 W
WA thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is a plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
 W
WAcrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F). ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
 W
WBoost is a trademarked polymer used by Adidas, in the form of pellets which are compressed and molded for various shoe models the company sells, especially the Ultraboost, Energy Boost and NMD lines of sneakers. The pellets consist of proprietary thermoplastic urethane (TPU) that is formed into a small pill shape. Adidas collaborated with the German chemical company BASF to develop this material. Boost in itself is not a raw material and its characteristic bounciness is obtained by processing the thermoplastic urethane. This material is claimed to be extremely comfortable on the wearer's feet.
 W
WCelluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common, celluloid's common contemporary uses are table tennis balls, musical instruments, combs, office equipment, and guitar picks.
 W
WCellulose acetate refers to any acetate ester of cellulose, usually cellulose diacetate. It was first prepared in 1865. A bioplastic, cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and as a frame material for eyeglasses; it is also used as a synthetic fiber in the manufacture of cigarette filters and playing cards. In photographic film, cellulose acetate film replaced nitrate film in the 1950s, being far less flammable and cheaper to produce.
 W
WThe Citroën Méhari is a lightweight utilitarian and recreational vehicle manufactured and marketed by Citroën over 18 years in a single generation in two-wheel (1968-1988) and four-wheel drive (1980-1983) variations — noted for its doorless ABS plastic bodywork and foldable, stowable, fabric convertible top.
 W
WCold stamping, also known as press working, is a manufacturing operation in which thermoplastics in sheet form are cold-formed using methods similar to those used in metalworking. A precut thermoplastic sheet, possibly reinforced, is softened by heating to a temperature particular to the plastic in use. The heated sheet is then shaped by stamping using a press. Fiberglass-reinforced thermoplastic sheets are formed using metal stamping presses after the sheets are preheated to about 200 °C (392 °F).
 W
WECTFE was designed to provide chemical resistance in heavy duty corrosion applications. It is a partially fluorinated polymer, semi-crystalline and can be processed in the melt. Chemically it is a copolymer of ethylene and chlorotrifluoroethylene. It is marketed under the brand name Halar ECTFE by Solvay Specialty Polymers, a subsidiary of Solvay.
 W
WElectroshapable materials are composite materials from the class of thermoplastic materials. Electroshapable materials are plastics rigid at room temperature, which can take the form of various objects or plastic elements. They can substitute for more common thermoplastic polymers such as PVC, PE, PC, EVA.
 W
WEnvironmental Stress Cracking (ESC) is one of the most common causes of unexpected brittle failure of thermoplastic polymers known at present. According to ASTM D883, stress cracking is defined as "an external or internal crack in a plastic caused by tensile stresses less than its short-term mechanical strength". This type of cracking typically involves brittle cracking, with little or no ductile drawing of the material from its adjacent failure surfaces. Environmental stress cracking may account for around 15-30% of all plastic component failures in service. This behavior is especially prevalent in glassy, amorphous thermoplastics. Amorphous polymers exhibit ESC because of their loose structure which makes it easier for the fluid to permeate into the polymer. Amorphous polymers are more prone to ESC at temperature higher than their glass transition temperature (Tg) due to the increased free volume. When Tg is approached, more fluid can permeate into the polymer chains.
 W
WEthylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) is a fluorine-based plastic. It was designed to have high corrosion resistance and strength over a wide temperature range. ETFE is a polymer and its source-based name is poly(ethene-co-tetrafluoroethene). It is also known under the brand name Tefzel. ETFE has a relatively high melting temperature, excellent chemical, electrical and high-energy radiation resistance properties. When burned, ETFE releases hydrofluoric acid.
 W
WEthylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), also known as poly (PEVA), is the copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. The weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 40%, with the remainder being ethylene. There are three different types of EVA copolymer, which differ in the vinyl acetate (VA) content and the way the materials are used.
 W
WFluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) is a copolymer of hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene. It differs from the polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) resins in that it is melt-processable using conventional injection molding and screw extrusion techniques. Fluorinated ethylene propylene was invented by DuPont and is sold under the brandname Teflon FEP. Other brandnames are Neoflon FEP from Daikin or Dyneon FEP from Dyneon/3M.
 W
WHigh-performance plastics are plastics that meet higher requirements than standard or engineering plastics. They are more expensive and used in smaller amounts.
 W
WKydex is a line of thermoplastic acrylic-polyvinyl chloride materials manufactured by Sekisui SPI. It has a wide variety of applications, including for aircraft bulkheads, firearm holsters, sheaths, and for knives.
 W
WPearloid is a plastic that is intended to resemble mother of pearl. It is commonly used in making musical instruments, especially for pickguards, electric guitars, and accordions.
 W
WPerfluoroalkoxy alkanes (PFA) are fluoropolymers. They are copolymers of tetrafluoroethylene (C2F4) and perfluoroethers (C2F3ORf, where Rf is a perfluorinated group such as trifluoromethyl (CF3)). The properties of these polymers are similar to those of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Compared to PTFE, PFA have better anti-stick properties, higher chemical resistance on expense of a lesser scratch resistance. Other than in PTFE, the alkoxy substituents allow the polymer to be melt-processed. On a molecular level, PFA have a smaller chain length and higher chain entanglement than other fluoropolymers. They also contain an oxygen atom at the branches. This results in materials that are more translucent and have improved flow, creep resistance, and thermal stability close to or exceeding PTFE. Thus, PFA are preferred when extended service is required in hostile environments involving chemical, thermal, and mechanical stress. PFA offer high melt strength, stability at high processing temperatures, excellent crack and stress resistance, a low coefficient of friction. Similarly advantaged processing properties are found in fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP), the copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and hexafluoropropylene. However FEP is ten times less capable to withstand repeated bending without fracture than PFA.
 W
WPoly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate), commonly known as PHBV, is a polyhydroxyalkanoate-type polymer. It is biodegradable, nontoxic, biocompatible plastic produced naturally by bacteria and a good alternative for many non-biodegradable synthetic polymers. It is a thermoplastic linear aliphatic polyester. It is obtained by the copolymerization of 3-hydroxybutanoic acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid. PHBV is used in speciality packaging, orthopedic devices and in controlled release of drugs. PHBV undergoes bacterial degradation in the environment.
 W
WPlastisol is a suspension of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or other polymer particles in a liquid plasticizer; it flows as a liquid and can be poured into a heated mold.
 W
WPoly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, or plexiglass, as well as by the trade names Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Astariglas, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex, among several others, is a transparent thermoplastic often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. The same material can be used as a casting resin or in inks and coatings, among many other uses.
 W
WPolyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is an organic polymer consisting of aromatic rings linked by sulfides. Synthetic fiber and textiles derived from this polymer resist chemical and thermal attack. PPS is used in filter fabric for coal boilers, papermaking felts, electrical insulation, film capacitors, specialty membranes, gaskets, and packings. PPS is the precursor to a conductive polymer of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The PPS, which is otherwise insulating, can be converted to the semiconducting form by oxidation or use of dopants.
 W
WPolyacrylonitrile (PAN), also known as polyvinyl cyanide and Creslan 61, is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (C3H3N)n. Though it is thermoplastic, it does not melt under normal conditions. It degrades before melting. It melts above 300 °C if the heating rates are 50 degrees per minute or above. Almost all PAN resins are copolymers made from mixtures of monomers with acrylonitrile as the main monomer. It is a versatile polymer used to produce large variety of products including ultra filtration membranes, hollow fibers for reverse osmosis, fibers for textiles, oxidized PAN fibers. PAN fibers are the chemical precursor of very high-quality carbon fiber. PAN is first thermally oxidized in air at 230 °C to form an oxidized PAN fiber and then carbonized above 1000 °C in inert atmosphere to make carbon fibers found in a variety of both high-tech and common daily applications such as civil and military aircraft primary and secondary structures, missiles, solid propellant rocket motors, pressure vessels, fishing rods, tennis rackets and bicycle frames. It is a component repeat unit in several important copolymers, such as styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic.
 W
WPolybutadiene [butadiene rubber BR] is a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production. Another 25% is used as an additive to improve the toughness of plastics such as polystyrene and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Polybutadiene rubber accounted for about a quarter of total global consumption of synthetic rubbers in 2012. It is also used to manufacture golf balls, various elastic objects and to coat or encapsulate electronic assemblies, offering high electrical resistivity.
 W
WPolybutylene succinate (PBS) is a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family. PBS is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester with properties that are comparable to polypropylene.
 W
WPolybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer that is used as an insulator in the electrical and electronics industries. It is a thermoplastic (semi-)crystalline polymer, and a type of polyester. PBT is resistant to solvents, shrinks very little during forming, is mechanically strong, heat-resistant up to 150 °C and can be treated with flame retardants to make it noncombustible. It was developed by Britain's Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI).
 W
WPolycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polyester with a low melting point of around 60 °C and a glass transition temperature of about −60 °C. The most common use of polycaprolactone is in the production of speciality polyurethanes. Polycaprolactones impart good resistance to water, oil, solvent and chlorine to the polyurethane produced.
 W
WPolycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code (RIC) and are identified as "Other", 7 on the RIC list. Products made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA).
 W
WPolychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE or PTFCE) is a thermoplastic chlorofluoropolymer with the molecular formula (CF2CClF)n, where n is the number of monomer units in the polymer molecule. It is similar to polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), except that it is a homopolymer of the monomer chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) instead of tetrafluoroethene. It has the lowest water vapor transmission rate of any plastic.
 W
WPolycyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate (PCT) is a thermoplastic polyester formed from the polycondensation of terephthalic acid and cyclohexanedimethanol. Its chemical structure is similar to that of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), with which it shares properties like dimensional stability and chemical resistance. PCT is also particularly resistant to high temperatures and hydrolysis. The melting point is 545 °F. Common brand names are Thermx (Ticona), Eastar (Eastman) and SkyPURA.
 W
WPolyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in the cutin of plant cuticles, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. The material is used extensively in clothing.
 W
WPolyetherketoneketone (PEKK) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic in the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family, with high heat resistance, chemical resistance and the ability to withstand high mechanical loads. PEKK's glass transition temperature (Tg) is 162°C.
 W
WPolyethylene or polythene is the most common plastic in use today. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging. As of 2017, over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market.
 W
WPolyethylene terephthalate, commonly abbreviated PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P, is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods, and thermoforming for manufacturing, and in combination with glass fibre for engineering resins.
 W
WPolyglycolide or poly(glycolic acid) (PGA), also spelled as polyglycolic acid, is a biodegradable, thermoplastic polymer and the simplest linear, aliphatic polyester. It can be prepared starting from glycolic acid by means of polycondensation or ring-opening polymerization. PGA has been known since 1954 as a tough fiber-forming polymer. Owing to its hydrolytic instability, however, its use has initially been limited. Currently polyglycolide and its copolymers are widely used as a material for the synthesis of absorbable sutures and are being evaluated in the biomedical field.
 W
WPolyhydroxyalkanoates or PHAs are polyesters produced in nature by numerous microorganisms, including through bacterial fermentation of sugars or lipids. When produced by bacteria they serve as both a source of energy and as a carbon store. More than 150 different monomers can be combined within this family to give materials with extremely different properties. These plastics are biodegradable and are used in the production of bioplastics.
 W
WPolyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a polymer belonging to the polyesters class that are of interest as bio-derived and biodegradable plastics. The poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (P3HB) form of PHB is probably the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoate, but other polymers of this class are produced by a variety of organisms: these include poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB), polyhydroxyvalerate (PHV), polyhydroxyhexanoate (PHH), polyhydroxyoctanoate (PHO) and their copolymers.
 W
WPolyimide is a polymer of imide monomers belonging to the class of high performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g. high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.
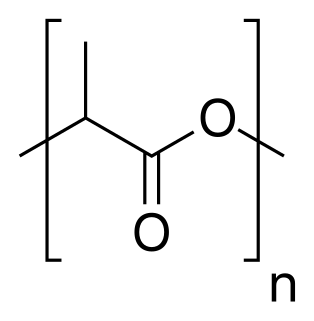 W
WPolylactic acid, or polylactide (PLA) is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula (C3H4O2)n or [–C(CH3)HC(=O)O–]n, formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid C(CH3)(OH)HCOOH with loss of water. It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide [–C(CH3)HC(=O)O–]2, the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit.
 W
WPolymethylpentene (PMP), also known as poly(4-methyl-1-pentene), is a thermoplastic polymer of 4-methyl-1-pentene. It is used for gas-permeable packaging, autoclavable medical and laboratory equipment, microwave components, and cookware. It is commonly called TPX, which is a trademark of Mitsui Chemicals.
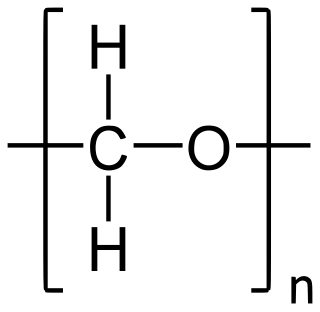 W
WPolyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, polyacetal, and polyformaldehyde, is an engineering thermoplastic used in precision parts requiring high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability. As with many other synthetic polymers, it is produced by different chemical firms with slightly different formulas and sold variously by such names as Delrin, Kocetal, Ultraform, Celcon, Ramtal, Duracon, Kepital, Polypenco, and Hostaform.
 W
WPolyphthalamide is a subset of thermoplastic synthetic resins in the polyamide (nylon) family defined as when 55% or more moles of the carboxylic acid portion of the repeating unit in the polymer chain is composed of a combination of terephthalic (TPA) and isophthalic (IPA) acids. The substitution of aliphatic diacids by aromatic diacids in the polymer backbone increases the melting point, glass transition temperature, chemical resistance and stiffness.
 W
WPolypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
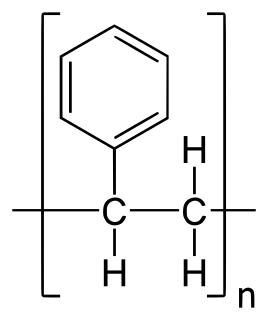 W
WPolystyrene (PS) is a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer made from the monomer known as styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and rather brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a rather poor barrier to oxygen and water vapour and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene can be naturally transparent, but can be coloured with colourants. Uses include protective packaging, containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery and in the making of models.
 W
WPolyvinyl chloride is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer. About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year.
 W
WPolyvinyl fluoride (PVF) or –(CH2CHF)n– is a polymer material mainly used in the flammability-lowering coatings of airplane interiors and photovoltaic module backsheets. It is also used in raincoats and metal sheeting. Polyvinyl fluoride is a thermoplastic fluoropolymer with the repeating vinyl fluoride unit:
 W
WPolyvinylcarbazole (PVK) is a temperature-resistant thermoplastic polymer produced by radical polymerization from the monomer N-vinylcarbazole. It is photoconductive and thus the basis for photorefractive polymers and organic light-emitting diodes.
 W
WPolyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer produced by the polymerization of vinylidene difluoride.
 W
WPVC clothing is shiny clothing made from the plastic polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC plastic is often called "vinyl" and this type of clothing is commonly known as "vinyl clothing". PVC is sometimes confused with the similarly shiny patent leather.
 W
WSpectralon is a fluoropolymer, which has the highest diffuse reflectance of any known material or coating over the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the spectrum. It exhibits highly Lambertian behavior, and can be machined into a wide variety of shapes for the construction of optical components such as calibration targets, integrating spheres, and optical pump cavities for lasers.