 W
WThe 1921 Massawa earthquake took place off the coast of Massawa, Eritrea, on August 14 with a moment magnitude of 6.1 and a Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The first aftershock after the initial earthquake was of similar magnitude. Significant damage was caused to the harbour at Massawa with a number of deaths reported. Aftershocks were felt as far away as Asmara and Dekemhare.
 W
WThe Attack on Convoy BN 7 was a naval engagement in the Red Sea during the Second World War between a British force defending a convoy of merchant ships and a flotilla of Italian destroyers. The Italian attack failed, with only one merchant ship being slightly damaged. After a chase, the British destroyer HMS Kimberley torpedoed the Italian destroyer Francesco Nullo which was beached on Harmil Island. Kimberley was hit, disabled by Italian shore batteries on the island and towed to safety by the cruiser HMS Leander.
 W
WThe Battle of Kunfuda Bay was a naval battle of the Italo-Turkish War between small squadrons of the Italian and Ottoman navies. On 7 January 1912, the Italian protected cruiser Piemonte and the Soldato-class destroyers Artigliere and Garibaldino, cruising the Red Sea, discovered six Ottoman gunboats, a tugboat, and a yacht in the harbor at Kunfuda. The vessels engaged for over three hours and five Ottoman vessels were sunk and four dhows were captured. Three of the gunboats were damaged during the battle and grounded on the beach to prevent them from sinking. The following morning, the Italian vessels returned to destroy the remaining three vessels; the yacht, which had been sunk, was later salvaged and seized by Italy. After the battle, the Italian squadron in the Red Sea was able to proclaim a blockade of Ottoman ports in the Red Sea and frequently bombarded Ottoman positions for the rest of the war.
 W
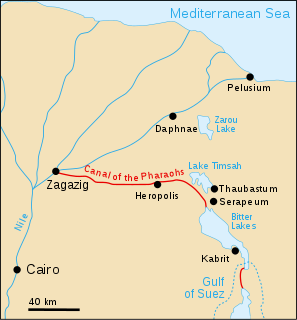
WThe Canal of the Pharaohs, also called the Ancient Suez Canal or Necho's Canal, is the forerunner of the Suez Canal, constructed in ancient times and kept in use, with intermissions, until being closed for good in 767 AD for strategic reasons during a rebellion. It followed a different course from its modern counterpart, by linking the Nile to the Red Sea via the Wadi Tumilat. Work began under the pharaohs. According to Darius the Great's Suez Inscriptions and Herodotus, the first opening of the canal was under Persian king Darius the Great, but later ancient authors like Aristotle, Strabo, and Pliny the Elder claim that he failed to complete the work. Another possibility is that it was finished in the Ptolemaic period under Ptolemy II, when engineers solved the problem of overcoming the difference in height through canal locks.
 W
WIn 1182 Raynald of Châtillon the Crusader Lord of Oultrejordain launched a squadron of ships on the Red Sea in order to conduct raids on Muslim Red Sea ports and to attack the Muslim holy cities of Mecca or Medina.
 W
WThe Gulf of Suez Rift is a continental rift zone that was active between the Late Oligocene and the end of the Miocene. It represented a continuation of the Red Sea Rift until break-up occurred in the middle Miocene, with most of the displacement on the newly developed Red Sea spreading centre being accommodated by the Dead Sea Transform. During its brief post-rift history, the deepest part of the remnant rift topography has been filled by the sea, creating the Gulf of Suez.
 W
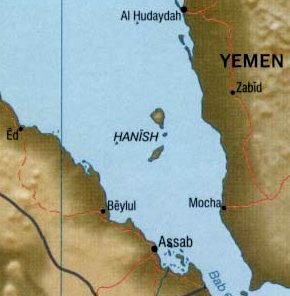
WThe Hanish Islands conflict was a dispute between Yemen and Eritrea over the island of Greater Hanish in the Red Sea, one of the largest in the then disputed Zukur-Hanish archipelago. Fighting took place over three days from 15 December to 17 December 1995. In 1998 the Permanent Court of Arbitration determined that most of the archipelago belonged to Yemen.
 W
WThe incense trade route included a network of major ancient land and sea trading routes linking the Mediterranean world with eastern and southern sources of incense, spices and other luxury goods, stretching from Mediterranean ports across the Levant and Egypt through Northeastern Africa and Arabia to India and beyond. The incense land trade from South Arabia to the Mediterranean flourished between roughly the 7th century BC and the 2nd century AD. The incense trade route served as a channel for the trading of goods such as Arabian frankincense and myrrh; from Southeast Asia Indian spices, precious stones, pearls, ebony, silk and fine textiles; and from the Horn of Africa, rare woods, feathers, animal skins, Somali frankincense, and gold.
 W
WThe Kinaidokolpitai were a people inhabiting the Hejaz in western Arabia in the 2nd and 3rd centuries AD, according to Greek and Latin authors. They are known from a small number of independent sources. Their capital was Zambram, but none of the named settlements in their territory can be identified with certainty. Their name is possibly related to that of Kinda. For a time they were raiders and pirates preying on the incense trade until defeated by the kingdom of Aksum, which imposed tribute on them.
 W
WThe Land of Punt was an ancient kingdom. A trading partner of Ancient Egypt, it was known for producing and exporting gold, aromatic resins, blackwood, ebony, ivory and wild animals. The region is known from ancient Egyptian records of trade expeditions to it. It is possible that it corresponds to Opone in Somalia, as later known by the ancient Greeks, while some biblical scholars have identified it with the biblical land of Put or Havilah.
 W
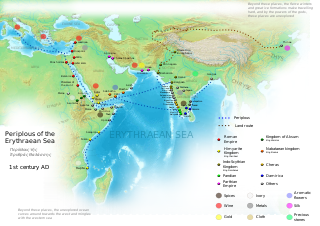
WThe Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, also known by its Latin name as the Periplus Maris Erythraei, is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports like Berenice Troglodytica along the coast of the Red Sea, and others along Horn of Africa, the Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean, including the modern-day Sindh region of Pakistan and southwestern regions of India. The text has been ascribed to different dates between the first and third centuries, but a mid-first century date is now the most commonly accepted. While the author is unknown, it is clearly a firsthand description by someone familiar with the area and is nearly unique in providing accurate insights into what the ancient Hellenic world knew about the lands around the Indian Ocean.
 W
WThe Red Sea Flotilla was part of the Regia Marina Italia based at Massawa in the colony of Italian Eritrea, part of Italian East Africa. In World War II, the Red Sea Flotilla was active against the East Indies Station of the Royal Navy, from the Italian declaration of war on 10 June 1940 until the fall of Massawa on 8 April 1941.