinful and that marriage can only exist two persons of the opposite sex. These disagreements are primarily centered on the interpretation of various scripture passages related to homosexuality, sacred Tradition, and in some churches on varying understandings of homosexuality in terms of psychology, genetics and other scientific data. While various Church bodies have widely varying practices and teachings, individual Christians of every major tradition are involved in practical (orthopraxy) discussions about how to respond to the issue.
 W
WA bra, short for brassiere or brassière, is a form-fitting undergarment designed to support or cover a woman's breasts. Bras are designed for a variety of purposes, including general breast support, enhancing breast size, creating cleavage, or for other aesthetic or practical considerations. Swimsuits, camisoles, and backless dresses may have built-in breast support with supportive bra cups. Nursing bras are designed to facilitate breastfeeding. Some people have a medical and surgical need for brassieres, but most wear them for fashion or cultural reasons. There is no evidence that bras prevent breasts from sagging and one study even suggests the opposite, with the exception of wearing them during sports exercises.
 W
WBread has a significance beyond mere nutrition in many cultures in the Western world and Greater Middle East because of its history and contemporary importance. Bread is also significant in Christianity as one of the elements of the Eucharist; see sacramental bread. The word companion comes from Latin com- "with" + panis "bread".
 W
WA bugle call is a short tune, originating as a military signal announcing scheduled and certain non-scheduled events on a military installation, battlefield, or ship. Historically, bugles, drums, and other loud musical instruments were used for clear communication in the noise and confusion of a battlefield. Naval bugle calls were also used to command the crew of many warships.
 W
WA chaff cutter is a mechanical device for cutting straw or hay into small pieces before being mixed together with other forage and fed to horses and cattle. This aids the animal's digestion and prevents animals from rejecting any part of their food.
 W
WChristian revivalism is increased spiritual interest or renewal in the life of a church congregation or society, with a local, national or global effect. This should be distinguished from the use of the term "revival" to refer to an evangelistic meeting or series of meetings. Proponents view revivals as the restoration of the church itself to a vital and fervent relationship with God after a period of moral decline.
 W
WA company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared goals. Companies take various forms, such as:voluntary associations, which may include nonprofit organizations business entities, whose aim is generating profit financial entities and banks programs or educational institutions.
 W
WA court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. In both common law and civil law legal systems, courts are the central means for dispute resolution, and it is generally understood that all people have an ability to bring their claims before a court. Similarly, the rights of those accused of a crime include the right to present a defense before a court.
 W
WDance music is music composed specifically to facilitate or accompany dancing. It can be either a whole musical piece or part of a larger musical arrangement. In terms of performance, the major categories are live dance music and recorded dance music. While there exist attestations of the combination of dance and music in ancient times, the earliest Western dance music that we can still reproduce with a degree of certainty are the surviving medieval dances. In the Baroque period, the major dance styles were noble court dances. In the classical music era, the minuet was frequently used as a third movement, although in this context it would not accompany any dancing. The waltz also arose later in the classical era. Both remained part of the romantic music period, which also saw the rise of various other nationalistic dance forms like the barcarolle, mazurka, ecossaise, ballade and polonaise.
 W
WA declaration of war is a formal act by which one state goes to war against another. The declaration is a performative speech act by an authorized party of a national government, in order to create a state of war between two or more states.
 W
WA dominatrix is a woman who takes the dominant role in BDSM activities. A dominatrix might be of any sexual orientation, but her orientation does not necessarily limit the genders of her submissive partners. The role of a dominatrix may not even involve physical pain toward the submissive; her domination can be verbal, involving humiliating tasks, or servitude. A dominatrix is typically a paid professional (pro-domme) as the term dominatrix is little-used within the non-professional BDSM scene.
 W
WAn epitaph is a short text honoring a deceased person. Strictly speaking, it refers to text that is inscribed on a tombstone or plaque, but it may also be used in a figurative sense. Some epitaphs are specified by the person themselves before their death, while others are chosen by those responsible for the burial. An epitaph may be written in prose or in poem verse; poets have been known to compose their own epitaphs prior to their death, as did William Shakespeare.
 W
WThe feminist movement refers to a series of political campaigns for reforms on issues such as reproductive rights, domestic violence, maternity leave, equal pay, women's suffrage, sexual harassment, and sexual violence. The movement's priorities vary among nations and communities, and range from opposition to female genital mutilation in one country, to opposition to the glass ceiling in another.
 W
WField artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, short range, long range, and extremely long range target engagement.
 W
WFirst contact is a common science fiction theme about the first meeting between humans and extraterrestrial life, or of any sentient species' first encounter with another one, given they are from different planets or natural satellites. The theme allows writers to explore such topics such as xenophobia, transcendentalism, and basic linguistics by adapting the anthropological topic of first contact to extraterrestrial cultures.
 W
WFlirting or coquetry is a social and sexual behavior involving spoken or written communication, as well as body language, by one person to another, either to suggest interest in a deeper relationship with the other person, or if done playfully, for amusement.
 W
WA government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
 W
WThe term inner city has been used, especially in the United States, as a euphemism for lower-income residential districts that often refer to African-American neighborhoods, in a downtown or city centre area. Sociologists sometimes turn the euphemism into a formal designation by applying the term "inner city" to such residential areas, rather than to more geographically-central commercial districts.
 W
WA levee breach or levee failure is a situation where a levee fails or is intentionally breached, causing the previously contained water to flood the land behind the levee.
 W
WLGBT culture is a culture shared by lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer individuals. It is sometimes referred to as queer culture, while the term gay culture may be used to mean "LGBT culture" or to refer specifically to homosexual culture.
 W
WNudity in film is the presentation in a film of at least one person who is nude, partially nude or wearing less clothing than contemporary norms. Since the development of the medium, inclusion in films of any form of sexuality has been controversial, and in the case of most nude scenes has had to be justified as being part of the story, in the concept of "artistically justifiable nudity". Many actors and actresses have appeared nude, or exposing parts of their bodies or dressed in ways considered provocative by contemporary standards at some point in their careers.
 W
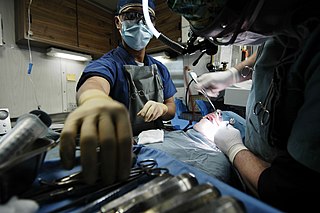
WOral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery.
 W
WPatriotism or national pride is the feeling of love, devotion, and sense of attachment to a homeland and alliance with other citizens who share the same sentiment. This attachment can be a combination of many different feelings relating to one's own homeland, including ethnic, cultural, political or historical aspects. It encompasses a set of concepts closely related to nationalism.
 W
WIn spiritual terminology, piety is a virtue which may include religious devotion, spirituality, or a mixture of both. A common element in most conceptions of piety is humility.
 W
WPolitical satire is satire that specializes in gaining entertainment from politics; it has also been used with subversive intent where political speech and dissent are forbidden by a regime, as a method of advancing political arguments where such arguments are expressly forbidden.
 W
WRemand, also known as pre-trial detention, preventive detention, or provisional detention, is the process of detaining a person until their trial after they have been arrested and charged with an offense. A person who is on remand is held in a prison or detention centre or held under house arrest. Varying terminology is used, but "remand" is generally used in common law jurisdictions and "preventive detention" elsewhere, However, in the United States, "remand" is rare except in official documents and "kept in custody until trial" is used in the media and even by judges and lawyers in addressing the public. Detention before charge is referred to as custody and continued detention after conviction is referred to as imprisonment.
 W
WThe term safe space refers to places created for individuals who feel marginalized to come together to communicate regarding their experiences with marginalization, most commonly located on university campuses in the western world, but also at workplaces, as in the case of Nokia.
 W
WSelf-insertion is a literary device in which a fictional character, who represents the real author of a work of fiction, appears as an idealized character within that fiction, either overtly or in disguise.
 W
WSexism in video gaming is prejudiced behavior or discrimination based on sex or gender as experienced by people who play and create video games, primarily women. This may manifest as sexual harassment or in the way genders are represented in games, such as when characters are presented according to gender-related tropes and stereotypes.
 W
WSmall businesses are privately owned corporations, partnerships, or sole proprietorships that have fewer employees and/or less annual revenue than a regular-sized business or corporation. Businesses are defined as "small" in terms of being able to apply for government support and qualify for preferential tax policy varies depending on the country and industry. Small businesses range from fifteen employees under the Australian Fair Work Act 2009, fifty employees according to the definition used by the European Union, and fewer than five hundred employees to qualify for many U.S. Small Business Administration programs. While small businesses can also be classified according to other methods, such as annual revenues, shipments, sales, assets, or by annual gross or net revenue or net profits, the number of employees is one of the most widely used measures.
 W
WThe sociology of race and ethnic relations is the study of social, political, and economic relations between races and ethnicities at all levels of society. This area encompasses the study of systemic racism, like residential segregation and other complex social processes between different racial and ethnic groups.
 W
WAlthough tropical Africa is mostly familiar to the West for its rainforests, this biogeographic realm of Africa is far more diverse. While the tropics are thought of as regions with warm to hot moist climates caused by latitude and the tropical rain belt, the geology of areas, particularly mountain chains, and geographical relation to continental and regional scale winds impact the overall parts of areas, also, making the tropics run from arid to humid in West Africa. The area is experiencing negative effects of rapid human population growth.
 W
WUnrequited love or one-sided love is love that is not openly reciprocated or understood as such by the beloved. The beloved may not be aware of the admirer's deep and strong romantic affection, or may consciously reject it. The Merriam Webster Online Dictionary defines unrequited as "not reciprocated or returned in kind".
 W
WPlanning theory is the body of scientific concepts, definitions, behavioral relationships, and assumptions that define the body of knowledge of urban planning. There are nine procedural theories of planning that remain the principal theories of planning procedure today: the Rational-Comprehensive approach, the Incremental approach, the Transformative Incremental (TI) approach, the Transactive approach, the Communicative approach, the Advocacy approach, the Equity approach, the Radical approach, and the Humanist or Phenomenological approach.
 W
WA walking bus is a form of student transport for schoolchildren who, chaperoned typically by two adults, walk to school along a set route, with some similarities to a school bus route. Like a real bus, walking buses have a fixed route with designated "bus stops" and "pick up times" at which they pick up and "drop off" children.
 W
WSince the industrial revolution, participation of women in the workforce outside of the home has increased in industrialized nations, with particularly large growth seen in the 20th century. Largely seen as a boon for industrial society, women in the workforce contribute to a higher national economic output as measure in GDP as well as decreasing labor costs by increasing the labor supply in a society.