 W
WThe Zambezian region is a large biogeographical region in Africa. The Zambezian region includes woodlands, savannas, grasslands, and thickets, extending from east to west in a broad belt across the continent. The Zambezian region lies south of the rainforests of the Guineo-Congolian region. The Zambezian region is bounded by deserts and xeric shrublands on the southwest, the Highveld grasslands of South Africa to the south, and the subtropical Maputaland forests on the southeast.
 W
WAngolan miombo woodlands cover most of central Angola and extend into the Democratic Republic of Congo. They are part of the larger miombo ecosystem that covers much of eastern and southern Africa.
 W
WAngolan mopane woodlands are situated in southwestern Angola, extending into northern Namibia. This ecosystem surrounds Etosha Pan, which is considered a separate ecoregion. The mopane trees are the main type of vegetation.
 W
WThe Bushveld is a sub-tropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa. It encompasses most of Limpopo Province and a small part of the North West Province of South Africa, the Central and North-East Districts of Botswana and the Matabeleland South and part of the Matabeleland North provinces of Zimbabwe. Kruger National Park in South Africa has a number of 'Bushveld' camps.
 W
WThe densely forested Central Zambezian miombo woodlands that cut across southern central Africa are one of the largest ecoregions on the continent and home to a great variety of wildlife, including many large mammals.
 W
WThe Eastern miombo woodlands (AT0706) are an ecoregion of grassland and woodland in northern Mozambique, southern Tanzania, and southeastern Malawi.
 W
WThe Etosha pan is a large endorheic salt pan, forming part of the Kalahari Basin in the north of Namibia. It is a hollow in the ground in which water may collect or in which a deposit of salt remains after water has evaporated. The 120-kilometre-long (75-mile-long) dry lakebed and its surroundings are protected as Etosha National Park, Namibia's second-largest wildlife park, covering 22,270 km2. The pan is mostly dry but after a heavy rain it will acquire a thin layer of water, which is heavily salted by the mineral deposits on the surface.
 W
WThe Itigi-Sumbu thicket is an ecoregion consisting of two small areas of thick shrubland in Tanzania and in Zambia, East Africa.
 W
WThe Makgadikgadi Pan, a salt pan situated in the middle of the dry savanna of north-eastern Botswana, is one of the largest salt flats in the world. The pan is all that remains of the formerly enormous Lake Makgadikgadi, which once covered an area larger than Switzerland, but dried up tens of thousands of years ago. Recent studies of human mitochondrial DNA suggest that modern Homo sapiens first began to evolve in this region some 200,000 years ago, when it was a vast, exceptionally fertile area of lakes, rivers, marshes, woodlands and grasslands especially favorable for habitation by evolving hominins and other mammals.
 W
WThe Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
 W
WThe Western Zambezian grasslands is a tropical grassland ecoregion of eastern Zambia and adjacent parts of Angola.
 W
WThe Zambezian and mopane woodlands is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of southeastern Africa.
 W
WThe Zambezian Baikiaea woodlands is an ecoregion in Africa. It includes dry deciduous forest and woodland, thicket, and grassland, dominated by the tree Baikiaea plurijuga. The ecoregion has a semi-arid climate, and is a transition between more humid miombo woodlands to the north, and the drier Kalahari Acacia-Baikiaea woodlands to the south.
 W
WThe Zambezian coastal flooded savanna is a flooded grasslands and savannas ecoregion in Mozambique. It includes the coastal flooded savannas and grasslands in the deltas of the Zambezi, Pungwe, Buzi, and Save rivers.
 W
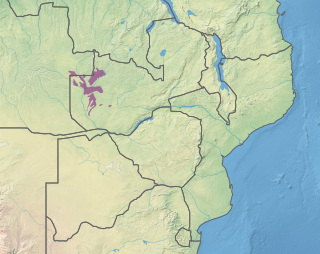
WThe Zambezian cryptosepalum dry forests, also known as the Zambezian evergreen dry forests, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of Southern Africa. It consists of several areas of thick forest in western Zambia and adjacent Angola. It is one of the largest areas of tropical evergreen forest outside the equatorial zone.
 W
WThe Zambezian flooded grasslands is an ecoregion of southern and eastern Africa that is rich in wildlife.