 W
WAnnapurna is a massif in the Himalayas in north-central Nepal that includes one peak over 8,000 metres (26,000 ft), thirteen peaks over 7,000 metres (23,000 ft), and sixteen more over 6,000 metres (20,000 ft). The massif is 55 kilometres (34 mi) long, and is bounded by the Kali Gandaki Gorge on the west, the Marshyangdi River on the north and east, and by Pokhara Valley on the south. At the western end, the massif encloses a high basin called the Annapurna Sanctuary. The highest peak of the massif, Annapurna I Main, is the tenth highest mountain in the world at 8,091 metres (26,545 ft) above sea level. Maurice Herzog led a French expedition to its summit through the north face in 1950, making it the first of the eight-thousanders to be climbed and the only 8,000 meter-peak to be conquered on the first try.
 W
WThe Dhaulagiri massif in Nepal extends 120 km (70 mi) from the Kaligandaki River west to the Bheri. This massif is bounded on the north and southwest by tributaries of the Bheri River and on the southeast by the Myagdi Khola. Dhaulagiri is the seventh highest mountain in the world at 8,167 metres (26,795 ft) above sea level, and the highest mountain within the borders of a single country (Nepal). It was first climbed on 13 May 1960 by a Swiss/Austrian/Nepali expedition.
 W
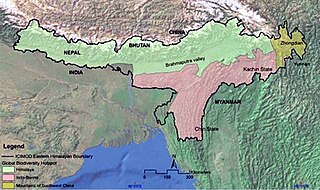
WThe Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is widely considered a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity.
 W
WGanesh Himāl is a sub-range of the Himalayas located mostly in north-central Nepal, but some peaks lie on the border with Tibet. The Trisuli Gandaki valley on the east separates it from the Langtang Himal; the Budhi (Buri) Gandaki valley and the Shyar Khola valley on the west separate it from the Sringi Himal and the Mansiri Himal. The range lies about 70 km north-northwest of Kathmandu.
 W
WThe Gurans Himal is a small subrange of the Himalayas in far western Nepal. It is little-known, since it does not contain any 8000 metre peaks, or even any peaks above 7,200 metres. Its highest peak is Api, 7,132 m (23,399 ft), which, despite its relatively low height compared to the major Himalayan peaks, rises dramatically from a low base, as do the other significant peaks of the Gurans Himal.
 W
WKangchenjunga, also spelled Kanchenjunga, is the third highest mountain in the world. It rises with an elevation of 8,586 m (28,169 ft) in a section of the Himalayas called Kangchenjunga Himal delimited in the west by the Tamur River, in the north by the Lhonak Chu and Jongsang La, and in the east by the Teesta River. It lies between Nepal and Sikkim, India, with three of the five peaks directly on the border, and the remaining two in Nepal's Taplejung District.
 W
WLangtang is a region in the north-central Himalayas of the Bagmati province of Nepal. Situated 51 kilometres north of the Kathmandu Valley, the region is renowned for hosting the Langtang national park which eventually constitutes the border with the Tibet autonomous region of China. About 4,500 people reside inside the park, and many more depend on it for timber and firewood.
 W
WThe Himachal Range – also called the Lower Himalayan Range or Lesser Himalaya – is a major east-west mountain range with elevations 3,700 to 4,500 m along the crest, paralleling the much higher High Himalayas range from the Indus River in Pakistan across northern India, Nepal and Bhutan but then the two ranges become increasingly difficult to differentiate east of Bhutan as the ranges approach the Brahmaputra River. The Himachal range also parallels the lower Shiwalik or Churia Range to the south. The Pir Panjal is the largest range of the Lesser Himalayas.
 W
WThe Himachal Range – also called the Lower Himalayan Range or Lesser Himalaya – is a major east-west mountain range with elevations 3,700 to 4,500 m along the crest, paralleling the much higher High Himalayas range from the Indus River in Pakistan across northern India, Nepal and Bhutan but then the two ranges become increasingly difficult to differentiate east of Bhutan as the ranges approach the Brahmaputra River. The Himachal range also parallels the lower Shiwalik or Churia Range to the south. The Pir Panjal is the largest range of the Lesser Himalayas.
 W
WThe Himachal Range – also called the Lower Himalayan Range or Lesser Himalaya – is a major east-west mountain range with elevations 3,700 to 4,500 m along the crest, paralleling the much higher High Himalayas range from the Indus River in Pakistan across northern India, Nepal and Bhutan but then the two ranges become increasingly difficult to differentiate east of Bhutan as the ranges approach the Brahmaputra River. The Himachal range also parallels the lower Shiwalik or Churia Range to the south. The Pir Panjal is the largest range of the Lesser Himalayas.
 W
WMahālangūr Himāl is a section of the Himalayas in northeast Nepal and south-central Tibet of China extending east from the pass Nangpa La between Rolwaling Himal and Cho Oyu, to the Arun River. It includes Mount Everest, Lhotse, Makalu, and Cho Oyu — four of Earth's six highest peaks. On the Tibetan side it is drained by the Rongbuk and Kangshung Glaciers and on the Nepali side by Barun, Ngojumba and Khumbu Glaciers and others. All are tributaries to the Koshi River via Arun River on the north and east or Dudh Kosi on the south.
 W
WMansiri Himal is a small, high subrange of the Himalayas in north-central Nepal, about 100 km (62 mi) northwest of Kathmandu. The Marsyangdi River separates the Mansiri from the Annapurnas to the southwest, then an upper tributary Dudh Khola separates Peri Himal to the northwest. On the east side, the Burhi (Budhi) Gandaki separates the Mansiri from Ganesh Himal, Serang or Sringi Himal and Kutang Himal. All these streams are tributary to the Gandaki.
 W
WRolwāling Himāl, , knows as a (Gaurishankar) rural municipality, is a section of the Himalayas in east-central Nepal along the Tibet border. Rolwaling Himal includes Melungtse 7181m and Melungtse II 7023m inside Tibet and Gaurishankar 7134m on the Nepal border with some 50 additional peaks over 6000m, all extending from the Nangpa La pass where the Mahalangur section begins, southwest to the Tamakosi River. The Labuche Himal section rises beyond the Tamakosi to the northwest. Rolwaling Himal is bounded on the south by the Rolwaling Valley which contain several small sherpa villages Tasi Nam, Simigau and Beding under rolwaling valley, Tasi Nam is the largest town of the area. Five to six days are required to reach Namche Bazaar after Tasilapcha pass. Visitors can trek to Everest base camp by crossing Tasilapcha or fly from Kathmandu to Lukla.
 W
WThe Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches from the Indus River about 2,400 km (1,500 mi) eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning across the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. It is 10–50 km (6.2–31.1 mi) wide with an average elevation of 1,500–2,000 m (4,900–6,600 ft). Between the Teesta and Raidāk Rivers in Assam is a gap of about 90 km (56 mi). In some Sanskrit texts, the region is called Manak Parbat. Sivalik literally means 'tresses of Shiva’. Sivalik region is home to the Soanian archaeological culture.
 W
WWestern Himalaya refers to the western half of the Himalayas, stretching from Badakhshan in northeastern Afghanistan/southern Tajikistan, Pakistan through North India (Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh and Himachal Pradesh.