 W
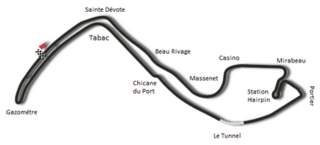
WThe 1929 Monaco Grand Prix was the first Grand Prix to be run in the Principality. It was set up by wealthy cigarette manufacturer, Antony Noghès, who had set up the Automobile Club de Monaco with some of his friends. This offer of a Grand Prix was supported by Prince Louis II, and the Monégasque driver of that time, Louis Chiron. On 14 April 1929, their plan became reality, when 16 invited participants turned out to race for a prize of 100,000 French francs.
 W
WThe 1936 Monaco Grand Prix was a Grand Prix motor race held at Circuit de Monaco on 13 April 1936.
 W
WThe 1937 Monaco Grand Prix was a Grand Prix motor race held at the Circuit de Monaco on 8 August 1937. The 100 lap event was won by Manfred von Brauchitsch.
 W
WThe 1948 Monaco Grand Prix was a Grand Prix motor race, held in Monte Carlo on 16 May 1948.
 W
WThe 1952 Monaco Grand Prix was a non-championship sports car race held on June 2, 1952, at Monaco.
 W
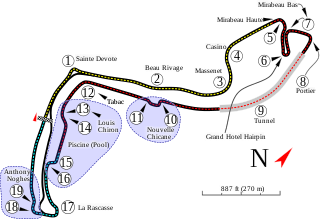
WResults from the 1992 Monaco Grand Prix Formula Three held at Monte Carlo on May 30, 1992, in the Circuit de Monaco. The race was a support of the 1992 Monaco Grand Prix of Formula 1.
 W
WThe 2005 Monaco GP2 round was a GP2 Series motor race held on 21 May 2005 at the Circuit de Monaco in Monte Carlo, Monaco. It was the third race of the 2005 GP2 Series season. The race was used to support the 2005 Monaco Grand Prix.
 W
WThe 2011 Monte-Carlo Rolex Masters, a men's tennis tournament for male professional players, was played from 9 April through 17 April 2011, on outdoor clay courts. It was the 105th edition of the annual Monte Carlo Masters tournament, which was sponsored by Rolex for the third time. It took place at the Monte Carlo Country Club in Roquebrune-Cap-Martin, France, near Monte Carlo, Monaco.
 W
WThe 2014 Historic Grand Prix of Monaco was a motor racing event featuring Formula 1 and Grand Prix motor racing cars from the early days of racing through to the mid 1970s. The event, which contained seven races of various categories, was run for the ninth time since its inception in 1997.
 W
WThe 2015 Monaco ePrix was a Formula E motor race held on 9 May 2015 on the Circuit de Monaco, a street circuit in Monte Carlo, Monaco. It was the seventh championship race of the single-seater, electrically powered racing car series' inaugural season. The race was won by Sébastien Buemi, who became the first multiple race winner in the series.
 W
WThe Automobile Club de Monaco is a motoring club based in Monaco. The club serves as the governing body for motorsport within Monaco, and organises the prestigious Monaco Grand Prix and Monte Carlo Rally. It is a member of the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile, representing Monaco as a mobility and sporting club.
 W
WThe Challenge Prince Rainier III is a domestic football cup in Monaco, featuring teams from across the country. The tournament has been organised annually since 1975 and since then has been known as the premier footballing tournament for amateur teams within the principality.
 W
WThe Junior Monaco Kart Cup is a kart racing event ruled by the CIK-FIA and organized by the Automobile Club de Monaco, it takes place each year in Monaco.
 W
WFootball is one of the leading sports in the small Principality of Monaco, enjoying large popularity alongside motor racing, yachting, and tennis. It is governed by the Monegasque Football Federation.
 W
WMonaco competed in the Summer Olympic Games for the first time at the 1920 Summer Olympics held in Antwerp, Belgium.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1924 Summer Olympics held in Paris, France.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1928 Summer Olympics held at Amsterdam in the Netherlands.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin, Germany. The nation returned to the Olympic Games after missing the 1932 Summer Olympics. Eight competitors, all men, took part in five events in two sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1948 Summer Olympics in London, England. Four competitors, all men, took part in two events in one sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki, Finland. Eight competitors, all men, took part in six events in two sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1960 Summer Olympics in Rome, Italy. The nation returned to the Olympic Games after missing the 1956 Summer Olympics. Eleven competitors, all men, took part in six events in three sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, Japan. One competitor competed in one sport.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City, Mexico. Two competitors, both men, took part in one event in one sport.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich, West Germany. Five competitors, all men, took part in four events in two sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The country didn't win any medals.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles, United States. The nation returned to the Summer Games after participating in the American-led boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympics. Eight competitors, all men, took part in seven events in five sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul, South Korea. Nine competitors, eight men and one woman, took part in nine events in seven sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona, Spain.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1992 Winter Olympics in Albertville, France.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer, Norway.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Georgia, United States.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Japan.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney, Australia.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2002 Winter Olympics in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens, Greece, from 13 to 29 August 2004.
 W
WMonaco (MON) competed at the 2005 Mediterranean Games in Almería, Spain. The nation had a total number of 16 participants.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2006 Winter Olympics in Turin, Italy. For the first time since 1984, the team did not include Prince Albert of Monaco, who became the ruler of the Principality following the death of his father Rainier III.
 W
WMonaco sent a team of sportsmen and women to compete at the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing, People's Republic of China.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2012 Summer Olympics in London from 27 July to 12 August 2012. This was the nation's nineteenth consecutive Olympiad since its debut in 1920.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2013 World Championships in Athletics in Moscow, Russia, from 10–18 August 2013. A team of one athlete was announced to represent the country in the event.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2014 Summer Youth Olympics, in Nanjing, China from 16 August to 28 August 2014.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, Russia, from 7 to 23 February 2014. Monaco's team consisted of five athletes plus one alternate for bobsleigh, competing in two sports.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2015 European Games, in Baku, Azerbaijan from 12 to 28 June 2015.
 W
WMonaco competed at the 2017 World Championships in Athletics in London, United Kingdom, from 4–13 August 2017.
 W
WMonaco competed at the World Games 2017 in Wroclaw, Poland, from 20 July 2017 to 30 July 2017.
 W
WMonaco first participated at the Olympic Games in 1920, and has sent athletes to compete in most Summer Olympic Games since then, missing only the 1932 Games, the 1956 Games, and the boycotted 1980 Games. Monaco has also participated in every Winter Olympic Games since 1984.
 W
WThe Monaco men's national basketball team is the national basketball team of the Principality of Monaco. Monaco has competed at the Games of the Small States of Europe, and winning gold in 1987.
 W
WMonaco national rugby union team has been playing since the 1990s. They currently only play friendly games and do not compete in the European Nations Cup, but they are still member of World Rugby. In October 2019, Monaco ranked 101st out of 105 national teams according to World Rugby.
 W
WThe Monaco Shooting Federation, Monégasque Fédération Monégasque de Tir is the Monacan association for shooting sport under the International Practical Shooting Confederation (IPSC), the International Shooting Sport Federation (ISSF) and the Fédération Internationale de Tir aux Armes Sportives de Chasse.
 W
WThe Monegasque Cycling Federation or FMC is the national governing body of cycle racing in Monaco.
 W
WThe Monégasque Football Federation is the governing body of football in the nation of Monaco. The association is not a member of FIFA or UEFA, but it does have membership to the NF-Board and its successor CONIFA.
 W
WThe Rainier III Nautical Stadium is a municipal sports complex on the Route de la Piscine in the La Condamine district of Monaco, in Port Hercules.
 W
WSalle Gaston Médecin, or Salle Omnisports, is an indoor sports arena that is located in Fontvieille, Monaco near the French border. It is used to host basketball, volleyball, and handball games, judo and fencing matches, and weightlifting and gymnastics competitions. The arena is a part of the Stade Louis II multi-sports complex, and is owned by the Monaco-based multi-sports club AS Monaco.
 W
WThe Fédération Monégasque de Voile is the national governing body for the sport of sailing in Monaco, recognised by the International Sailing Federation. This organisation is in effect part of the Yacht Club de Monaco, which is the only Sailing Club in the country.