 W
WMapuche or Mapudungun is an Araucanian language related to Huilliche spoken in south-central Chile and west central Argentina by the Mapuche people. It is also spelled Mapuzugun and Mapudungu. It was formerly known as Araucanian, the name given to the Mapuche by the Spaniards; the Mapuche avoid it as a remnant of Spanish colonialism.
 W
WAntilhue is a village in Chile, South America. It is located in the commune of Los Lagos on the shores of Calle-Calle River just east of Valdivia. Two petroleum-fueled power plants, Antilhue I and Antilhue II, with a combined production capacity of 101.3 MW, are located near the village.
 W
WThe Biosphere Reserve of Ñacuñan is located in the Mendoza Province, Argentina. It is a composed of three main geomorphological areas.
 W
WCarahue is a city and commune in southern Chile. It is located 56 km west of Temuco, on the northern bank of the Imperial River.
 W
WThe Lago Colhué Huapí Formation is a Late Cretaceous geologic formation of the Chubut Group in the Golfo San Jorge Basin in Patagonia, Argentina. The formation, named after Lake Colhué Huapí, is overlain by the Salamanca Formation of the Río Chico Group and in some areas by the Laguna Palacios Formation.
 W
WLake Musters and Lake Colhué Huapí form the terminal stage of the Senguerr River endorheic basin, located in the patagonic central region of Argentina in the south of Chubut province. Closest populated area is Sarmiento, an 8,000 inhabitant former Welsh immigrant colony. The lakes gave their names to the Mustersan and Colhuehuapian South American land mammal ages.
 W
WCollón Curá is a department located in the southeast of Neuquén Province, Argentina.
 W
WThe Collón Curá Formation is a Middle Miocene fossiliferous geological formation of the southern Neuquén Basin in northwestern Patagonia and the western Cañadón Asfalto Basin of central Patagonia, Argentina. The formation crops out from the southern Neuquén Province, the western Río Negro Province to the northern Chubut Province.
 W
WThe Collón Curá River is a geographical feature of Neuquén Province, Argentina. It flows southward from the confluence of the Aluminé and Chimehuin Rivers, near the town of Junín de los Andes, for around 70 kilometres (43 mi), past which it becomes a tributary of the Limay River. The Collón Curá Formation and in turn the South American land mammal age Colloncuran are named after the river.
 W
WAbelisaurus is a genus of predatory abelisaurid theropod dinosaur alive during the Late Cretaceous Period (Campanian) of what is now South America. It was a bipedal carnivore that probably reached about 7.4 metres in length, although this is uncertain as it is known from only one partial skull.
 W
WComahuesuchus is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Santonian Bajo de la Carpa Formation of Argentina. It was described by palaeontologist José Bonaparte in 1991. The type species is C. brachybuccalis.
 W
WCopahue is a stratovolcano in the Andes on the border of Bío Bío Region, Chile and Neuquén Province, Argentina. There are nine volcanic craters along a 2 km (1.2 mi) line, the easternmost of which is historically the most active, and contains a 300 m (1000 ft) wide crater lake with a pH ranging between 0.18 and 0.30. Eruptions from this crater lake have ejected pyroclastic rocks and chilled liquid sulfur fragments. Although the lake emptied during the 2000 eruption, it later returned to its previous levels. Copahue means "sulphur waters" in Mapuche.
 W
WThe coypu, also known as the nutria, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent. Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, Myocastor is now included within Echimyidae, the family of the spiny rats. The coypu lives in burrows alongside stretches of water, and feeds on river plant stems. Originally native to subtropical and temperate South America, it has since been introduced to North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, primarily by fur farmers. Although it is still hunted and trapped for its fur in some regions, its destructive burrowing and feeding habits often bring it into conflict with humans, and it is considered an invasive species.
 W
WCurarrehue is a town and commune in Cautín Province of Araucanía Region, Chile. The origin of Curarrehue dates back to the occupation of Araucanía and the Conquest of the Desert by the Chilean and Argentine army respectively in the 1870s and 1880s when Mapuches were pushed by the Argentine Army through Mamuil Malal Pass into the valley of Curarrehue where they settled.
 W
WCushamen is a town in Chubut Province, Argentina. It is the head town of the Cushamen Department.
 W
WCushamen is a department located in the north west of Chubut Province in Argentina.
 W
WIlokelesia is an extinct genus of abelisaurid theropod, preserved in the layers of the earliest Late Cretaceous of the Huincul Formation, Neuquén Group, located near Plaza Huincul, Neuquén Province, Argentina. The specimen, consisting of very fragmentary elements of the skull and the axial and appendicular skeleton, was described by Rodolfo Coria and Leonardo Salgado in late 1998.
 W
WKaikaifilu is a genus of tylosaurine mosasaur from the Late Cretaceous part of the Lopez de Bertodano Formation of Antarctica, just before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. It is among the largest members of the tylosaurines, a group of marine lizards that lived during the Cretaceous, and the only really large Antarctic tylosaurine.
 W
WKaikaifilusaurus is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalians in the family Sphenodontidae from the Late Cretaceous of South America. Fossils of the genus were found in Cenomanian sediments of the Candeleros Formation and Turonian layers of the Huincul Formation, both of the Neuquén Basin and the Albian strata of the Cerro Barcino Formation in the Cañadón Asfalto Basin, all in Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains two species, K. minimus and the type species K. calvoi.
 W
WThe Lefipán Formation is a Maastrichtian to Danian, straddling the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary, geologic formation of the Cañadón Asfalto Basin in Chubut Province, Patagonia, Argentina. The up to 380 metres (1,250 ft) thick stratigraphic unit comprises mudstones, sandstones, siltstones and conglomerates, sourced from the North Patagonian Massif and deposited in a deltaic to shallow marine environment with a strong tidal influence. The basin that in those times was connected to the widening South Atlantic Ocean with a seaway connection to the Austral Basin and possibly with the Pacific Ocean.
 W
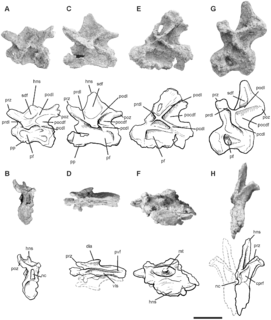
WLeinkupal is a genus of diplodocine sauropod known from the Early Cretaceous of the Bajada Colorada Formation, southeastern Neuquén Basin in the Neuquén Province of Argentina. It contains a single species, Leinkupal laticauda.
 W
WThe Río Limay Subgroup is a geological unit of the Neuquén Group in the Neuquén Basin of Neuquén, Mendoza and Río Negro Provinces, northern Patagonia, Argentina. The strata date back to the Late Cretaceous (Early Cenomanian to Early Turonian. The Río Limay Subgroup overlies the Lohan Cura Formation, separated by an unconformity dated to 98 Ma. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formations it contains.
 W
WThe Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault is major geological fault that runs a length of roughly 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) in a NNE-SSW orientation and exhibits current seismicity. It is located in the Chilean Northern Patagonian Andes. It is a dextral intra-arc strike-slip fault. Most large stratovolcanoes of the Southern Volcanic Zone of the Andes are aligned by the fault which allows for the movement of magma and hydrothermal fluids.
 W
WLoncoche is a city and commune in the Araucanía Region, southern Chile. It is located near the border to Los Ríos Region and the city of Lanco.
 W
WThe Maihue Lake is a lake located east of Ranco Lake in the Andean mountains of southern Chile. The lake is of glacial origin and it is enclosed by mountain ranges of the Andes, by all sides, and drains west to Ranco Lake.
 W
WMapusaurus was a giant carcharodontosaurid carnosaurian dinosaur from the early Late Cretaceous of what is now Argentina and Chile.
 W
WThe Río Neuquén Subgroup is a geological subgroup in the Neuquén Basin, Neuquén Province, Argentina, whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. The subgroup, formerly defined as a formation, is the middle unit of the Neuquén Group and contains the Plottier, Sierra Barrosa Formation, Los Bastos Formation, and Portezuelo Formations. The subgroup overlies the Río Limay Subgroup and is overlain by the Río Colorado Subgroup. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WNeuquén Basin is a sedimentary basin covering most of Neuquén Province in Argentina. The basin originated in the Jurassic and developed through alternating continental and marine conditions well into the Tertiary. The basin bounds to the west with the Andean Volcanic Belt, to the southeast with the North Patagonian Massif and to the northeast with the San Rafael Block and to the east with the Sierra Pintada System. The basin covers an area of approximately 120,000 square kilometres (46,000 sq mi). One age of the SALMA classification, the Colloncuran, is defined in the basin, based on the Collón Curá Formation, named after the Collón Curá River, a tributary of the Limay River.
 W
WThe Neuquén Group is a group of geologic formations found in Argentina. Rocks in the Neuquén Group fall within the Cenomanian to early Campanian stages of the Late Cretaceous Period. It overlies the older Lohan Cura Formation and is itself overlain by the younger Allen Formation of the Malargüe Group, separated from both by unconformities, dated to 98 and 79 Ma respectively.
 W
WNeuquenraptor is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Portezuelo Formation of Argentina. It is one of the first dromaeosaurids found in the Southern Hemisphere.
 W
WNeuquensaurus is a genus of saltasaurid sauropod dinosaur that lived in the Late Cretaceous, about 80 million years ago in Argentina and Uruguay in South America. Its fossils were recovered from outcrops of the Anacleto Formation around Cinco Saltos, near the Neuquén river from which its name is derived.
 W
WPanguipulli is a city and commune in Valdivia Province, southern Chile, administered by the Municipality of Panguipulli. The town is known for its natural environment, and is called "City of roses". Panguipulli is located on the western edge of Panguipulli Lake, and is on a moraine in the Chilean Central Valley. Most of the commune lies on Andean mountains and valleys.
 W
WThe Panguipulli Batholith is a granitic batholith of Jurassic age located in the Andes around Panguipulli Lake in southern Chile.
 W
WThe Panguipulli Lake is one of the "Seven Lakes" in Panguipulli municipality, southern Chile. The lake is of glacial origin and it is enclosed by mountain ranges of the Andes, on all sides except the west, where the town of Panguipulli lies in the Chilean Central Valley. The lake is drained by the Enco River that flows south to Riñihue Lake.
 W
WPirihueico Lake is one of Seven Lakes in Panguipulli Commune, southern Chile. The lake is of glacial origin and it is enclosed mountains of the Andes. It is located in a geological fault that includes Panguipulli Lake and Lácar Lake in Argentina. The lake is drained by Fui River. Pirihueico Lake is used as a waterway due to its elonged shape. It is used mostly by vehicles traveling to or from Argentina by the nearby Huahum Pass. For that reason there is a ferry operating between Puerto Fuy and Puerto Pirihueico in the western respectively eastern extreme of the lake.
 W
WPitrufquén is a Chilean city and commune in Cautín Province, Araucanía Region. The city is located 30 km south of Temuco and lies immediately south of the Toltén River, along Chile Highway 5.
 W
WThe Puduhuapi Formation is a sedimentary formation whose only known outcrops are on Puduhuapi Island of the Chiloé Archipelago, west of Chaitén in western Patagonia, Chile. Lithologies vary from sandstone and siltstone to conglomerate. The sediment that now forms the rock deposited during the Miocene no earlier than 23 million years ago.
 W
WPuyehue Lake, is an Andean piedmont lake on the border of Los Lagos Region with Los Ríos Region of Chile.
 W
WThe Quiriquina Formation is a geological formation in Chile whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. The glauconitic sandstones and conglomerates of the formation were deposited in a marine environment.
 W
WThe Riñihuazo is the name given to the landslide damming of Riñihue Lake on 22 May 1960, after a landslide caused by the Great Chilean earthquake blocked its outflow. According to the chronicler Mariño de Lobera a similar event occurred after the 1575 Valdivia earthquake.
 W
WThe Work is a lake of glacial origin in eastern Valdivia Province, southern Chile. It is surrounded by several mountains. The eastern side receives the waters of the Panguipulli Lake by the Enco River, its main contributor. It is the last of the Seven Lakes chain. In the west it is cut into two arms by the Tralcán Mount, and on the east side lies the Mocho-Choshuenco volcano. In the south the lake is bounded by the Cerros de Quimán mountains.