 W
WIn the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted from the 5th to the late 15th century. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages.
 W
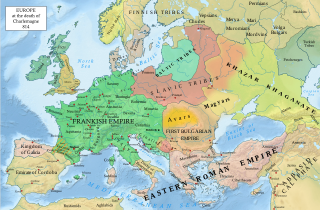
WThe Early Middle Ages or Early Medieval Period, sometimes referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century AD. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of European history. The alternative term "Late Antiquity" emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while "Early Middle Ages" is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period. As such the concept overlaps with Late Antiquity, following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, and precedes the High Middle Ages.
 W
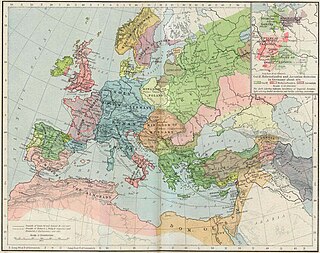
WThe High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from around 1000 to 1250 AD. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around 1500 AD.
 W
WThe Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from 1250 to 1500 AD. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period.
 W
WThe Holy Roman Empire was a multi-ethnic complex of territories in Western and Central Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. The largest territory of the empire after 962 was the Kingdom of Germany, though it also included the neighboring Kingdom of Bohemia and Kingdom of Italy, plus numerous other territories, and soon after the Kingdom of Burgundy was added. However, while by the end of the 15th century the Empire was still in theory composed of three major blocks – Italy, Germany, and Burgundy – in practice only the Kingdom of Germany remained, with the Burgundian territories lost to France and the Italian territories, ignored in the Imperial Reform, although formally part of the Empire, splintered into numerous de facto independent territorial entities. The external borders of the Empire did not change noticeably from the Peace of Westphalia – which acknowledged the exclusion of Switzerland and the Northern Netherlands, and the French protectorate over Alsace – to the dissolution of the Empire. By then, it largely contained only German-speaking territories, plus the Kingdom of Bohemia, the southern Netherlands and lands of Carniola. At the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, most of the Holy Roman Empire was included in the German Confederation.
 W
WThe medieval art of the Western world covers a vast scope of time and place, over 1000 years of art in Europe, and at certain periods in Western Asia and Northern Africa. It includes major art movements and periods, national and regional art, genres, revivals, the artists' crafts, and the artists themselves.
 W
WThe Scunthorpe problem is the unintentional blocking of websites, e-mails, forum posts or search results by a spam filter or search engine because their text contains a string of letters that appear to have an obscene or otherwise unacceptable meaning. Names, abbreviations, and technical terms are most often cited as being affected by the issue.
 W
WPahargarh estate was a Zamindari estate under the surganty of Lodi Dynasty from year 1446-1947 and later under Mughal Empire, Jhansi Estate and, British Raj. Pahargarh is located in Madhya Pradesh, in Morena District. It was ruled by the Sakarwar Rajputs of Maharaja Zamindar family of Pahargarh who were the descendants of Rao Anup Dev Sikarwar or his grandson Maharaja Kam Dev Misir. When Kam Dev Misir shifted to Ghazipur District in 1530 the estate was handled by his second, third, and fourth sons' family. Half of their family went with Kam Dev in Ghazipur District in Uttar Pradesh and half lived here. The First ruler of Pahargarh estate was Rao Anup Dev Sikandar. Rao Anup Dev Sikarwar was originally a ruler of Fatehpur Sikri estate but he captured the parts of Morena, Gwalior and Jhansi and established Pahargarh and built Pahargarh Fort.