 W
WThe culture of the Native Hawaiians is about 1,500 years old and has its origins in the Polynesians who voyaged to and settled Hawaii. Polynesia is made of multiple islands that include Hawaii, New Zealand, Samoa, among others within the Pacific Ocean. These voyagers developed Hawaiian cuisine, Hawaiian art, and the Native Hawaiian religion.
 W
WAhupuaʻa is a Hawaiian term for a large traditional socioeconomic, geologic, and climatic subdivision of land.
 W
WThe ʻAhu ʻula, and the mahiole were symbols of the highest rank of the chiefly aliʻi class of ancient Hawaii. The feathered cloaks and capes were believed to provide spiritual protection for Hawaiian chiefs. There are over 160 examples of this traditional clothing in museums around the world. At least six of these cloaks were collected during the voyages of Captain Cook. These cloaks are made from a woven netting decorated with bird feathers and are examples of fine featherwork techniques. One of these cloaks was included in a painting of Cook's death by Johann Zoffany.
 W
WAliʻiōlani Hale is a building located in downtown Honolulu, Hawaiʻi, currently used as the home of the Hawaiʻi State Supreme Court. It is the former seat of government of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi and the Republic of Hawaiʻi.
 W
WThe Hawaiian people practiced aquaculture through development of fish ponds, the most advanced fish husbandry among the original peoples of the Pacific. These fishponds were typically shallow areas of a reef flat surrounded by a low lava rock wall built out from the shore. Several species of edible fish thrive in such ponds, and Hawaiians developed methods to make them easy to catch.
 W
WHawaiian architecture is a distinctive architectural style developed and employed primarily in the Hawaiian Islands, buildings and various other structures indicative of the people of Hawaiʻi and the environment and culture in which they live. Though based on imported Western styles, unique Hawaiian traits make Hawaiian architecture stand alone against other styles. Hawaiian architecture reflects the history of the islands from antiquity through the kingdom era, from its territorial years to statehood and beyond.
 W
WThe Bernice Pauahi Bishop Museum, designated the Hawaiʻi State Museum of Natural and Cultural History, is a museum of history and science in the historic Kalihi district of Honolulu on the Hawaiian island of O'ahu. Founded in 1889, it is the largest museum in Hawai'i and has the world's largest collection of Polynesian cultural artifacts and natural history specimens. Besides the comprehensive exhibits of Hawaiiana, the museum's total holding of natural history specimens exceeds 24 million, of which the entomological collection alone represents more than 13.5 million specimens.
 W
WThe Curse of Lono is a book by Hunter S. Thompson describing his experiences in Hawaii in 1980. Originally published in 1983, the book was only in print for a short while. In 2005 it was re-released as a limited edition. Only 1000 copies were produced, each one being signed by the author and artist Ralph Steadman.The book is now available as a smaller hardcover edition.
 W
WThe Daughters of Hawaiʻi was founded in 1903 by seven women who were daughters of American Protestant missionaries. They were born in Hawaiʻi, were citizens of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi before annexation, and foresaw the inevitable loss of much of the Hawaiian culture. They founded the organization "to perpetuate the memory and spirit of old Hawaiʻi and of historic facts, and to preserve the nomenclature and correct pronunciation of the Hawaiian language."' They run the Huliheʻe Palace and the Queen Emma Summer Palace.
 W
WThe East Hawaii Cultural Center (EHCC) is an art gallery, community theater, and cultural center in downtown Hilo, Hawaii. EHCC features regular art exhibitions with free or suggested donation entry to the general public. Administered by the East Hawaii Cultural Council, an umbrella group of local arts organizations, the Center is housed in a historic former police station facing Kalakaua Park.
 W
WHanafuda are a style of Japanese playing cards, made from paper and cardboard. They are typically smaller than Western playing cards, only 2⅛ by 1¼ inches. On the face of each card is a depiction of flowers, tanzaku, subjects, or culturally-significant scenes. The back side is usually plain, without a pattern or design of any kind. Hanafuda are used to play a variety of games like Koi-Koi and Hachi-Hachi.
 W
W"Hawaiʻi Ponoʻī" is the regional anthem of the U.S. state of Hawaii. It previously served as the national anthem of the independent Kingdom of Hawaii in the 19th Century, and has continued to be Hawaii's official anthem ever since annexation by the United States in 1898.
 W
WHōkūleʻa is a performance-accurate waʻa kaulua, a Polynesian double-hulled voyaging canoe. Launched on 8 March 1975 by the Polynesian Voyaging Society, she is best known for her 1976 Hawaiʻi to Tahiti voyage completed with exclusively Polynesian navigation techniques The primary goal of the voyage was to explore the anthropological theory of the Asiatic origin of native Oceanic people, of Polynesians and Hawaiians in particular, as the result of purposeful trips through the Pacific, as opposed to passive drifting on currents, or sailing from the Americas. A secondary project goal was to have the canoe and voyage "serve as vehicles for the cultural revitalization of Hawaiians and other Polynesians".
 W
WKaloko-Honokōhau National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park located in the Kona District on the Big island of Hawaiʻi in the U.S. state of Hawaiʻi. It includes the National Historic Landmarked archaeological site known as the Honokōhau Settlement. The park was established on November 10, 1978, for the preservation, protection and interpretation of traditional native Hawaiian activities and culture.
 W
WA hukilau is a way of fishing invented by the ancient Hawaiians. The word comes from huki, meaning pull, and lau, meaning leaves. A large number of people, usually family and friends, would work together in casting the net from shore and then pulling it back. The net was lined with ti leaves, which would help scare the fish into the center of the net. Consistent with the Hawaiian subsistence economy, anybody who helped could share in the catch. Hukilau Beach, in Lā'ie, is named after the technique, which has been used there for centuries.
 W
WA kāhili is a symbol of the aliʻi chiefs and families of the Hawaiian Islands. It was taken by the Kamehamehas as a Hawaiian royal standard and used by the Royal Families to indicate their lineage.
 W
WKamaʻāina is a word describing Hawaii residents regardless of their racial background, as opposed to kanaka which means a person of Native Hawaiian ancestry.
 W
WKānāwai Māmalahoe, or Law of the Splintered Paddle, is a precept in Hawaiian law, originating with King Kamehameha I in 1797. The law, "Let every elderly person, woman and child lie by the roadside in safety," is enshrined in the state constitution, Article 9, Section 10, and has become a model for modern human rights law regarding the treatment of civilians and other non-combatants during times of war. It was created when Kamehameha was on a military expedition in Puna. His party encountered a group of commoners on a beach. While chasing two fishermen who had stayed behind to cover the retreat of a man carrying a child, Kamehameha's leg was caught in the reef. One of the fisherman, Kaleleiki, hit him mightily on the head with a paddle in defense, which broke into pieces. Kamehameha could have been killed at that point but the fisherman spared him. Years later, the same fisherman was brought before Kamehameha. Instead of ordering for him to be killed, Kamehameha ruled that the fisherman had only been protecting his land and family, and so the Law of the Splintered Paddle was declared.The complete original 1797 law in HawaiianKānāwai Māmalahoe : E nā kānaka, E mālama 'oukou i ke akua A e mālama ho‘i ke kanaka nui a me kanaka iki; E hele ka 'elemakule, ka luahine, a me ke kama A moe i ke ala 'A‘ohe mea nāna e ho‘opilikia. Hewa nō, make.English translationLaw of the Splintered Paddle: Oh people, Honor thy god; respect alike [the rights of] people both great and humble; May everyone, from the old men and women to the children Be free to go forth and lie in the road Without fear of harm. Break this law, and die.
 W
WKapu Kuʻialua; Kuʻialua; or Lua; is an ancient Hawaiian martial art based on bone breaking, joint locks, throws, pressure point manipulation, strikes, usage of various weapons, battlefield strategy, open ocean warfare as well as the usage of introduced firearms from the Europeans.
 W
WKōnane is a two-player strategy board game from Hawaii. It was invented by the ancient Hawaiian Polynesians. The game is played on a rectangular board. It begins with black and white counters filling the board in an alternating pattern. Players then hop over one another's pieces, capturing them similar to checkers. The first player unable to capture is the loser; their opponent is the winner.
 W
WLāhainā Noon is a bi-annual tropical solar phenomenon when the Sun culminates at the zenith at solar noon, passing directly overhead. The term Lāhainā Noon was coined by the Bishop Museum in Hawai'i.
 W
WA lanai or lānai is a type of roofed, open-sided veranda, patio, or porch originating in Hawaii. Many homes, apartment buildings, hotels and restaurants in Hawaii are built with one or more lānais.
 W
WLei is a garland or wreath. More loosely defined, a lei is any series of objects strung together with the intent to be worn. The most popular concept of a lei in Hawaiian culture is a wreath of flowers presented upon arriving or leaving as a symbol of affection. This concept was popularized through tourism between the Hawaiian Islands and the continental United States in the 19th and 20th centuries.
 W
WA Lei niho palaoa is a Hawaiian neck ornament traditionally worn by aliʻi (chiefs) of both sexes. The 19th century examples are most commonly made of a whale tooth carved into a hook-shape suspended by plaited human hair. The symbolism is not known; it may represent a tongue that speaks the law, or may represent a vessel for mana. Precontact lei niho palaoa were less than two inches in length, and were not only made of whale ivory, but also of shell, bone, wood, stone, and coral. Sometimes, several of these smaller pendants were strung on twisted human hair. The Bishop Museum has a lei niho palaoa with a hair bundle having a circumference of 7.5 inches. It is made from a single eight-ply square braid cord, measuring 1,708 feet, looped back and forth over 1000 times on each side.
 W
WThe leiomano is a shark-toothed club used by various Polynesian cultures, but mostly by the native Hawaiians.
 W
WA lūʻau is a traditional Hawaiian party or feast that is usually accompanied by entertainment. It may feature food such as poi, kālua puaʻa, poke, lomi salmon, ʻopihi, and haupia, beer, and entertainment such as traditional Hawaiian music and hula. Among people from Hawaiʻi, the concepts of "lūʻau" and "party" are often blended, resulting in graduation lūʻau, wedding lūʻau, baby lūʻau, and birthday lūʻau.
 W
WHawaiian feather helmets, known as mahiole in the Hawaiian language, were worn with feather cloaks. These were symbols of the highest rank reserved for the men of the aliʻi, the chiefly class of Hawaii. There are examples of this traditional headgear in museums around the world. At least sixteen of these helmets were collected during the voyages of Captain Cook. These helmets are made from a woven frame structure decorated with bird feathers and are examples of fine featherwork techniques. One of these helmets was included in a painting of Cook's death by Johann Zoffany.
 W
WMālia is a Hawaiian-style wooden racing canoe crafted by James Takeo Yamasaki. The canoe was hewn out of blonde koa wood in Kailua-Kona, Hawaii, in 1933. Its wooden hull provided the founding model for all subsequent outrigger canoeing hulls, including those later molded from fiberglass. Hawaiian racing canoeist Tommy Holmes observed that Malia "remains a prototype for contemporary racing canoes [and] was among the first canoes built exclusively for the sport." The canoe was listed on the State and National Register of Historic Places in 1993.
 W
WAhupuaʻa is a Hawaiian term for a large traditional socioeconomic, geologic, and climatic subdivision of land.
 W
W W
WPa'u riders, , are wahine horseback riders who wear long, colorful skirts and characteristically ride astride, rather than sidesaddle. This equestrian tradition's roots are from the early 19th century, when horses were introduced to Hawaii and aliʻi women dressed up to ride for formal occasions. It declined after the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii, but was revitalized in the early 20th century with the establishment of formal riding organizations called Pa'u Riders. Today, they participate in Kamehameha Day floral parades and other parades and festivals throughout the islands.
 W
WPenile subincision is a form of genital modification or mutilation consisting of a urethrotomy, in which the underside of the penis is incised and the urethra slit open lengthwise, from the urethral opening (meatus) toward the base. The slit can be of varying lengths.
 W
WThe Polynesian Voyaging Society (PVS) is a non-profit research and educational corporation based in Honolulu, Hawaiʻi. PVS was established to research and perpetuate traditional Polynesian voyaging methods. Using replicas of traditional double-hulled canoes, PVS undertakes voyages throughout Polynesia navigating without modern instruments.
 W
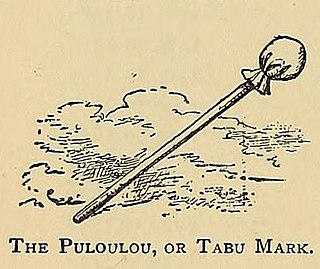
WPūloʻuloʻu, often called "kapu sticks", are symbols denoting the kapu of Hawaiian aliʻi and symbolizing the deceased ancestors of the aliʻi. They are traditional symbols of authority which are used in modern times including the Seal of the State of Hawaii.
 W
WPulu is a silky material obtained from the fibers of the hapuʻu pulu, a tree fern of Hawaii. It is made of the brown hairs that cover the young fiddlehead as it uncoils.
 W
WThe Royal Order of Kalākaua I was instituted on 28 September 1874 by King Kalākaua I to commemorate his accession to the throne of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi on 12 February 1874.
 W
WThe Royal Order of Kapiʻolani was instituted on August 30, 1880 by King Kalākaua to recognize services in the cause of humanity, for merit in Science and the Arts, or for special services rendered to the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi. He named the Order in honor of his ancestor High Chiefess Kapiʻolani the Great, an early exponent of Christianity in the Hawaiian Islands. It also honored his wife Queen Kapiʻolani, the namesake of the first Kapiʻolani. This Order was awarded 177 times in all grades during Kalākaua's reign, and three more times by his successor, Queen Liliʻuokalani. The last award of the Order took place on June 2, 1892; in 1893 the Order became obsolete.
 W
WSennit is a type of cordage made by plaiting strands of dried fibre or grass. It can be used ornamentally in crafts, like a kind of macrame, or to make straw hats. Sennit is an important material in the cultures of Oceania, where it is used in traditional architecture, boat building, fishing and as an ornamentation.
 W
WThe shaka sign, sometimes known as "hang loose", is a gesture of friendly intent often associated with Hawaii and surf culture. It consists of extending the thumb and smallest finger while holding the three middle fingers curled, and gesturing in salutation while presenting the front or back of the hand; the hand may be rotated back and forth for emphasis. While the shaka sign has spread internationally from its Hawaiian cultural roots to surf culture and beyond, the hand gesture also bears a variety of meaning in different contexts and regions of the world.
 W
WThe Society of Seven (SOS) is a musical group that performs a variety show of the same name. Based in Hawaii, it was formed in 1969 from the pop group known as the Fabulous Echoes, which originated in Hong Kong in the early 1960s. The group mainly performed at the Main Showroom of the Outrigger Waikiki in Hawaii, and has toured Las Vegas, Los Angeles, San Francisco, and other major cities in the West Coast of the United States. Its original members were Tony Ruivivar, Bert Sagum, Don Gay, Terry Lucido, Roberto Nievera, Stan Robertson, and Danny Ruivivar.
 W
WSurfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer, uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitable for surfing are primarily found in the ocean, but can also be found in lakes or rivers in the form of a standing wave or tidal bore.
 W
WFederal recognition of Native Hawaiians refers to proposals for the federal government of the United States to give legal recognition to Native Hawaiians, providing them with some form of indigenous sovereignty within a framework similar to that afforded to Native Americans and Alaska Natives.