 W
WAyu fishing is one of the several narrowly defined styles of fishing in Japan.
 W
WElectric pulse fishing is a fishing technique sometimes used in trawl fisheries which produces a limited electric field above the seabed to catch fish. The pulse trawl gear consists of a number of electrodes, attached to the gear in the tow direction, that emit short electric pulses. The electrodes replace the tickler chains that are used in traditional beam trawl fishery. The pulse trawl fishery is mainly aimed at flatfish like sole, with by-catch plaice. In addition, the pulse trawl gear is applied in shrimp fisheries on a limited scale. Technically, the use of electricity to catch fish is prohibited in European waters. However, the European Union is able to provide exemptions to this rule since 2007. These exemptions are now mainly used by Dutch and British trawlers in the North Sea.
 W
WFishing techniques are methods for catching fish. The term may also be applied to methods for catching other aquatic animals such as molluscs and edible marine invertebrates.
 W
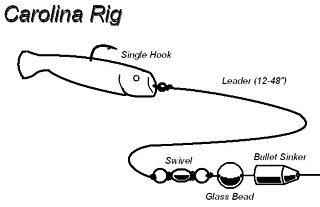
WA rig is an arrangement of items used for fishing. It can be assembled of one or more lines, hooks, sinkers, bobbers, swivels, lures, beads, and other fishing tackle. A rig might be held by a rod, by hand, or attached to a boat or pier. Some rigs are designed to float near the surface of the water, others are designed to sink to the bottom. Some rigs are designed for trolling. Many rigs are designed especially for catching a single species of fish, but will work well for many different species.
 W
WBait fish are small fish caught for use as bait to attract large predatory fish, particularly game fish. Species used are typically those that are common and breed rapidly, making them easy to catch and in regular supply.
 W
WBank fishing is fishing from places where the land meets the water's edge. Fishing from rocks is usually called rock fishing. Like rock fishing, bank fishing is typically done by casting fishing bait or lures into the water in an attempt to catch fish. Bank fishing is usually performed with a rod and reel but nets, traps, and spears, and fishing lines used without rods can also be used. People who fish from a boat can sometimes access more areas in prime locations with greater ease than bank fishermen. However, many people who don't use boats find fishing from a bank has its own advantages. Many factors contribute to success in bank fishing, such as local knowledge, water depth, bank structure, location, time of day, and the types of bait and lures.
 W
WBasnig or balasnig are lift nets (salambaw) operated by a large outrigger boat called Basnigan. They use a large bag net suspended directly below or beside the ship. This net is attached to multiple temporary booms projecting from the ship's outriggers and detachable auxiliary masts. Modern basnig typically use generators and electric lights to attract fish and squid. This method is unique to the Philippines. It is common in the Visayas, particularly in the provinces of Capiz and Iloilo.
 W
WBlast fishing, Fish Bombing, or dynamite fishing is a destructive fishing practice using explosives to stun or kill schools of fish for easy collection. This often illegal practice is extremely destructive to the surrounding ecosystem, as the explosion often destroys the underlying habitat that supports the fish. The frequently improvised nature of the explosives used means danger for the fishermen as well, with accidents and injuries.
 W
WBowfishing is a method of fishing that uses specialized archery equipment to shoot and retrieve fish. Fish are shot with a barbed arrow that is attached with special line to a reel mounted on the bow. Some freshwater species commonly hunted include common carp, grass carp, bighead carp, alligator gar, and bowfin. In saltwater, rays and sharks are regularly pursued.
 W
WA casting net, also called a throw net, is a net used for fishing. It is a circular net with small weights distributed around its edge.
 W
WIn angling, casting is the act of throwing bait or a lure using a fishing line out over the water using a flexible fishing rod. The usual technique is for the angler to quickly flick the rod from behind toward the water. The term may also be used for setting out a net.
 W
WCatch and release is a practice within recreational fishing intended as a technique of conservation. After capture, the fish are unhooked and returned to the water. Often, a fast measurement and weighing of the fish, followed by photography of the catch is worthwhile. Using barbless hooks, it is often possible to release the fish without removing it from the water.
 W
WChinese fishing nets are a type of stationary lift net in India. They are fishing nets that are fixed land installations for fishing. While commonly known as "Chinese fishing nets" in India, the more formal name for such nets is "shore operated lift nets". Huge mechanical contrivances hold out horizontal nets of 20 m or more across. Each structure is at least 10 m high and comprises a cantilever with an outstretched net suspended over the sea and large stones suspended from ropes as counterweights at the other end. Each installation is operated by a team of up to six fishermen. While such nets are used throughout coastal southern China and Indochina, in India they are mostly found in the Indian cities of Kochi and Kollam, where they have become a tourist attraction. This way of fishing is unusual in India and almost unique to the area, as it was introduced by Chinese explorers who landed there in the 14th century. Indeed, one interpretation of the city name Kochi is ‘co-chin', meaning ‘like China.’
 W
WCormorant fishing is a traditional fishing method in which fishermen use trained cormorants to fish in rivers. Historically, cormorant fishing has taken place in Japan and China, as well as Greece, North Macedonia, and, briefly, England and France. It is first attested as a method used by the ancient Japanese in the Book of Sui, the official history of the Sui Dynasty of China, completed in 636 CE. This technique has also been used in other countries but is currently under threat in China.
 W
WCormorant fishing on the Nagara River has played a vital role in the history of the city of Gifu, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. Throughout its long history, it evolved from a means to live, to a profitable industry, to a major tourist draw. It runs from May 11 to October 15 of each year.
 W
WDrift netting is a fishing technique where nets, called drift nets, hang vertically in the water column without being anchored to the bottom. The nets are kept vertical in the water by floats attached to a rope along the top of the net and weights attached to another rope along the bottom of the net. Drift nets generally rely on the entanglement properties of loosely affixed netting. Folds of loose netting, much like a window drapery, snag on a fish's tail and fins and wrap the fish up in loose netting as it struggles to escape. However the nets can also function as gill nets if fish are captured when their gills get stuck in the net. The size of the mesh varies depending on the fish being targeted. These nets usually target schools of pelagic fish.
 W
WAn eel buck or eel basket is a type of fish trap that was prevalent in the River Thames in England up to the 20th century. It was used particularly to catch eels, which were a staple part of the London diet.
 W
WElectrofishing uses direct current electricity flowing between a submerged cathode and anode. This affects the movement of the fish so that they swim toward the anode, where they can be caught or stunned.
 W
WA fish decoy is an object in the shape of a fish or some other animal that is used as a decoy to attract fish. It is often used during ice fishing. Unlike a fishing lure, a fish decoy doesn't have a hook.
 W
WA fish trap is a trap used for fishing. Fish traps can have the form of a fishing weir or a lobster trap. Some fishing nets are also called fish traps, for example fyke nets.
 W
WA fish wheel, also known as a salmon wheel, is a device situated in rivers for catching fish which looks and operates like a watermill. However, in addition to paddles, a fish wheel is outfitted with wire baskets designed to catch and carry fish from the water and into a nearby holding tank. The current of the river presses against the submerged paddles and rotates the wheel, passing the baskets through the water where they intercept fish that are swimming or drifting. Naturally a strong current is most effective in spinning the wheel, so fish wheels are typically situated in shallow rivers with brisk currents, close to rapids, or waterfalls. The baskets are built at an outward-facing slant with an open end so the fish slide out of the opening and into the holding tank where they await collection. Yield is increased if fish swimming upstream are channeled toward the wheel by weirs.
 W
WGathering seafood by hand can be as easy as picking shellfish or kelp up off the beach, or doing some digging for clams or crabs, or perhaps diving under the water for abalone or lobsters.
 W
WGigging is the practice of hunting fish or small game with a gig or similar multi-pronged spear. Commonly harvested wildlife include freshwater suckers, saltwater flounder, and small game, such as frogs. A gig can refer to any long pole which has been tipped with a multi-pronged spear. The gig pole ranges in length from 8 to 14 feet for fish gigs and 5 to 8 feet for frog gigs. A gig typically has three or four barbed tines similar to a trident; however gigs can be made with any number of tines. In the past people would attach illuminated pine knots to the end of gigs at night to give them light.
 W
WGillnetting is a fishing method that uses gill nets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is generally referred to as a "cork line." The line along the bottom of the panels is generally weighted. Traditionally this line has been weighted with lead and may be referred to as "lead line." A gillnet is normally set in a straight line. Gillnets can be characterized by mesh size, as well as colour and type of filament from which they are made. Fish may be caught by gill nets in three ways:Wedged – held by the mesh around the body. Gilled – held by mesh slipping behind the opercula. Tangled – held by teeth, spines, maxillaries, or other protrusions without the body penetrating the mesh.
 W
WGreen-sticking, also referred to as green stick fishing, is a technique for fishing for tuna by trolling synthetic squid from a fiberglass pole around 30 feet (9.1 m) above the water surface. As part of the technique, the squid spend very little time submerged in the water and more of it suspended in the air above— in this way it resembles kite fishing. It is named for the green tint of the extremely long fiberglass poles originally made in Japan specifically for this purpose. The poles come in sections of 11 feet (3.4 m), and are hollow and tapered so that they can be nested inside one another. The assembled pole is normally between 34 feet (10 m) and 45 feet (14 m) long.
 W
WHaaf net fishing is an ancient type of salmon and sea trout net fishing practised in Britain, and is particularly associated with the Solway Firth, the estuary forming part of the border between England and Scotland. The technique involves fishermen standing chest-deep in the sea and using large submerged framed nets to scoop up fish that swim towards them. It is a form of fishing that is believed to have been brought to Britain by the Vikings more than a thousand years ago and to have been practised in the Solway Firth since then.
 W
WA hand net, also called a scoop net or dip net, is a net or mesh basket held open by a hoop. It may or may not be on the end of a handle. Hand nets have been used since antiquity and can be used for scooping fish near the surface of the water, such as muskellunge or northern pike.
 W
WHandline fishing, or handlining, is a fishing technique where a single fishing line is held in the hands. It is not to be confused with handfishing. One or more fishing lures or baited hooks are attached to the line. A hook, fishing lure, or a fishing jig and many times a weight and/or a fishing float can be attached to the line. Handlining is among the oldest forms of fishing and is commonly practiced throughout the world today.
 W
WIce fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities.
 W
WA jiggerpole is a long fishing pole that is used with a short and heavy line, usually a foot or less of 50 lbf test or heavier. Then a large lure or bait is attached and manually worked around the shoreline and cover. In deep cover, the lure or bait can be presented by placing the tip of the fishing pole into the water. A jiggerpole may refer to a spar that extends a mast.
 W
WJug fishing is an unlimited class tackle method of fishing that uses lines suspended from floating jugs to catch fish in lakes or rivers. Often, many jugs are used when jug fishing. In many states, a fisherman could use up to twenty, and jug sets of around twenty are common in practice. Jug fishing is most common in southern states where many different kinds of people jug fish. Jugs are often put out at sunset and picked up at sunrise by the whole family. Jug fishing consists of a simple setup where lines are tied onto jugs and weights can be added to the line to keep the jug's location fixed. Jug fishing is also subjected to numerous Department of Natural Resources and local water regulations that could include: the number of jugs, dates and times when jug fishing is allowed, and if jug fishing is even allowed. Many fish can be caught on jugs, but the main target of jug fishing is often catfish.
 W
WA lave net is a type of fishing net used in river estuaries, particularly in the Severn Estuary in Wales and England to catch salmon.
 W
WLift nets, also called lever nets, are a method of fishing using nets that are submerged to a certain depth and then lifted out of the water vertically. The nets can be flat or shaped like a bag, a rectangle, a pyramid, or a cone. Lift nets can be hand-operated, boat-operated, or shore-operated. They typically use bait or a light-source as a fish-attractor. Lift nets are also sometimes called "dip nets", though that term applies more accurately to hand nets.
 W
WLongline fishing, or longlining, is a commercial fishing technique. It uses a long line, called the main line, with baited hooks attached at intervals by means of branch lines called snoods. A snood is a short length of line, attached to the main line using a clip or swivel, with the hook at the other end. Longlines are classified mainly by where they are placed in the water column. This can be at the surface or at the bottom. Lines can also be set by means of an anchor, or left to drift. Hundreds or even thousands of baited hooks can hang from a single line. Longliners – fishing vessels rigged for longlining – commonly target swordfish, tuna, halibut, sablefish and many other species.
 W
WNoodling is fishing for catfish using one's bare hands, and is practiced primarily in the southern United States. The noodler places their hand inside a discovered catfish hole. Many other names are used in different regions for the same activity.
 W
WOtter fishing is a fishing technique which uses trained otters to fish in rivers. This method has been practised since the 6th century in various parts of the world, and is still practiced in southern Bangladesh.
 W
WPearl hunting, also known as pearling, is the activity of recovering pearls from wild molluscs, usually oysters or mussels, in the sea or freshwater. Pearl hunting used to be prevalent in the Persian Gulf region and Japan. Pearl diving began in the 1850s on the northern and north-western coast of Australia, and started in the Torres Strait, off Far North Queensland in the 1870s.
 W
WPutcher fishing is a type of fishing which employs multiple putcher baskets, set in a fixed wooden frame, against the tide in a river estuary, notably on the River Severn, in England and South East Wales. Putchers are placed in rows, standing four or five high, in a wooden "rank" set out against the incoming and/or outgoing tides.
 W
WThe reach cast is a casting technique used in fly fishing. The reach cast involves casting the fly lure over flowing water, such as a stream, and then just before the fly lands, moving the arm and fly rod in the upstream direction to arrange the fishing line so that it produces less apparent drag in the water. The technique allows the lure to more closely resemble a free-floating insect, resulting in greater chance of it being taken by a fish. Reach casting also allows an experienced caster to pitch curved casts in order to get the lures into difficult places.
 W
WRecreational fishermen usually fish either from a boat or from a shoreline or river bank. When fishing from a boat, or fishing vessel, most fishing techniques can be used, from nets to fish traps, but some form of angling is by far the most common. Compared to fishing from the land, fishing from a boat allows more access to different fishing grounds and different species of fish.
 W
WSalambáw, is a type of lift net used by indigenous fishermen in the Philippines. They are found throughout the Philippine islands but are most prevalent in large lakes like Laguna de Bay, and sheltered coastal areas like the Manila Bay, Ragay Gulf, and Batan Bay. Variations of salambáw lift nets include the bintol, panak, tangkal, and the basnig. Salambáw rafts were also known as saraboa or salakab.
 W
WSeine fishing is a method of fishing that employs a fishing net, called a seine, that hangs vertically in the water with its bottom edge held down by weights and its top edge buoyed by floats. Seine nets can be deployed from the shore as a beach seine, or from a boat.
 W
WThe live sharksucker or slender sharksucker is a species of marine fish in the family Echeneidae, the remoras.
 W
WShortfloating or Short fishing is a fishing method that has been employed in running water by river anglers for many decades, and is also used by lake anglers. The method that allows the angler to selectively target species of fish by controlling hook length. Short floating is used in the river pools alongside runs, where resting fish have time to consider and take bait.
 W
WSpearfishing is a method of fishing that has been used throughout the world for millennia. Early civilizations were familiar with the custom of spearing fish from rivers and streams using sharpened sticks.
 W
WSurf fishing is the sport of catching fish standing on the shoreline or wading in the surf. A general term, surf fishing may or may not include casting a lure or bait, and refers to all types of shore fishing – from sandy and rocky beaches, rock jetties, or even fishing piers. The terms surfcasting or beachcasting refer more specifically to surf fishing from the beach by casting into the surf at or near the shoreline. With few exceptions, surf fishing is done in saltwater. The most common misconception about surf fishing is the idea that one must cast as far out as possible in order to reach the fish. At beaches on the west coast of the United States, and in fact, at most beaches around the world, you only really need to get your bait into knee deep water. This is referred to as surf fishing the "skinny".
 W
WSimilar to a gillnet, the tangle net, or tooth net, is a type of nylon fishing net. Left in the water for no more than two days, and allowing bycatch to be released alive, this net is considered to be less harmful that other nets. The tangle net is used in the Philippines by commercial fishermen, as well as by the scientific community. When spent, these nets can be bundled, and left on the sea floor to collect smaller species. These bundles are known locally as lumen lumen nets.
 W
WThe trabucco is an old fishing machine typical of the coast of Abruzzi region and also in the coast of Gargano, where they are protected as historical monuments in the Gargano National Park. Trabucchi are spread along the coast of the southern Adriatic, especially in the Italian provinces of Chieti, Campobasso, and Foggia, and also in some parts of the coast of the southern Tyrrhenian Sea.
 W
WTrawling is a method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch different species of fishes or sometimes targeted species. Trawls are often called towed gear or dragged gear.
 W
WTrepanging is the act of collection or harvesting of sea cucumbers, known in Indonesian as trepang, Malay těripang, and used as food. The collector, or fisher, of trepang is a trepanger.
 W
WTrolling is a method of fishing where one or more fishing lines, baited with lures or bait fish, are drawn through the water. This may be behind a moving boat, or by slowly winding the line in when fishing from a static position, or even sweeping the line from side-to-side, e.g. when fishing from a jetty. Trolling is used to catch pelagic fish such as salmon, mackerel and kingfish.
 W
WWagenya is the name of a place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and of the people living there; situated in the northern part of Congo, by the city of Kisangani and on the lower reaches of the Boyoma Falls. As a result, the seventh and last cataract on the Boyoma is named the Wagenia Falls.
 W
WA Zeese is a traditional type of fishing gear used for bottom trawling in the shallow coastal waters (Bodden) of Pomerania. Depending on the type of the Zeese, it is drawn by one or two boats.