 W
WA parasitic cone is the cone-shaped accumulation of volcanic material not part of the central vent of a volcano. It forms from eruptions from fractures on the flank of the volcano. These fractures occur because the flank of the volcano is unstable. Eventually, the fractures reach the magma chamber and generate eruptions called flank eruptions, which, in turn, produce a parasitic cone.
 W
WFormica Leo, named for its similar shape to the pitfall built by the antlion, is a small volcanic crater of the Piton de la Fournaise, the active volcano on the eastern side of Réunion island in the Indian Ocean. It is located at the bottom of the caldera called Enclos Fouqué, just beneath the mountain pass Pas de Bellecombe.
 W
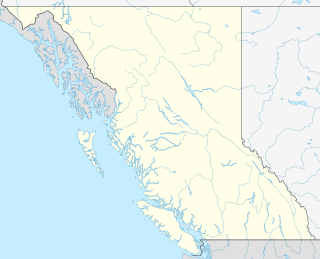
WMachmell River Cone is a cinder cone in the Silverthrone Caldera complex in the Pacific Ranges section of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia, Canada. It is believed the volcano last erupted during the Holocene, making it one of the most recent eruptions of the Silverthrone complex.
 W
WLake Mashū is an endorheic crater lake formed in the caldera of a potentially active volcano. It is located in Akan National Park on the island of Hokkaidō, Japan. The lake has been called the clearest lake in the world.
 W
WMount Ashigara (足柄山), also known as Mount Kintoki (金時山), is the northernmost peak of the Hakone caldera, on the border of Kanagawa and Shizuoka prefectures, in the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park in Japan. Ashigara is not a remnant of the collapse of the old Hakone volcano itself, but rather a parasitic cone growing from its flank.
 W
WOpal Cone is a cinder cone located on the southeast flank of Mount Garibaldi in the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It is the source of a 15 km (9 mi) long broad dacite lava flow with prominent wrinkled ridges. The lava flow is unusually long for a silicic lava flow.
 W
WParasite Cone is a small parasitic cone on the northwest flank of Mount Overlord, 6.5 nautical miles (12 km) distant from the latter's summit, in the Mountaineer Range, Victoria Land. Given this descriptive name by the northern party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1962–63.
 W
WPuʻu ʻŌʻō is a volcanic cone in the eastern rift zone of the Kīlauea volcano of the Hawaiian Islands. Until the end of April 2018, Puʻu ʻŌʻō had been erupting nearly continuously since January 3, 1983, making it the longest-lived rift-zone eruption of the last two centuries.
 W
WSchriebers Meadow Cone is a small parasitic cone on the southeastern flank of Mount Baker in the U.S. state of Washington. It was formed about 9,800 years ago by the only known Holocene flank eruption of Mount Baker. A basaltic lava flow traveled down the Sulphur Creek valley and across the Baker River valley; this is the most recent lava flow at Mount Baker. Future eruptions from Schriebers Meadow Cone are unlikely to occur as it is considered a short-lived feature.
 W
WMount Scott is a small stratovolcano and a so-called parasitic cone on the southeast flank of Crater Lake in southern Oregon. It is approximately 420,000 years old. Its summit is the highest point within Crater Lake National Park, and the tenth highest peak in the Oregon Cascades. A small fire lookout tower stands on the summit, at the end of a trail that zigzags approximately 1,500 feet up the mountain. The mountain is named for Oregon pioneer Levi Scott, founder of Scottsburg, Oregon.
 W
WShastina is the highest satellite cone of Mount Shasta, and one of four overlapping volcanic cones which together form the most voluminous stratovolcano in the Cascade Range. At 12,335 feet (3,760 m), Shastina is taller than Mount Adams and would rank as the third highest volcano in the Cascades behind Mount Rainier and Shasta were it not nestled on the western flank of its higher neighbor. Shastina has a topographic prominence of over 450 ft (137 m) above the saddle connecting it with Shasta and easily exceeds the typical mountaineering standard of 300 feet (91 m) for a peak to qualify as an independent summit, yet most lists of Cascade volcanoes omit it nonetheless. The name "Shastina" is a diminutive of Shasta.