 W
WA clock is a device used to measure, verify, keep, and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units: the day, the lunar month, and the year. Devices operating on several physical processes have been used over the millennia.
 W
WThe Allan variance (AVAR), also known as two-sample variance, is a measure of frequency stability in clocks, oscillators and amplifiers. It is named after David W. Allan and expressed mathematically as . The Allan deviation (ADEV), also known as sigma-tau, is the square root of the Allan variance, .
 W
WA candle clock is a thin candle with consistently spaced marking that when burned, indicate the passage of periods of time. While no longer used today, candle clocks provided an effective way to tell time indoors, at night, or on a cloudy day. A candle clock could be easily transformed into a timer by sticking a heavy nail into the candle at the mark indicating the desired interval. When the wax surrounding the nail melts, the nail clatters onto a plate below.
 W
WA chemical clock is a complex mixture of reacting chemical compounds in which the onset of an observable property occurs after a predictable induction time. In cases where one of the reagents has a visible color, crossing a concentration threshold can lead to an abrupt color change after a reproducible time lapse.
 W
WA chronometer is a specific type of mechanical timepiece. In Switzerland, only timepieces certified by the Contrôle Officiel Suisse des Chronomètres (COSC) may use the word certified chronometer or officially certified chronometer on them. Outside Switzerland, equivalent bodies, such as the Japan Chronometer Inspection Institute, have in the past certified timepieces to the same internationally recognised standards, although use of the term has not always been strictly controlled.
 W
WThe Cifra 3 [ˈtʃifra treː] is a digital flip clock manufactured by Solari di Udine, S.p.A., Italy designed by Italian architect Gino Valle (1923–2003) in 1965, with significant contribution from John Myer, a Belgian inventor. The Cifra 3 is widely considered a masterpiece of industrial design, using a split-flap display to display hours and minutes. The clock won the prestigious Compasso d'Oro prize for design and is on permanent display in the "Humble Masterpieces" exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art in New York and holds a place in the permanent collection of the Science Museum in London.
 W
WThe Climate Clock is a graphic to demonstrate how quickly the planet is approaching 1.5℃ of global warming, given current emissions trends. It also shows the amount of CO2 already emitted, and the global warming to date.
 W
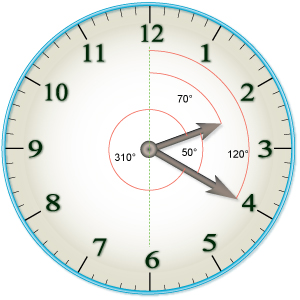
WClock angle problems are a type of mathematical problem which involve finding the angle between the hands of an analog clock.
 W
WA clock network or clock system is a set of synchronized clocks designed to always show exactly the same time by communicating with each other. Clock networks usually consist of a central master clock kept in sync with an official time source, and one or more slave clocks which receive and display the time from the master.
 W
WA clock position, or clock bearing, is the direction of an object observed from a vehicle, typically a vessel or an aircraft, relative to the orientation of the vehicle to the observer. The vehicle must be considered to have a front, a back, a left side and a right side. These quarters may have specialized names, such as bow and stern for a vessel, or nose and tail for an aircraft. The observer then measures or observes the angle made by the intersection of the line of sight to the longitudinal axis, the dimension of length, of the vessel, using the clock analogy.
 W
WA clockkeeper, sometimes seen as clock keeper, refers to a form of employment seen prevalently during Middle Age Europe involving the tracking of time and the maintaining of clocks and other timekeeping devices. However, the practice and its appearance throughout history fluctuated in centuries following the Middle Ages, and the necessity of an attendant to clockkeep remained long after the invention of the mechanical clock.
 W
WA computus clock is a clock equipped with a mechanism that automatically calculates and displays, or helps determine, the date of Easter. A computus watch carries out the same function.
 W
WThe conservation and restoration of clocks refers to the care given to the physical and functional aspects of time measuring devices featuring “moving hands on a dial face” exclusive of watches. Care for clocks constitutes regulating the external environment, cleaning, winding, lubrication, pest-management, and repairing or replacing mechanical and aesthetic components to preserve or achieve the desired state as specified by the owner. Clocks are typically composed of multiple types of materials such as wood, metal, paint, plastic, etc., which have unique behaviors and environmental interactions, making treatment options complex. The materials used and the complexity of clockwork warrant having a Horological Conservator complete the work.
 W
WMouse Trap is a board game first published by Ideal in 1963 for two to four players. It is one of the first mass-produced three-dimensional board games. Over the course of the game, players at first cooperate to build a working Rube Goldberg-like mouse trap. Once the mouse trap has been built, players turn against each other, attempting to trap opponents' mouse-shaped game pieces.
 W
WThe cuckoo clock, more than any other kind of timepiece, has often featured in literature, music, cinema, television, etc., in the Western culture, as a metaphor or allegory of innocence, childhood, old age, past, fun, mental disorder, etc. It has apparently been viewed more as a symbol or a toy -a folksy musical apparatus with animated figures- fascinating and a bit mysterious rather than as a serious timekeeper.
 W
WA dipleidoscope is an instrument used to determine true noon, its name comes from the Greek for double image viewer. It consists of a small telescope and a prism that creates a double image of the sun. When the two images overlap, it is local true noon. The instrument is capable of determining true noon to within ten seconds.
 W
W"The East Is Red" is a Chinese revolutionary song that was the de facto national anthem of the People's Republic of China during the Cultural Revolution in the 1960s. The lyrics of the song were attributed to Li Youyuan (李有源), a farmer from Shaanbei, and the melody was derived from a local peasant love song from the Loess Plateau entitled "Bai Ma Diao" 《白马调》, also known as "Zhima You" 《芝麻油》, which was widely circulated in the area around Yan'an in the 1930s. He allegedly got his inspiration upon seeing the rising sun in the morning of a sunny day.
 W
WAn equation clock is a mechanical clock which includes a mechanism that simulates the equation of time, so that the user can read or calculate solar time, as would be shown by a sundial. The first accurate clocks, controlled by pendulums, were patented by Christiaan Huyghens in 1657. For the next few decades, people were still accustomed to using sundials, and wanted to be able to use clocks to find solar time. Equation clocks were invented to fill this need.
 W
WA flyback chronograph is a complication watch, in which the user can use the reset function without the need to first stop the chronograph. In regular chronographs, the user must stop, reset, and restart the chronograph in order to time an event after the chronograph has started.
 W
WGeochron, Inc. is an American company founded in 1965 by James Kilburg, an inventor from Luxembourg. It is also the name of their flagship product, the Geochron Global Time Indicator. The Geochron was the first world clock to display day and night on a world map, showing the familiar "bell curve" of light and darkness. The Geochron employs an intricate analog clockwork mechanism for its display, that shows the month, date, day of the week, hours and minutes, the areas of the world currently experiencing day and night, and the meridian passage of the sun. The main display is dominated by a world map, with time zones prominently indicated. At the top of the map are arrows corresponding to each time zone. As each day progresses, the map is scrolled from left to right by gear mechanisms, and the arrows for each time zone shift their positions relative to a stationary band fixed at the top that has a horizontal series of numbers representing hours. The viewer may read the time by seeing what number his time zone's arrow is currently pointing to. The map is backlit, and a mechanism behind the map defines well-lit and shaded areas that are also stationary relative to the movement of the map. In this way, as time progresses, different areas are shown to be experiencing daytime and night. The center of the lit area lines up with the 12 noon on the stationary time strip. There is also a day-and-month readout below the map, and a minutes readout above.
 W
WIn physics, the gravitomagnetic clock effect is a deviation from Kepler's third law that, according to the weak-field and slow-motion approximation of general relativity, will be suffered by a particle in orbit around a (slowly) spinning body, such as a typical planet or star.
 W
WA pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is a harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates. From its invention in 1656 by Christiaan Huygens, inspired by Galileo Galilei, until the 1930s, the pendulum clock was the world's most precise timekeeper, accounting for its widespread use. Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, pendulum clocks in homes, factories, offices, and railroad stations served as primary time standards for scheduling daily life, work shifts, and public transportation. Their greater accuracy allowed for the faster pace of life which was necessary for the Industrial Revolution. The home pendulum clock was replaced by less-expensive, synchronous, electric clocks in the 1930s and '40s. Pendulum clocks are now kept mostly for their decorative and antique value.
 W
WThe incense clock is an Indian timekeeping device that was popularised by China during the Song Dynasty (960-1279) and spread to neighboring East Asian countries such as Japan and Korea. The clocks' bodies are effectively specialized censers that hold incense sticks or powdered incense that have been manufactured and calibrated to a known rate of combustion, used to measure minutes, hours, or days. The clock may also contain bells and gongs which act as strikers. Although the water clock and astronomical clock were known in China, incense clocks were commonly used at homes and temples in dynastic times.
 W
WA marine chronometer is a precision timepiece that is carried on a ship and employed in the determination of the ship's position by celestial navigation. It is used to determine longitude by comparing Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and the time at the current location found from observations of celestial bodies. When first developed in the 18th century, it was a major technical achievement, as accurate knowledge of the time over a long sea voyage is necessary for navigation, lacking electronic or communications aids. The first true chronometer was the life work of one man, John Harrison, spanning 31 years of persistent experimentation and testing that revolutionized naval navigation and enabling the Age of Discovery and Colonialism to accelerate.
 W
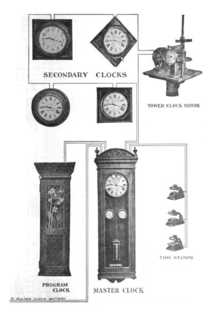
WA master clock is a precision clock that provides timing signals to synchronise slave clocks as part of a clock network. Networks of electric clocks connected by wires to a precision master pendulum clock began to be used in institutions like factories, offices, and schools around 1900. Today, many radio clocks are synchronised by radio signals or Internet connections to a worldwide time system called Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is governed by master atomic clocks in many countries.
 W
WMoondials are time pieces similar to a sundial. The most basic moondial, which is identical to a sundial, is only accurate on the night of the full moon. Every night after it becomes an additional 48 minutes slow, while every night preceding the full moon it is 49 minutes fast, assuming there is even enough light to take a reading by. Thus, one week to either side of the full moon the moondial will read 5 hours and 36 minutes before or after the proper time.
 W
WOil-lamp clocks are clocks consisting of a graduated glass reservoir to hold oil - usually whale oil, which burned cleanly and evenly - supplying the fuel for a built-in lamp. As the level in the reservoir dropped, it provided a rough measure of the passage of time.
 W
WA pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is a harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates. From its invention in 1656 by Christiaan Huygens, inspired by Galileo Galilei, until the 1930s, the pendulum clock was the world's most precise timekeeper, accounting for its widespread use. Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, pendulum clocks in homes, factories, offices, and railroad stations served as primary time standards for scheduling daily life, work shifts, and public transportation. Their greater accuracy allowed for the faster pace of life which was necessary for the Industrial Revolution. The home pendulum clock was replaced by less-expensive, synchronous, electric clocks in the 1930s and '40s. Pendulum clocks are now kept mostly for their decorative and antique value.
 W
WA radio clock or radio-controlled clock (RCC), and often (incorrectly) referred to as an atomic clock is a type of quartz clock or watch that is automatically synchronized to a time code transmitted by a radio transmitter connected to a time standard such as an atomic clock. Such a clock may be synchronized to the time sent by a single transmitter, such as many national or regional time transmitters, or may use the multiple transmitters, or may use the multiple transmitters used by satellite navigation systems such as Global Positioning System. Such systems may be used to automatically set clocks or for any purpose where accurate time is needed. RC clocks may include any feature available for a clock, such as alarm function, display of ambient temperature and humidity, broadcast radio reception, etc.
 W
WA real-time clock (RTC) is an electronic device that measures the passage of time.
 W
WThe Riefler escapement is a mechanical escapement for precision pendulum clocks invented and patented by German instrument maker Sigmund Riefler in 1889. It was used in the astronomical regulator clocks made by his German firm Clemens Riefler from 1890 to 1965, which were perhaps the most accurate all-mechanical pendulum clocks made.
 W
WThe scaphe was a sundial said to have been invented by Aristarchus of Samos. There are no original works still in existence by Aristarchus, but the adjacent image is an image of what it might have looked like; only his would have been made of stone. It consisted of a hemispherical bowl which had a vertical gnomon placed inside it, with the top of the gnomon level with the edge of the bowl. Twelve gradations inscribed perpendicular to the hemisphere indicated the hour of the day.
 W
WA skeleton clock is any clock or wristwatch, though typically mechanical in nature, in which the parts that usually conceal the inner workings of the mechanism have been removed or significantly modified so as to display these inner parts.
 W
WIn telecommunication and horology, a slave clock is a clock that depends for its accuracy on another clock, a master clock. Many modern clocks are synchronized, either through the Internet or by radio time signals, to a worldwide time standard called Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) based on a network of master atomic clocks in many countries. For scientific purposes, precision clocks can be synchronized to within a few nanoseconds by dedicated satellite channels. Slave clock synchronization is usually achieved by phase-locking the slave clock signal to a signal received from the master clock. To adjust for the transit time of the signal from the master clock to the slave clock, the phase of the slave clock may be adjusted with respect to the signal from the master clock so that both clocks are in phase. Thus, the time markers of both clocks, at the output of the clocks, occur simultaneously.
 W
WA speaking clock or talking clock is a live or recorded human voice service, usually accessed by telephone, that gives the correct time. The first telephone speaking clock service was introduced in France, in association with the Paris Observatory, on 14 February 1933.
 W
WA station clock is a clock at a railway station that provides a standard indication of time to both passengers and railway staff.
 W
WThe Stoppomat is a time measure system for cyclists.
 W
WA striking clock is a clock that sounds the hours audibly on a bell or gong. In 12-hour striking, used most commonly in striking clocks today, the clock strikes once at 1:00 A.M., twice at 2:00 A.M., continuing in this way up to twelve times at 12:00 P.M., then starts again, striking once at 1:00 P.M., twice at 2:00 P.M., up to twelve times at 12:00 A.M.
 W
WA sundial is a device that tells the time of day when there is sunlight by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a flat plate and a gnomon, which casts a shadow onto the dial. As the Sun appears to move across the sky, the shadow aligns with different hour-lines, which are marked on the dial to indicate the time of day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, though a single point or nodus may be used. The gnomon casts a broad shadow; the shadow of the style shows the time. The gnomon may be a rod, wire, or elaborately decorated metal casting. The style must be parallel to the axis of the Earth's rotation for the sundial to be accurate throughout the year. The style's angle from horizontal is equal to the sundial's geographical latitude.
 W
WThe Swiss railway clock was designed in 1944 by Hans Hilfiker, a Swiss engineer and SBB employee, together with Moser-Baer, a clock manufacturer, for use by the Swiss Federal Railways as a station clock. In 1953, Hilfiker added a red second hand in the shape of the baton used by train dispatch staff.
 W
WA tide clock is a specially designed clock that keeps track of the Moon's apparent motion around the Earth. Along many coastlines, the Moon contributes the major part (67%) of the combined lunar and solar tides. The exact interval between tides is influenced by the position of the Moon and Sun relative to the Earth, as well as the specific location on Earth where the tide is being measured. Due to the Moon's orbital prograde motion, it takes a particular point on the Earth 24 hours and 50.5 minutes to rotate under the Moon, so the time between high lunar tides fluctuates between 12 and 13 hours. A tide clock is divided into two roughly 6 hour tidal periods that shows the average length of time between high and low tides in a semi-diurnal tide region, such as most areas of the Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WA time clock, sometimes known as a clock card machine or punch clock or time recorder, is a device that records start and end times for hourly employees at a place of business.
 W
WIn horology, a tourbillon is an addition to the mechanics of a watch escapement to increase accuracy. It was developed around 1795 and patented by the French-Swiss watchmaker Abraham-Louis Breguet on June 26, 1801. In a tourbillon the escapement and balance wheel are mounted in a rotating cage, in order to negate the effects of gravity when the timepiece is stuck in a certain position. By continuously rotating the entire balance wheel/escapement assembly at a slow rate, the tourbillon averages out positional errors.
 W
WClock towers are a specific type of building which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another building. Some other buildings also have clock faces on their exterior but these structures serve other main functions.
 W
WThe U.S. and World Population Clock presents the United States Census Bureau's continuously active approximations of both the population of the United States and the world's total population. The population totals are based on the latest census information and national population estimates, which are used in the algorithms that run the two clocks.
 W
WA world clock is a clock which displays the time for various cities around the world. The display can take various forms:The clock face can incorporate multiple round analogue clocks with moving hands or multiple digital clocks with numeric readouts, with each clock being labelled with the name of a major city or time zone in the world. It could also be a picture map of the world with embedded analog or digital time-displays. A moving circular map of the world, rotating inside a stationary 24-hour dial ring. Alternatively, the disc can be stationary and the ring moving. Light projection onto a map representing daytime, used in the Geochron, a brand of a particular form of world clock.
 W
W