 W
WThis is a list of writing systems, classified according to some common distinguishing features.
 W
WA writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form of information storage and transfer. Writing systems require shared understanding between writers and readers of the meaning behind the sets of characters that make up a script. Writing is usually recorded onto a durable medium, such as paper or electronic storage, although non-durable methods may also be used, such as writing on a computer display, on a blackboard, in sand, or by skywriting. Reading a text can be accomplished purely in the mind as an internal process, or expressed orally.
 W
WAsemic writing is a wordless open semantic form of writing. The word asemic means "having no specific semantic content", or "without the smallest unit of meaning". With the non-specificity of asemic writing there comes a vacuum of meaning, which is left for the reader to fill in and interpret. All of this is similar to the way one would deduce meaning from an abstract work of art. Where asemic writing distinguishes itself among traditions of abstract art is in the asemic author's use of gestural constraint, and the retention of physical characteristics of writing such as lines and symbols. Asemic writing is a hybrid art form that fuses text and image into a unity, and then sets it free to arbitrary subjective interpretations. It may be compared to free writing or writing for its own sake, instead of writing to produce verbal context. The open nature of asemic works allows for meaning to occur across linguistic understanding; an asemic text may be "read" in a similar fashion regardless of the reader's natural language. Multiple meanings for the same symbolism are another possibility for an asemic work, that is, asemic writing can be polysemantic or have zero meaning, infinite meanings, or its meaning can evolve over time. Asemic works leave for the reader to decide how to translate and explore an asemic text; in this sense, the reader becomes co-creator of the asemic work.
 W
WBasahan script, also known as Guhit, is one of the ancient scripts of the Philippines used by the early native Bicolanos before the Spanish conquest of the Philippines.
 W
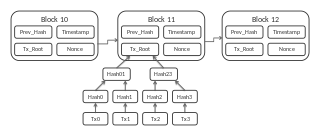
WA blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of its data. This is because once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks.
 W
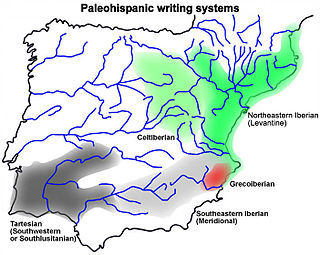
WThe Celtiberian script is a Paleohispanic script that was the main writing system of the Celtiberian language, an extinct Continental Celtic language, which was also occasionally written using the Latin alphabet. This script is a direct adaptation of the northeastern Iberian script, the most frequently used of the Iberian scripts.
 W
WChinese bronze inscriptions, also commonly referred to as bronze script or bronzeware script, are writing in a variety of Chinese scripts on ritual bronzes such as zhōng bells and dǐng tripodal cauldrons from the Shang dynasty to the Zhou dynasty and even later. Early bronze inscriptions were almost always cast, while later inscriptions were often engraved after the bronze was cast. The bronze inscriptions are one of the earliest scripts in the Chinese family of scripts, preceded by the oracle bone script.
 W
WThe Chinese family of scripts are writing systems descended from the Chinese Oracle Bone Script and used for a variety of languages in East Asia. They include logosyllabic systems such as the Chinese script itself, and adaptations to other languages, such as Kanji (Japanese), Hanja (Korean), Chữ nôm (Vietnamese) and Sawndip (Zhuang). More divergent are Tangut, Khitan large script, and its offspring Jurchen, as well as the Yi script and possibly Korean Hangul, which were inspired by Chinese although not directly descended from it. The partially deciphered Khitan small script may be another. In addition, various phonetic scripts descend from Chinese characters, of which the best known are the various kana syllabaries, the zhuyin semi-syllabary, nüshu, and some influence on hangul.
 W
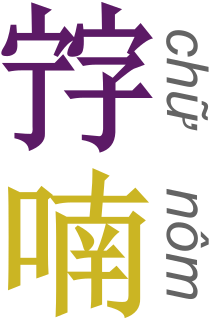
WChữ Nôm is a logographic writing system formerly used to write the Vietnamese language. It uses borrowed Chinese characters to represent Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary and some native Vietnamese words, while new characters were created on the Chinese model to represent other words.
 W
WThe clerical script, also formerly chancery script, is an archaic style of Chinese calligraphy which evolved from the Warring States period to the Qin dynasty, was dominant in the Han dynasty, and remained in use through the Wei-Jin periods. Due to its high legibility to modern readers, it is still used for artistic flavor in a variety of functional applications such as headlines, signboards, and advertisements. This legibility stems from the highly rectilinear structure, a feature shared with modern regular script (kaishu). In structure and rectilinearity, it is generally similar to the modern script; however, in contrast with the tall to square modern script, it tends to be square to wide, and often has a pronounced, wavelike flaring of isolated major strokes, especially a dominant rightward or downward diagonal stroke. Some structures are also archaic.
 W
WConjunct consonants are a type of letters, used for example in Brahmi or Brahmi derived modern scripts such as Balinese, Bengali, Devanagari, Gujarati, etc to write consonant clusters such as or. Although most of the time, letters are formed by using a simple consonant with the inherent value vowel "a", or by combining a consonant with an vowel in the form of a diacritic, the usage of conjunct consonant permits the creation of more sophisticated sounds. Conjuncts are often used with loan words. Native words typically use the basic consonant and native speakers know to suppress the vowel.
 W
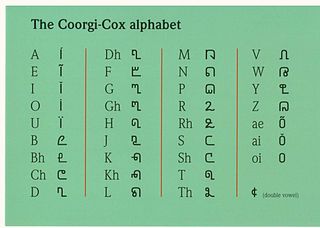
WThe Coorgi–Cox alphabet is an abugida developed by the linguist Gregg M. Cox that is used by a number of individuals within Kodagu district of India to write the endangered Dravidian language of Kodava, also known sometimes as Coorgi.
 W
WCursive script, often mistranslated as grass script, is a script style used in Chinese and East Asian calligraphy. Cursive script is faster to write than other styles, but difficult to read for those unfamiliar with it. It functions primarily as a kind of shorthand script or calligraphic style. People who can read standard or printed forms of Chinese or related scripts may not be able to read this script.
 W
WIn sociolinguistics, digraphia refers to the use of more than one writing system for the same language. Synchronic digraphia is the coexistence of two or more writing systems for the same language, while diachronic digraphia is the replacement of one writing system by another for a particular language.
 W
WThe Elifba alphabet was the main writing system for the Albanian language during the time of the Ottoman Empire from 14th century to 1911. This Albanian variant of the Abjad Ottoman-Persian script was used to write the Albanian language. The last version of the Elifbaja shqip was invented by the leader of the Albanian National Awakening, Muslim scholar Rexhep Voka (1847-1917).
 W
WThe Ersu Shaba script, also called Ersu Shaba Picture Writing and known in Ersu as, is the writing system used in texts of the indigenous religion of the Ersu people, which is rendered in Chinese as Shābā (沙巴). These scriptures are recited in divination and when treating the sick. The script is used for non-scriptural texts as well, such as astrological almanacs, but predominantly ones which concern religion. Only Shaba priests are literate in the script.
 W
WThe Gjirokastër alphabet also known as Veso Bey alphabet is one of the original Albanian language alphabets of the 19th century. It is named after the town of Gjirokastër in South Albania where it was first encountered by the scholar Johann Georg von Hahn, also after Veso Bey, a rich local bey from the influential Alizoti family who provided it to Hahn. Hahn published in 1854 in his "Albanesische Studien", in Jena.
 W
WGreek minuscule was a Greek writing style which was developed as a book hand in Byzantine manuscripts during the 9th and 10th centuries. It replaced the earlier style of uncial writing, from which it differed in using smaller, more rounded and more connected letter forms, and in using many ligatures. Many of these forms had previously developed as parts of more informal cursive writing. The basic letter shapes used in the minuscule script are the ancestors of modern lower case Greek letters.
 W
WDuring ancient times, the ancestors of the Vietnamese were considered to have been Proto-Austroasiatic speaking people, possibly traced to the ancient Dong Son culture before Chinese rule. Modern linguists describe Vietnamese as having lost many Proto-Austroasiatic phonological and morphological features that the original Vietnamese language had, and is especially noted in the linguistic separation of Vietnamese and Muong around a thousand years ago. From 111 BC up to the 20th century, Vietnamese literature was written in Traditional Chinese, using Chữ Hán and chữ Nôm.
 W
WHieratic is the name given to a cursive writing system used for Ancient Egyptian and the principal script used to write that language from its development in the third millennium BC until the rise of Demotic in the mid-first millennium BC. It was primarily written in ink with a reed pen on papyrus.
 W
WKaramanlı Turkish is both a form of written Turkish and a dialect of Turkish spoken by the Karamanlides, a community of Turkish-speaking Orthodox Christians in Ottoman Turkey. The official Ottoman Turkish was written in the Arabic script, but the Karamanlides used the Greek alphabet to write their form of Turkish. Karamanlı Turkish had its own literary tradition and produced numerous published works in print during the 19th century, some of them published by Evangelinos Misailidis by the Anatoli or Misailidis publishing house.
 W
WThere are two scripts in Southeast Asia called Khom script. This article describes the obscure script from Laos that Sidwell (2008) and Jacq (2001) have described under the name "Khom script".
 W
WLitema is a form of Sesotho mural art composed of decorative and symbolic geometric patterns, commonly associated with Sesotho tradition today practised in Lesotho and neighbouring areas of South Africa. Basotho women generate litema on the outer walls and inside of homesteads by means of engraving, painting, relief mouldings and/or mosaic. Typically the geometric patterns are combed or scratched into the wet top layer of fresh clay and dung plaster of the wall, and later painted with earth ochers or, in contemporary times, manufactured paint. Patterns most often mimic ploughed fields through a combed texture, or the patterns refer to plant life, and more occasionally to other aspects of the natural world, such as referring to clan totem animal. Litema are transient; they may desiccate and crumble or be washed away by heavy rain. It is common for women of an entire village to apply litema on such special occasions as a wedding or a religious ceremony.
 W
WThe Lycian alphabet was used to write the Lycian language of the Asia Minor region of Lycia. It was an extension of the Greek alphabet, with half a dozen additional letters for sounds not found in Greek. It was largely similar to the Lydian and the Phrygian alphabets.
 W
WLydian script was used to write the Lydian language. Like other scripts of Anatolia in the Iron Age, the Lydian alphabet is related to the East Greek alphabet, but it has unique features.
 W
WThe Naxi language of southwestern China may be written in the syllabic geba script. There is also a Naxi tradition of pictographic symbols called dongba; this may sometimes be glossed with geba for clarification, since a dongba text may be intelligible only to its author.
 W
WA numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner.
 W
WNyctography is a form of substitution cipher writing created by Lewis Carroll in 1891.
 W
WOkinawan, spoken in Okinawa Island, was once the official language of the Ryukyu Kingdom. At the time, documents were written in kanji and hiragana, derived from Japan.
 W
WPahawh Hmong, known also as Ntawv Pahawh, Ntawv Keeb, Ntawv Caub Fab, Ntawv Soob Lwj) is an indigenous semi-syllabic script, invented in 1959 by Shong Lue Yang, to write two Hmong languages, Hmong Daw (Hmoob Dawb White Miao) and Hmong Njua AKA Hmong Leng (Moob Leeg Green Miao).
 W
WThe Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script. Most of them are unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic, despite having supposedly developed, in part, from the Phoenician alphabet.
 W
WA pasigraphy is a writing system where each written symbol represents a concept.
 W
WPazend or Pazand is one of the writing systems used for the Middle Persian language. It was based on the Avestan alphabet, a phonetic alphabet originally used to write Avestan, the language of the Avesta, the primary sacred texts of Zoroastrianism.
 W
WReading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of letters, symbols, etc., especially by sight or touch.
 W
WRegular script, also called 正楷, 真書 (zhēnshū), 楷體 (kǎitǐ) and 正書 (zhèngshū), is the newest of the Chinese script styles. It is the most common style in modern writings and third most common in publications.
 W
WScriptio continua, also known as scriptura continua or scripta continua, is a style of writing without spaces, or other marks between the words or sentences. The form also lacks punctuation, diacritics, or distinguished letter case. In the West, the oldest Greek and Latin inscriptions used word dividers to separate words in sentences; however, Classical Greek and late Classical Latin both employed scriptio continua as the norm.
 W
WSeal script is an ancient style of writing Chinese characters that was common throughout the latter half of the 1st millennium BC. It evolved organically out of the Zhou dynasty bronze script. The Qin variant of seal script eventually became the standard, and was adopted as the formal script for all of China during the Qin dynasty. It was still widely used for decorative engraving and seals in the Han dynasty. The literal translation of the Chinese name for seal script, 篆書, is decorative engraving script, a name coined during the Han dynasty, which reflects the then-reduced role of the script for the writing of ceremonial inscriptions.
 W
WSemi-cursive script is a semi-cursive style of writing Chinese characters. Because it is not as abbreviated as cursive script, most people who can read regular script can read semi-cursive. It is useful when one wants to write quickly and is also a form of calligraphy.
 W
WThe southeastern Iberian script, also known as Meridional Iberian, was one of the means of written expression of the Iberian language, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet. About the relation between northeastern Iberian and southeastern Iberian scripts, it is necessary to point out that they are two different scripts with different values for the same signs; however it is clear that they had a common origin and the most accepted hypothesis is that northeastern Iberian script derives from southeastern Iberian script. In fact, the southeastern Iberian script is very similar, both considering the shape of the signs or their values, to the Southwestern script used to represent an unknown language usually named Tartessian. The main difference is that southeastern Iberian script does not show the vocalic redundancy of the syllabic signs. Unlike the northeastern Iberian script the decipherment of the southeastern Iberian script is not yet complete, because there are a significant number of signs on which scholars have not yet reached a consensus. Although it is believed that the southeastern Iberian script does not show any system to differentiate between voiced and unvoiced occlusives, unlike the northeastern Iberian script, a recent paper defends the existence of a dual system also in the southeastern Iberian script.
 W
WA tally stick was an ancient memory aid device used to record and document numbers, quantities, or even messages. Tally sticks first appear as animal bones carved with notches during the Upper Palaeolithic; a notable example is the Ishango Bone. Historical reference is made by Pliny the Elder about the best wood to use for tallies, and by Marco Polo (1254–1324) who mentions the use of the tally in China. Tallies have been used for numerous purposes such as messaging and scheduling, and especially in financial and legal transactions, to the point of being currency.
 W
WThe Telugu-Kannada alphabet is a writing system used in southern India. Despite, some differences, the scripts used for the Telugu and Kannada languages remain quite similar.
 W
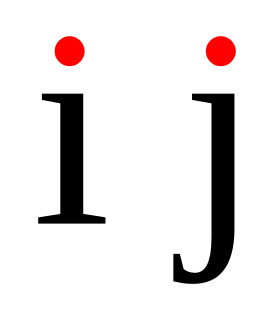
WA tittle or superscript dot is a small distinguishing mark, such as a diacritic in the form of a dot on a lowercase i or j. The tittle is an integral part of the glyph of i and j, but diacritic dots can appear over other letters in various languages. In most languages, the tittle of i or j is omitted when a diacritic is placed in the tittle's usual position, but not when the diacritic appears elsewhere.
 W
WThe Tocharian script, also known as Central Asian slanting Gupta script or North Turkestan Brāhmī, is an abugida which uses a system of diacritical marks to associate vowels with consonant symbols. Part of the Brahmic scripts, it is a version of the Indian Brahmi script. It is used to write the Central Asian Indo-European Tocharian languages, mostly from the 8th century that were written on palm leaves, wooden tablets and Chinese paper, preserved by the extremely dry climate of the Tarim Basin. Samples of the language have been discovered at sites in Kucha and Karasahr, including many mural inscriptions. Mistakenly identifying the speakers of this language with the Tokharoi people of Tokharistan, early authors called these languages "Tocharian". This naming has remained, although the names Agnean and Kuchean have been proposed as a replacement.
 W
WVellara script or Vellara alphabet is one of the original Albanian alphabets, encountered for the first time in the early 19th century. It is named after the Greek doctor, lyricist and writer Ioannis Vilaras, the author of a manuscript where this alphabet is documented for the first and so far the only time.
 W
WVisible Language is an American journal presenting visual communication research. Founded in 1967 as The Journal of Typographical Research by Merald Wrolstad, occasional Visible Language issues are co-edited with a guest editor-author.
 W
WThere are various non-Latin-based writing systems of Southeast Asia. The writing systems below are listed by language family.