 W
WAngry Asian Man is an Internet blog founded in 2001 by Phil Yu. The blog focuses on Asian American news, media, and politics. The Washington Post calls Angry Asian Man "a daily must-read for the media-savvy, socially conscious, pop-cultured Asian American." An accompanying podcast, entitled Sound and Fury: The Angry Asian Podcast, was launched in May 2012 and features interviews with Asian Americans.
 W
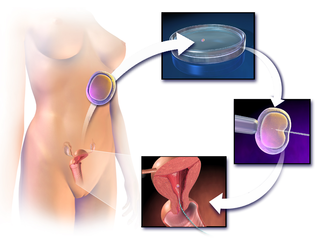
WAssisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes or embryos, and/or the use of fertility medication. When used to address infertility, ART may also be referred to as fertility treatment. ART mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Some forms of ART may be used with regard to fertile couples for genetic purpose. ART may also be used in surrogacy arrangements, although not all surrogacy arrangements involve ART.
 W
WBak Jeongyang(korean:박정양, hanja:朴定陽, 1841–1904) was a Korean Joseon dynasty politician and edification activist. a member of Independence Club(독립협회;獨立協會) and People's joint association(만민공동회;萬民共同會).He was a supporter of slow modernization of Joseon dynasty korea,and his family was Pannam Park clan. He is also the father of famous Korean play writer Park Seung-hee (1901-1964). Bak Jeongyang was dispatched by Korean King to be the ambassador to the United States in 1887. He went to United States and caused an international outcry from the Chinese Empire which viewed Korea as a vassal state. After many years' conflict, Park was punished and was pushed aside. This episode reveals Korea's desire for complete independence, but demonstrates China's plan to stick to the traditional tributary tie. Park became a victim of this conflict. Park was also the author of a few books.
 W
WBak Jungyang was a Korean Joseon and Japanese-ruled Korean bureaucrat, politician, liberal and social activist. He demolished the castle of Daegueup and the Old Gyungsangdo Provincial Office, and contributed to city planning and road maintenance in Daegu. He also participated in the destruction of the Castle of Jinju. He was a conscientious Japanese colonial supporter with pro-Japanese group ideology as well as an advocate for civil rights.
 W
WSir Isaiah Berlin was a Latvian-born British social and political theorist, philosopher, and historian of ideas. Although he became increasingly averse to writing for publication, his improvised lectures and talks were sometimes recorded and transcribed, and many of his spoken words were converted into published essays and books, both by himself and by others, especially his principal editor from 1974, Henry Hardy.
 W
WThe Cortes of Cádiz was a revival of the traditional cortes, which as an institution had not functioned for many years, but it met as a single body, rather than divided into estates as with previous ones. The General and Extraordinary Cortes that met in the port of Cádiz starting 24 September 1810, "claimed legitimacy as the sole representative of Spanish sovereignty," following the French invasion and occupation of Spain during the Napoleonic Wars and the abdication of the monarch Ferdinand VII and his father Charles IV. It met as one body and its members represented the entire Spanish Empire, that is, not only Spain, but also Spanish America and the Philippines. The Cortes of Cádiz was seen then, and by historians today, as a major step towards liberalism and democracy in the history of Spain and Spanish America. The liberal Cortes drafted and ratified the Spanish Constitution of 1812, which established a constitutional monarchy and eliminated many institutions that privileged some groups over others.
 W
WThe "Citizens' Ministry" (Bürgerministerium) is a term used in a political debate, and later in historical literature. It also applies to the "Doctors' Ministry" (Doktorenministerium). They are used as summary descriptions for the four governments of the Austrian part of Austria-Hungary (Cisleithania), from 30 December 1867 to 4 April 1870, when the government tendered its resignation, and was dismissed on 12 April 1870. These were the initial administrations after the Austro-Hungarian Compromise (Ausgleich) of 1867 that divided the empire's internal administration.
 W
WThe Coppet group, also known as the Coppet circle, was an informal intellectual and literary gathering centred on Germaine de Staël during the time period between the establishment of the Napoleonic First Empire (1804) and the Bourbon Restoration of 1814-1815. The name comes from Coppet Castle in Switzerland.
 W
WThe Democratic Paradox is a collection of essays by the Belgian political theorist Chantal Mouffe, published in 2000 by Verso Books. The essays offer further discussion of the concept of radical democracy that Mouffe explored in Hegemony and Socialist Strategy, co-authored by Ernesto Laclau. In this collection, Mouffe deals with the specific conflicts between the post-Marxist democratic theory that she and Laclau theorized in Hegemony and Socialist Strategy and the competing democratic theories proposed by Jürgen Habermas and John Rawls. Verso's UK blog characterizes The Democratic Paradox as Mouffe's most accessible review of her perspectives on radical democracy.
 W
WEconomic liberalism is a political and economic philosophy based on strong support for a market economy and private property in the means of production. Although economic liberals can also be supportive of government regulation to a certain degree, they tend to oppose government intervention in the free market when it inhibits free trade and open competition. Economic liberalism has been described as representing the economic expression of classical liberalism.
 W
WEmbedded liberalism is a term for the global economic system and the associated international political orientation as they existed from the end of World War II to the 1970s. The system was set up to support a combination of free trade with the freedom for states to enhance their provision of welfare and to regulate their economies to reduce unemployment. The term was first used by the American political scientist John Ruggie in 1982.
 W
WThe Empire of Liberty is a theme developed first by Thomas Jefferson to identify the responsibility of the United States to spread freedom across the world. Jefferson saw the mission of the U.S. in terms of setting an example, expansion into western North America, and by intervention abroad. Major exponents of the theme have been James Monroe, Andrew Jackson and James K. Polk, Abraham Lincoln, Theodore Roosevelt, Woodrow Wilson, Franklin D. Roosevelt, Harry Truman, Ronald Reagan, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush.
 W
WThe Frankfurter Zeitung was a German language newspaper that appeared from 1856 to 1943. It emerged from a market letter that was published in Frankfurt. In Nazi Germany it was considered the only mass publication not completely controlled by the Propagandaministerium under Joseph Goebbels.
 W
WFrente Despertar is a political coalition in Argentina. It participated in the 2019 Argentine general election, formed by Unite for Freedom and Dignity, the Union of the Democratic Centre, the Libertarian Party and the Democratic Party.
 W
WGeorgism, also called in modern times geoism and known historically as the single tax movement, is an economic ideology holding that, although people should own the value they produce themselves, the economic rent derived from land – including from all natural resources, the commons, and urban locations – should belong equally to all members of society. Developed from the writings of American economist and social reformer Henry George, the Georgist paradigm seeks solutions to social and ecological problems, based on principles of land rights and public finance which attempt to integrate economic efficiency with social justice.
 W
WGladstonian liberalism is a political doctrine named after the British Victorian Prime Minister and leader of the Liberal Party, William Ewart Gladstone. Gladstonian liberalism consisted of limited government expenditure and low taxation whilst making sure government had balanced budgets and the classical liberal stress on self-help and freedom of choice. Gladstonian liberalism also emphasised free trade, little government intervention in the economy and equality of opportunity through institutional reform. It is referred to as laissez-faire or classical liberalism in the United Kingdom and is often compared to Thatcherism.
 W
WHigher Superstition: The Academic Left and Its Quarrels with Science is a 1994 book about the philosophy of science by the biologist Paul R. Gross and the mathematician Norman Levitt.
 W
WThe history of the kingdom of Portugal and the Algarves, from the First Treaty of San Ildefonso and the beginning of the reign of Queen Maria I in 1777, to the end of the Liberal Wars in 1834, spans a complex historical period in which several important political and military events led to the end of the absolutist regime and to the installation of a constitutional monarchy in the country.
 W
WDavid Hume was a Scottish Enlightenment philosopher, historian, economist, librarian and essayist, who is best known today for his highly influential system of philosophical empiricism, skepticism, and naturalism. Beginning with A Treatise of Human Nature (1739–40), Hume strove to create a naturalistic science of man that examined the psychological basis of human nature. Hume argued against the existence of innate ideas, positing that all human knowledge derives solely from experience. This places him with Francis Bacon, Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, and George Berkeley as a British Empiricist.
 W
WThe Iron Front was a German paramilitary organization in the Weimar Republic which consisted of social democrats, trade unionists, and liberals. Its main goal was to defend liberal democracy against totalitarian ideologies on the far right and far left. The Iron Front chiefly opposed the Sturmabteilung (SA) wing of the Nazi Party and the Antifaschistische Aktion wing of the Communist Party of Germany. Formally independent, it was intimately associated with the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). The Three Arrows, originally designed for the Iron Front, became a well-known social democratic symbol representing resistance against monarchism, Nazism, and communism during the parliamentary elections in November 1932. The Three Arrows were later adopted by the SPD itself.
 W
W"A Man's a Man for A' That", also known as "Is There for Honest Poverty" or "For a' That and a' That", is a 1795 song by Robert Burns, written in Scots and English, famous for its expression of egalitarian ideas of society, which may be seen as expressing the ideas of republicanism that arose in the 18th century.
 W
WThe Levellers were a political movement during the English Civil War (1642–1651) committed to popular sovereignty, extended suffrage, equality before the law and religious tolerance. The hallmark of Leveller thought was its populism, as shown by its emphasis on equal natural rights, and their practice of reaching the public through pamphlets, petitions and vocal appeals to the crowd.
 W
WLiberté, égalité, fraternité, French for "liberty, equality, fraternity", is the national motto of France and the Republic of Haiti, and is an example of a tripartite motto. Although it finds its origins in the French Revolution, it was then only one motto among others and was not institutionalized until the Third Republic at the end of the 19th century. Debates concerning the compatibility and order of the three terms began at the same time as the Revolution. It is also the motto of the Grand Oriente and the Grande Loge de France.
 W
WMoral Man and Immoral Society: A Study in Ethics and Politics is a 1932 book by Reinhold Niebuhr, an American Protestant theologian at Union Theological Seminary (UTS) in New York City. The thesis of the book is that people are more likely to sin as members of groups than as individuals. Niebuhr wrote the book in a single summer. He drew the book's contents from his experiences as a pastor in Detroit, Michigan prior to his professorship at UTS. The book attacks liberalism, both secular and religious, and is particularly critical of John Dewey and the Social Gospel. Moral Man and Immoral Society generated much controversy and raised Niebuhr's public profile significantly. Initial reception of the book by liberal Christian critics was negative, but its reputation soon improved as the rise of fascism throughout the 1930s was seen as having been predicted in the book. Soon after the book's publication, Paul Lehmann gave a copy to Dietrich Bonhoeffer, who read it and was impressed by the book's thesis but disliked the book's critique of pacifism. The book eventually gained significant readership among American Jews because, after a period of considerable anti-theological sentiment among Jews in the United States, many Jews began to return to the study of theology and, having no Jewish works of theology to read, turned to Protestant theological works.
 W
WJohann Jakob Moser was a German jurist, publicist and researcher, whose work earned him the title "The Father of German Constitutional Law" and whose political commitment to the principles of Liberalism caused him to lose academic positions and spend years as a political prisoner.
 W
WMuscular liberalism is a form of liberalism advocated by former British Prime Minister David Cameron that describes his policy towards state multiculturalism.
 W
WMutual liberty is an idea first developed by Alexis de Tocqueville in his 1835 work Democracy in America. In effect, Tocqueville was referring to the general nature of American society during the 19th century. It appeared to him, at least on the surface, that every citizen in the United States had the opportunity to participate in the civic activities of the country. Another way to look at mutual liberty is by accounting for the collective free wills of every rational being in a community.
 W
WThe National Liberal Club (NLC) is a London private members' club, open to both men and women. It was established by William Ewart Gladstone in 1882 to provide club facilities for Liberal Party campaigners among the newly enlarged electorate following the Third Reform Act in 1884, and was envisioned as a more accessible version of a traditional London club.
 W
WNordic Center Youth is a Nordic political organisation for centrist youth and student organisations. It was founded in 1965 and today has 16 000 individual members.
 W
W"Objectivity and Liberal Scholarship" is an essay by the American academic Noam Chomsky. It was first published as part of Chomsky's American Power and the New Mandarins. Parts of the essay were delivered as a lecture at New York University in March 1968, as part of Albert Schweitzer Lecture Series. The first third of the essay, "The Menace of Liberal Scholarship" by Noam Chomsky in The New York Review of Books, January 2, 1969, was taken "almost verbatim" from this essay.
 W
WThe Paraguayan Civil War (1922), took place between 27 May 1922 and 10 July 1923, within the borders of Paraguay. It started when supporters of candidate Adolfo Chirife attempted to forcefully restore the implementation of presidential elections canceled by President Eusebio Ayala. Chirife represented the so-called Constitutionalist or Schaererist side ideologically supporting liberal politician Eduardo Schaerer, while troops under Ayala were named Loyalists or Gondrists ideologically pledging allegiance to former President Manuel Gondra. The conflict concluded when Gondrist forces defeated the remnants of the Schaererist army in Asunción.
 W
WA parliamentary republic is a republic that operates under a parliamentary system of government where the executive branch derives its legitimacy from and is accountable to the legislature. There are a number of variations of parliamentary republics. Most have a clear differentiation between the head of government and the head of state, with the head of government holding real power, much like constitutional monarchies. Some have combined the roles of head of state and head of government, much like presidential systems, but with a dependency upon parliamentary power.
 W
WA parliamentary system or parliamentary democracy is a system of democratic governance of a state where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the confidence of the legislature, typically a parliament, and is also held accountable to that parliament. In a parliamentary system, the head of state is usually a person distinct from the head of government. This is in contrast to a presidential system, where the head of state often is also the head of government and, most importantly, where the executive does not derive its democratic legitimacy from the legislature.
 W
WRegressive left is a pejorative term for a branch of left-wing politics that are accused of holding views that conflict with liberal principles, especially tolerating Islamism.
 W
WThe Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in European history.
 W
WThe Revolutions of 1917–1923 was a revolutionary wave that included political unrest and revolts around the world inspired by the success of the Russian Revolution and the disorder created by the aftermath of World War I. The uprisings were mainly socialist or anti-colonial in nature. Many attempted socialist revolts failed to have a long-term impact.
 W
WRights of Man (1791), a book by Thomas Paine, including 31 articles, posits that popular political revolution is permissible when a government does not safeguard the natural rights of its people. Using these points as a base it defends the French Revolution against Edmund Burke's attack in Reflections on the Revolution in France (1790).
 W
WSEALDs, short for Students Emergency Action for Liberal Democracy , was a student activist organisation in Japan that organised protests against the ruling coalition headed by Prime Minister Shinzō Abe in 2015 and 2016. Its focus was on the security-related bills enacted in 2015 that allow the Japanese Self-Defense Force to be deployed overseas.
 W
WSocial Darwinism refers to various theories that emerged in Western Europe and North America in the 1870s that applied biological concepts of natural selection and survival of the fittest to sociology, economics, and politics. Social Darwinism posits that the strong see their wealth and power increase while the weak see their wealth and power decrease. Various social Darwinist schools of thought differ on which groups of people are the strong and which are the weak, and also differ on the precise mechanisms that reward strength and punish weakness. Many such views stress competition between individuals in laissez-faire capitalism, while others, emphasizing struggle between national or racial groups, support nationalism, authoritarianism, eugenics, racism, imperialism, and/or fascism. The ideology of social Darwinism inspired the perpetrators of genocides including the Armenian Genocide and the Holocaust.
 W
WThe Spanish confiscation was the Spanish government's seizure and sale of property, including from the Catholic Church, from the late 18th century to the early 20th century. It was a long historical, economic, and social process beginning with the so-called "Confiscation of Godoy" in 1798—although there was an earlier precedent during the reign of Charles III of Spain—and ending on 16 December 1924.
 W
WBertrando Spaventa was a leading Italian philosopher of the 19th century whose ideas had an important influence on the changes that took place during the unification of Italy and on philosophical thought in the 20th century.
 W
WKaarlo Juho Ståhlberg was a Finnish jurist and academic, which was one of the most important pioneers of republicanism in the country. He was the first President of Finland (1919–1925) and a liberal nationalist.
 W
WA tricolour or tricolor is a type of flag or banner design with a triband design which originated in the 16th century as a symbol of republicanism, liberty or indeed revolution. The flags of France, Italy, Romania, Mexico, and Ireland were all first adopted with the formation of an independent republic in the period of the French Revolution to the Revolutions of 1848, with the exception of the Irish tricolour, which dates from 1848 but was not popularised until the Easter Rising in 1916 and adopted in 1919.
 W
WA victimless crime is an illegal act that typically either directly involves only the perpetrator or occurs between consenting adults. Because it is consensual in nature, whether there involves a victim is a matter of debate. Definitions of victimless crimes vary in different parts of the world and different law systems, but usually include possession of any illegal contraband, recreational drug use, prostitution and prohibited sexual behavior between consenting adults, assisted suicide, and smuggling among other similar infractions.