 W
WIn contemporary education, mathematics education is the practice of teaching and learning mathematics, along with the associated scholarly research
 W
WThe American Mathematical Association of Two-Year Colleges (AMATYC) is an organization dedicated to the improvement of education in the first two years of college mathematics in the United States and Canada. AMATYC hosts an annual conference, summer institutes, workshops and mentoring for teachers in and outside math, and a semiannual math competition. AMATYC publishes one refereed journal, MathAMATYC Educator, and issues position statements on matters of mathematics education.
 W
WThe Garden of Archimedes is a museum for mathematics in Florence, Italy. It was founded on March 26, 2004 and opened its doors to the public on April 14 of that year. The mission of the museum is to enhance public understanding and perception of mathematics, to bring mathematics out of the shadows and into the limelight. It has been compared to the National Museum of Mathematics in New York City, the only museum in North America devoted to mathematics.
 W
WArithmetic is a branch of mathematics that consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations on them—addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation and extraction of roots. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory, and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.
 W
WArithmetic for Parents is a book about mathematics education aimed at parents and teachers.
 W
WThe Australian Science and Mathematics School (ASMS) is a coeducational public senior high school for Years 10 - 12 located on the campus of Flinders University in Bedford Park, a southern suburb of Adelaide, the capital of South Australia. As the school is unzoned, it attracts students from all across the Adelaide metropolitan area as well as some regional and interstate locations, in addition to international students. The goal of the school is to prepare its students for university, particularly in the fields of mathematics and science. The ASMS is unconventional in its approach to education, emphasising a love of learning in both students and teaching staff; students are given the freedom to take control of their own education. ASMS aims to make students aware of their own learning and for them to become self-directed in the way they complete academic tasks.
 W
WBirla Industrial & Technological Museum (BITM), a unit under National Council of Science Museums (NCSM), Ministry of Culture, Government of India, is at Gurusaday Road, Kolkata.
 W
WThe Budapest Semesters in Mathematics program is a study abroad opportunity for North American undergraduate students in Budapest, Hungary. The coursework is primarily mathematical and conducted in English by Hungarian professors whose primary positions are at Eötvös Loránd University or the Alfréd Rényi Institute of Mathematics of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. Originally started by László Lovász, László Babai, Vera Sós, and Pál Erdős, the first semester was conducted in Spring 1985. The North- American part of the program is currently run by Tina Garrett out of St. Olaf College in Northfield, MN. She is supported by Kendra Killpatrick and Eileen Shimota. The former North American Directors were Paul D. Humke (1988–2011) and Tom Trotter. The Hungarian director is Dezső Miklós. The first Hungarian director was Gábor J. Székely (1985–1995).
 W
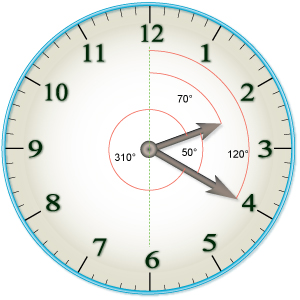
WClock angle problems are a type of mathematical problem which involve finding the angle between the hands of an analog clock.
 W
WCore-Plus Mathematics is a high school mathematics program consisting of a four-year series of print and digital student textbooks and supporting materials for teachers, developed by the Core-Plus Mathematics Project (CPMP) at Western Michigan University, with funding from the National Science Foundation. Development of the program started in 1992. The first edition, entitled Contemporary Mathematics in Context: A Unified Approach, was completed in 1995. The third edition, entitled Core-Plus Mathematics: Contemporary Mathematics in Context, was published by McGraw-Hill Education in 2015.
 W
WElementary arithmetic is the simplified portion of arithmetic that includes the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It should not be confused with elementary function arithmetic.
 W
WEmbodied design grows from the idea of embodied cognition: that the actions of the body can play a role in the development of thought and ideas. Embodied design brings mathematics to life; studying the effects of the body on the mind, researchers learn how to design objects and activities for learning. Embodiment is an aspect of pattern recognition in all fields of human endeavor.
 W
WFemale education in STEM includes child and adult female represented in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). In 2017, 33% of students in STEM fields were women.
 W
WFraction Bars are a type of mathematical manipulative, developed to meet educational needs of real teachers by Albert B. Bennett, Jr. They provide visual illustrations of mathematical operations with fractions to gain better understanding of these operations.
 W
WThe freshman's dream is a name sometimes given to the erroneous equation (x + y)n = xn + yn, where n is a real number (usually a positive integer greater than 1). Beginning students commonly make this error in computing the power of a sum of real numbers, falsely assuming powers distribute over sums. When n = 2, it is easy to see why this is incorrect: (x + y)2 can be correctly computed as x2 + 2xy + y2 using distributivity (commonly known as the FOIL method). For larger positive integer values of n, the correct result is given by the binomial theorem.
 W
WFSU Young Scholars Program (YSP) is a six-week residential science and mathematics summer program for 40 high school students from Florida, USA, with significant potential for careers in the fields of science, technology, engineering and mathematics. The program was developed in 1983 and is currently administered by the Office of Science Teaching Activities in the College of Arts and Sciences at Florida State University (FSU).
 W
WThe Guidelines for Assessment and Instruction in Statistics Education (GAISE) are a framework for statistics education in grades Pre-K–12 published by the American Statistical Association (ASA) in 2007. The foundations for this framework are the Principles and Standards for School Mathematics published by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2000. A second report focused on statistics education at the collegiate level, the GAISE College Report, was published in 2005. Both reports were endorsed by the ASA. Several grants awarded by the National Science Foundation explicitly reference the GAISE documents as influencing or guiding the projects, and several popular introductory statistics textbooks have cited the GAISE documents as informing their approach.
 W
WResearchers have suggested a link between handedness and ability with mathematics. This link has been proposed by Geschwind, Galaburda, Annett, and Kilshaw. The suggested link is that a brain without extreme bias towards locating language in the left hemisphere would have an advantage in mathematical ability.
 W
WHow to Solve It (1945) is a small volume by mathematician George Pólya describing methods of problem solving.
 W
WIMAGINARY is an open platform dedicated to the communication of modern mathematics. With over 100 different exhibits, software, films, texts, and images for free use and editing, IMAGINARY connects users from over 50 countries. Science museums such as the German Museum in Munich or the Museum of Mathematics (MoMath) in New York have some of the exhibits in their collections. IMAGINARY also acted as an independent organizer of exhibitions.
 W
WiNERDE is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit social enterprise seeking to provide underprivileged students in numerous African countries access to STEM education, in addition to encouraging the growth of STEAM education, adding arts to the foundational curriculum. Founded in 2014 by Mohamed T. Kante and Rakibou Ouro-Djobo, iNERDE has been dedicated to creating partnerships with worldwide leaders of STEM organizations to not only reach African students, but also to encourage engagement of employees of technology enterprises in nonprofit and charitable causes. Kante and iNERDE have been featured in Fortune magazine as well as in the Boston Globe for their 2014 Colonie de Vacances education camp. Although their first camp focused on 4th and 5th graders, they have since expanded their reach to provide students from the 4th to 12th grades with appropriate education. iNERDE partners directly with local schools in Africa, providing them with professional teachers, curricula, and computers, in addition to other equipment integral to an elementary and middle school STEM education.
 W
WInnumeracy: Mathematical Illiteracy and its Consequences is a 1988 book by mathematician John Allen Paulos about "innumeracy", a term he embraced to describe the mathematical equivalent of illiteracy: incompetence with numbers rather than words. Innumeracy is a problem with many otherwise educated and knowledgeable people. While many people would be ashamed to admit they are illiterate, there is very little shame in saying "I'm a people person, not a numbers person", or "I always hated math".
 W
WA Lénárt sphere is a teaching and educational research model for spherical geometry. The Lénárt sphere is a modern replacement of a "spherical blackboard". It can be used for visualizing spherical polygons showing the relationships between the sides and the angles.
 W
WThe Mars Generation is an American non-governmental nonprofit organization involved in public outreach and advocating for human space exploration and science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education.
 W
WMathematica: A World of Numbers… and Beyond is a kinetic and static exhibition of mathematical concepts designed by Charles and Ray Eames, originally debuted at the California Museum of Science and Industry in 1961. Duplicates have since been made, and they have been moved to other institutions.
 W
WMathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences is a 1966 textbook by mathematician Mary L. Boas intended to develop skills in mathematical problem solving needed for junior to senior-graduate courses in engineering, physics, and chemistry. The book provides a comprehensive survey of analytic techniques and provides careful statements of important theorems while omitting most detailed proofs. Each section contains a large number of problems, with selected answers. Numerical computational approaches using computers are outside the scope of the book.
 W
WA Mathematician's Lament, often referred to informally as Lockhart's Lament, is a short book on mathematics education by Paul Lockhart, originally a research mathematician at Brown University and U.C. Santa Cruz, and subsequently a math teacher at Saint Ann's School in Brooklyn, New York City for many years. This strongly worded opinion piece is organized into two parts. The first part, "Lamentation", criticizes the way mathematics is typically taught in American schools and argues for an aesthetic, intuitive, and problem-oriented approach to teaching. The second part, "Exultation", gives specific examples of how to teach mathematics as an art.
 W
WMathnasium is an American education brand and supplemental math learning franchise consisting of over 1,000 learning centers in North America, South America, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia that provides instruction to students in pre-kindergarten through high school. The curriculum employs the Mathnasium Method™, a proprietary system that was developed by a team of education experts with co-founder Lawrence Martinek.
 W
WMathPath is a mathematics enrichment summer program for students ages 11–14. It is four weeks long, and moves to a different location each year. MathPath is visited by mathematicians such as John H. Conway and Francis Su. It was probably the original, and is still one of the few, international residential high-end summer camps exclusively for mathematics and exclusively for students of middle school age.
 W
WIn mathematics, a multiplication table is a mathematical table used to define a multiplication operation for an algebraic system.
 W
WFounded in 1920, The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) is the world's largest mathematics education organization.
 W
WThe National Museum of Mathematics or MoMath is a museum dedicated to mathematics in Manhattan, New York City. It opened on December 15, 2012. It is located at 11 East 26th Street between Fifth and Madison Avenues, across from Madison Square Park in the NoMad neighborhood. It is the only museum dedicated to mathematics in North America, and features over thirty interactive exhibits. The mission of the museum is to "enhance public understanding and perception of mathematics". The museum is known for a special tricycle with square wheels, which operates smoothly on a catenary surface.
 W
WNew Mathematics or New Math was a dramatic change in the way mathematics was taught in American grade schools, and to a lesser extent in European countries and elsewhere, during the 1950s–1970s. Curriculum topics and teaching practices were changed in the U.S. shortly after the Sputnik crisis. The goal was to boost students' science education and mathematical skill to meet the technological threat of Soviet engineers, reputedly highly skilled mathematicians.
 W
WThe Number Devil: A Mathematical Adventure is a book for children and young adults that explores mathematics. It was originally written in 1997 in German by Hans Magnus Enzensberger and illustrated by Rotraut Susanne Berner. The book follows a young boy named Robert, who is taught mathematics by a sly "number devil" called Teplotaxl over the course of twelve dreams.
 W
WNumeracy is the ability to reason and to apply simple numerical concepts. Basic numeracy skills consist of comprehending fundamental arithmetical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. For example, if one can understand simple mathematical equations such as 2 + 2 = 4, then one would be considered to possess at least basic numeric knowledge. Substantial aspects of numeracy also include number sense, operation sense, computation, measurement, geometry, probability and statistics. A numerically literate person can manage and respond to the mathematical demands of life.
 W
WOut in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, Inc., abbreviated oSTEM, is a 501(c)(3) non-profit professional society dedicated to LGBTQ+ individuals within the science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) community.
 W
WPart III of the Mathematical Tripos is a one-year Masters-level taught course in mathematics offered at the Faculty of Mathematics, University of Cambridge. It is regarded as one of the hardest and most intensive mathematics courses in the world and is taken by approximately 200 students each year. Roughly one third of the students take the course as a fourth year of mathematical study at Cambridge, whilst the remaining two thirds take the course as a one-year course.
 W
WPattern Blocks are a set of mathematical manipulatives developed in the 1960s. The six shapes are both a play resource and a tool for learning in mathematics, which serve to develop spatial reasoning skills that are fundamental to the learning of mathematics. Among other things, they allow children to see how shapes can be composed and decomposed into other shapes, and introduce children to ideas of tilings. Pattern blocks sets are multiple copies of just six shapes:Equilateral triangle (Green) 60° rhombus (Blue) that can be matched with two of the green triangles 30° Narrow rhombus (Beige) with the same side-length as the green triangle Trapezoid (Red) that can be matched with three of the green triangles Regular Hexagon (Yellow) that can be matched with six of the green triangles Square (Orange) with the same side-length as the green triangle
 W
WThe relationship between mathematics and physics has been a subject of study of philosophers, mathematicians and physicists since Antiquity, and more recently also by historians and educators. Generally considered a relationship of great intimacy, mathematics has been described as "an essential tool for physics" and physics has been described as "a rich source of inspiration and insight in mathematics".
 W
WPresidential Physics and Mathematics Lyceum No. 239, is a public high school in Saint Petersburg, Russia that specializes in mathematics and physics. The school opened in 1918 and it became a specialized city school in 1961. The school is noted for its strong academic programs. It is the alma mater of numerous winners of International Mathematical Olympiads and it has produced many notable alumni. The lyceum has been named the best school in Russia in 2015, 2016, and 2017.
 W
WSanta Cruz High School is a comprehensive public school in Santa Cruz, California which originally opened in 1897 and now serves an enrollment of about 1,040 students in grades nine through twelve. It is part of the Santa Cruz City School District. The school's mascot is a cardinal.
 W
WIn scientific disciplines, a toy problem or a puzzlelike problem is a problem that is not of immediate scientific interest, yet is used as an expository device to illustrate a trait that may be shared by other, more complicated, instances of the problem, or as a way to explain a particular, more general, problem solving technique. A toy problem is useful to test and demonstrate methodologies. Researchers can use toy problems to compare the performance of different algorithms. They are also good for game designing.
 W
WIn mathematics, transformation geometry is the name of a mathematical and pedagogic take on the study of geometry by focusing on groups of geometric transformations, and properties that are invariant under them. It is opposed to the classical synthetic geometry approach of Euclidean geometry, that focuses on proving theorems.
 W
WThe Wolfram Demonstrations Project is an organized, open-source collection of small interactive programs called Demonstrations, which are meant to visually and interactively represent ideas from a range of fields. It is hosted by Wolfram Research, whose stated goal is to bring computational exploration to the widest possible audience. At its launch, it contained 1300 demonstrations but has grown to over 10,000. The site won a Parents' Choice Award in 2008.
 W
WConrad Wolfram is a British technologist and businessman known for his work in information technology and mathematics education reform. In June 2020, Conrad released his first book, The Math(s) Fix: An Education Blueprint for the AI Age.
 W
W