 W
WAcanthopholis is a genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur in the family Nodosauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period of England. A single species, A. horrida, exists.
 W
WAnkistrodon is an extinct genus of archosauriform known from the Early Triassic Panchet Formation of India. First thought to be a theropod dinosaur, it was later determined to be a proterosuchid. The type species is A. indicus, described by prolific British zoologist Thomas Henry Huxley in 1865. One authority in the 1970s classified Ankistrodon as a senior synonym of Proterosuchus.
 W
WDasyceps is an extinct genus of zatracheidid temnospondyl from the early Permian of England.
 W
WEuskelosaurus is a semi-bipedal plateosaurid sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Late Triassic of South Africa and Lesotho. Fossils have only been recovered from the lower Elliot Formation in South Africa and Lesotho, and in one locality in Zimbabwe.
 W
WHomalodotherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals native to South America. Fossils of Homalodotherium have been found in the Middle Miocene Santa Cruz Formation of Argentina and the Río Frías Formation of Chile.
 W
WHyperodapedon is a genus of rhynchosaurs from the Late Triassic period. Fossils of the genus have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe and North and South America. Its first discovery and naming was found by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1859. Hyperodapedon was a herbivore that used its beaked premaxilla and hindlimbs to dig for plants in dry land.
 W
WHypsilophodon is an ornithischian dinosaur genus from the Early Cretaceous period of England. It has traditionally been considered an early member of the group Ornithopoda, but recent research has put this into question.
 W
WHyraxes, also called dassies, are small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Typically, they measure between 30 and 70 centimetres long and weigh between 2 and 5 kilograms. They are superficially similar to pikas and marmots, but are more closely related to elephants and manatees.
 W
WHyraxes, also called dassies, are small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Typically, they measure between 30 and 70 centimetres long and weigh between 2 and 5 kilograms. They are superficially similar to pikas and marmots, but are more closely related to elephants and manatees.
 W
WMegalosauridae is a monophyletic family of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea, closely related to the family Spinosauridae. Some members of this family include Megalosaurus, Torvosaurus, Eustreptospondylus, and Afrovenator. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dinosaurs, although they became extinct by the end of the Jurassic period. They were a relatively primitive group of basal tetanurans containing two main subfamilies, Megalosaurinae and Afrovenatorinae, along with the basal genus Eustreptospondylus, an unresolved taxon which differs from both subfamilies.
 W
WMicropholis is an extinct genus of dissorophoid temnospondyl. Fossils have been found from the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Karoo Basin in South Africa and are dated to the Induan. Micropholis is the only post-Permian dissorophoid and the only dissorophoid in what is presently the southern hemisphere and what would have been termed Gondwana during the amalgamation of Pangea.
 W
WThe Parastacidae are the family of freshwater crayfish found in the Southern Hemisphere. The family is a classic Gondwana-distributed taxon, with extant members in South America, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand, and New Guinea, and extinct taxa also in Antarctica.
 W
WPholidogaster is an extinct genus of tetrapod that lived during the Middle Carboniferous period. Pholidogaster is known from only two specimens found in Gilmerton, Scotland. Historically it was one of the first to show science the evolutionary link between fish and amphibians.
 W
WPristerodon is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Late Permian of South Africa, Zambia and India.
 W
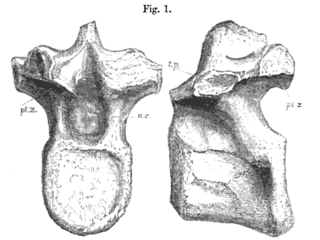
WSyngonosaurus is an extinct genus of ornithopod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. It was an iguanodontian discovered in England and was first described in 1879. The type species, S. macrocercus, was described by British paleontologist Harry Seeley in 1879 and it was later synonymised with Acanthopholis, but the genus was reinstated in a 2020 study, when Syngonosaurus and Eucercosaurus were reinterpreted as basal iguanodontians.
 W
WOrycteropodidae is a family of afrotherian mammals. Although there are many fossil species, the only species surviving today is the aardvark, Orycteropus afer. Orycteropodidae is recognized as the only family within the order Tubulidentata, so the two are effectively synonyms.