 W
WThe Central Atlantic magmatic province (CAMP) is the Earth's largest continental large igneous province, covering an area of roughly 11 million km2. It is composed mainly of basalt that formed before Pangaea broke up in the Mesozoic Era, near the end of the Triassic and the beginning of the Jurassic periods. The subsequent breakup of Pangaea created the Atlantic Ocean, but the massive igneous upwelling provided a legacy of basaltic dikes, sills, and lavas now spread over a vast area around the present central North Atlantic Ocean, including large deposits in northwest Africa, southwest Europe, as well as northeast South and southeast North America. The name and CAMP acronym were proposed by Andrea Marzoli and adopted at a symposium held at the 1999 Spring Meeting of the American Geophysical Union.
 W
WThe Chon Aike Formation is an extensive geological formation, present in the Deseado Massif in north-central Santa Cruz Province, Patagonia, Argentina. It covers an area of approximately 100,000 square kilometres (39,000 sq mi) and consists of rhyolitic volcanic rocks, particularly ignimbrites and lavas, with smaller amounts of agglomerates and tuffs. Within dacitic rocks, plant fossils have been found.
 W
WThe Drakensberg Group is a geological group named after the Drakensberg mountain range where in its uppermost sections the rocks are found. The Drakensberg Group lies over most of Lesotho and localities in the Eastern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal, and Free State provinces of South Africa. It forms part of the greater Karoo Igneous Province, which occurs over an extensive area of southern Africa.
 W
WEagle Heights is an elevated area located south of Koksilah Ridge on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It is centered at 48°40′N, 123°46′W. Its summit lies about 836 meters above sea level. Populated areas where it is visible include North Saanich, Sidney, and Shawnigan Lake.
 W
WThe Fundy Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin on the Atlantic coast of southeastern Canada. It contains three sub-basins; the Fundy sub-basin, the Minas Basin and the Chignecto Basin. These arms meet at the Bay of Fundy, which is contained within the rift valley. From the Bay of Fundy, the Minas Basin trends northeast to Nova Scotia. Chignecto Bay runs from the Bay of Fundy northwest between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia which is separated from the waters of the Northumberland Strait by the Isthmus of Chignecto. The Fundy Basin is best known for the bay it contains. The Bay of Fundy is home to huge tidal changes and tidal bores. It is part of the system of Eastern North America Rift Basins.
 W
WNacientes del Biobío Formation is a geological formation that crops out near the uppermost reaches of Bío Bío River, in south-central Chile, and nearby areas of Argentina. The formation is made up of basalt and pyroclastic rocks and marine sedimentary rocks, such as sandstone and mudstone. Some less abundant sedimentary lithologies are conglomerate, volcaniclastic sedimentary rock. The formation is intruded by Grupo Plutónico Galletué which is of Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous age. Further north in Chile the formation is similar to Nacientes del Teno Formation while in Argentina it is similar to Los Molles Formation and Lotena Formation.
 W
WLa Negra Formation is a geologic formation of Jurassic age, composed chiefly of volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks, located in the Coast Range of northern Chile. The formation originated in marine and continental (terrestrial) conditions, and bears evidence of submarine volcanism as well as large explosive eruptions. The volcanism of La Negra Formation is thought to have lasted for about five million years.
 W
WThe Noreán Formation is a geological formation of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, the Serranía de San Lucas and as basement underlying the southernmost Lower and northern Middle Magdalena Valleys. The formation consists of volcanic and pyroclastic lavas that range from andesites to rhyolites. Vitric, lithic and crystal tuffs and andesitic dikes and hypabyssal bodies are also present in the formation.
 W
WThe Ochoco Mountains are a mountain range in central Oregon in the United States, located at the western end of the Blue Mountains. They were formed when Permian, Triassic, and Jurassic rocks were slowly uplifted by volcanic eruptions to form the Clarno Formation. Today, the highest point in the range is Lookout Mountain. The dominant vegetation on the west side of the range is old-growth ponderosa pine; on the east side, western juniper is common. The western area of the mountains is administered by the Ochoco National Forest, while the southeastern section is part of the Malheur National Forest. The Ochoco Mountains are used for hiking, camping, bird watching, rockhounding, and hunting, as well as cross-country skiing in the winter.
 W
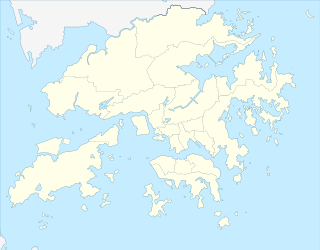
WTai Mo Shan is the highest peak in Hong Kong, with an elevation of 957 metres (3,140 ft). It is also the tallest coastal peak in Southern China and second tallest coastal peak in China after Mount Lao, and located at approximately the geographical centre of the New Territories.
 W
WTobífera Formation is a volcano-sedimentary formation of Middle to Late Jurassic age. The formation is crops out in the Magallanes Region in southern Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego of Chile, the Santa Cruz Province of southern Argentina, and in the subsurface of the Malvinas Basin offshore Argentina and the Falkland Islands.
 W
WThe Watchung Mountains are a group of three long low ridges of volcanic origin, between 400 and 500 feet high, lying parallel to each other in northern New Jersey in the United States. The Watchung Mountains are known for their numerous scenic vistas overlooking New York City, Newark and New Jersey skylines, as well as their isolated ecosystems containing rare plants, endangered wildlife, rich minerals, and globally imperiled trap rock glade communities. The ridges traditionally contained the westward spread of urbanization, forming a significant geologic barrier beyond the piedmont west of the Hudson River; the town of Newark, for example, once included lands from the Hudson to the base of the mountains. Later treaties moved the boundary to the top of the mountain, to include the springs.