 W
WThe Adamantina Formation is a geological formation in the Bauru Basin of western São Paulo state, in southeastern Brazil.
 W
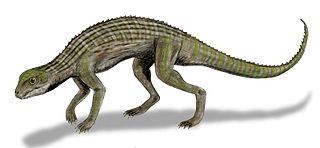
WAdamantinasuchus is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorph from and named after the Late Cretaceous Adamantina Formation of Brazil. It is known from only one fossil, holotype UFRJ-DG 107-R, collected by William Nava. The fossil consists of a partial skull, fragmentary limb bones and a few brokenen vertebrae, and was found 25 km SW of the town of Marilia, near a reservoir dam. Adamantinasuchus was approximately 60 cm long from nose to tail, and would have only weighed a few kilograms.
 W
WAdamantisaurus is a poorly-known genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. It is only known from six tail vertebrae but, as a sauropod, it can be assumed that this dinosaur was a very large animal with a long neck and tail.
 W
WAeolosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. Like most sauropods, it would have been a quadrupedal herbivore with a long neck and tail. Aeolosaurus is well known for a titanosaur, as it is represented by the remains of several individuals belonging to at least three species. However, like most titanosaurs, no remains of the skull are known. The holotype of Aeolosaurus rionegrinus consists of a series of seven tail vertebrae, as well as parts of both forelimbs and the right hindlimb. It was discovered in the Angostura Colorada Formation in Argentina, which dates from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 83 to 74 million years ago.
 W
WAntarctosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. The type species, Antarctosaurus wichmannianus, and a second species, Antarctosaurus giganteus, were described by prolific German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene in 1929. Three additional species of Antarctosaurus have been named since then but later studies have considered them dubious or unlikely to pertain to the genus.
 W
WAplestosuchus is an extinct genus of baurusuchid mesoeucrocodylian known from the Late Cretaceous Adamantina Formation of São Paulo, southern Brazil. It contains a single species, Aplestosuchus sordidus. A. sordidus is represented by a single articulated and nearly complete skeleton, preserving the remains of an unidentified sphagesaurid crocodyliform in its abdominal cavity. The specimen represents direct evidence of predation between different taxa of crocodyliforms in the fossil record.
 W
WArmadillosuchus is an extinct genus of sphagesaurid crocodylomorph. It was described in February 2009 from the late Campanian to early Maastrichtian Adamantina Formation of the Bauru Basin in Brazil, dating to approximately 70 Ma. Armadillosuchus length was estimated on 2 metres (6.6 ft) with an estimated body mass of 120 kg (260 lb).
 W
WBaurusuchus is an extinct member of the ancestral crocodilian lineage, which lived in Brazil from 90 to 83.5 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period. Technically, it is a genus of baurusuchid mesoeucrocodylian. It was a terrestrial predator and scavenger, about 3.5 to 4 metres long and 80 kilograms (176 lb) in weight. Baurusuchus lived during the Turonian to Santonian stages of the Late Cretaceous Period, in Adamantina Formation, Brazil. It gets its name from the Brazilian Bauru Group. It was related to the earlier-named Cynodontosuchus rothi, which was smaller, with weaker dentition. The three species are B. pachechoi, named after Eng Joviano Pacheco, its discoverer, B. salgadoensis and B. albertoi. The latter species is disputed. Its relatives include the similarly sized Stratiotosuchus from the Adamantina Formation, and Pabweshi, from the Pakistani Pab Formation.
 W
WCaipirasuchus is an extinct genus of sphagesaurid notosuchians known from the Late Cretaceous of northern São Paulo State, southeastern Brazil. The type species, C. paulistanus, was named in 2011. A second species, C. montealtensis, was referred to Caipirasuchus in 2013 after having been named in 2008 as a species of Sphagesaurus. A third species, C. stenognathus, was described in 2014. A fourth species, C. minerius, was described in 2018.
 W
WCampinasuchus is an extinct genus of baurusuchid mesoeucrocodylian from Minas Gerais State of Brazil.
 W
WGoniopholis is an extinct genus of goniopholidid crocodyliform that lived in Europe and Africa during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. Being semi-aquatic it is very similar to modern crocodiles. It ranged from 2–4 metres in length, and would have had a very similar lifestyle to the American alligator or Nile crocodile.
 W
WMariliasuchus is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous notosuchian mesoeucrocodylian found near Marilia, Brazil. The first bone remains were found and collected in 1995 by Brazilian paleontologist William Nava, in red rocks from the fossiliferous Adamantina Formation. Four years later, it was described as Mariliasuchus amarali, by Brazilian paleontologists Ismar de Souza Carvalho and Reinaldo J. Bertini.
 W
WMaxakalisaurus is a genus of aeolosaurid dinosaur, found in the Adamantina Formation of Brazil, 45 kilometers from the city of Prata, in the state of Minas Gerais in 1998. It was related to Saltasaurus, a sauropod considered unusual because it had evolved apparently defensive traits, including bony plates on its skin and vertical plates along its spine; such osteoderms have also been found for Maxakalisaurus. The genus name is derived from the tribe of the Maxakali; Topa is one of their divinities.
 W
WMontealtosuchus was an extinct genus of terrestrial crocodyliform. It was discovered in 2004 in the Bauru Basin of Brazil, from Turonian-Santonian deposits of the Adamantina Formation. The species was described in 2007, and assigned to the family Peirosauridae. The type species is M. arrudacamposi. The genus takes its name from the type locality in Monte Alto municipality.
 W
WMorrinhosuchus is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodyliform from the Late Cretaceous Adamantina Formation of Brazil. It is known from a mandible and a portion of the front of the skull collected from the municipality of Monte Alto in São Paulo state. Morrinhosuchus refers to Morrinho de Santa Luzia, a hill nearby the collection site of the holotype, while luziae refers to the chapel of Santa Luzia, which is located on top of the hill.
 W
WPycnonemosaurus is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that belonged to the family Abelisauridae. It was found in the Upper Cretaceous red conglomerate sandstones of the "Cabembe Unit", Mato Grosso, Brazil, and it lived about 70 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous.
 W
WRoxochampsa is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph from the Late Cretaceous of Brazil belonging to the sebecosuchian clade Itasuchidae. The type species is R. paulistanus.
 W
WStratiotosuchus is an extinct genus of baurusuchid mesoeucrocodylian from the Adamantina Formation in Brazil. It lived during the Late Cretaceous. The first fossils were found in the 1980s, and the type species Stratiotosuchus maxhechti was named in 2001. A hyperpredator, it and other baurusuchids may have filled niches occupied elsewhere by theropod dinosaurs.