 W
WThe 1762 Arakan earthquake occurred at about 17:00 local time on 2 April, with an epicentre somewhere on the coast from Chittagong to Arakan in modern Burma. It had an estimated magnitude of as high as 8.8 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum estimated intensity of XI (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a local tsunami in the Bay of Bengal and caused at least 200 deaths. The earthquake was associated with major areas of both uplift and subsidence. It is also associated with a change in course of the Brahmaputra River to from east of Dhaka to 150 kilometres (93 mi) to the west via the Jamuna River.
 W
WThe 1839 Ava earthquake, also known as the Amarapura earthquake or Inwa earthquake was a catastrophic disaster that struck Burma at around 04:00 in the morning of March 23. This earthquake was one of the biggest in the country since 1762.
 W
WThe 1912 Maymyo earthquake was a powerful earthquake that struck Burma on the morning of May 23 1912, with an epicenter near Taunggyi and Pyin Oo Lwin. It was one of the largest earthquakes in the country.
 W
WThe 1930 Bago earthquake, also known as the Swa earthquake struck Burma on May 5 with a magnitude between 7.3 and 7.5. This earthquake was one of the most destructive to hit the country and one of several earthquakes to affect the country between 1929 and 1931.
 W
WThe 1930 Pyu earthquake occurred on December 4 at 01:21 local time. The epicenter was located north to Bago, Burma, then part of British India. The magnitude of the earthquake was estimated at Mw 7.3, or Ms 7.3.
 W
WThe 1931 Myitkyina earthquake, or also known as the 1931 Kamaing earthquake, occurred on January 28 at 02:35 local time. It was located in northern Burma, then part of British India. The magnitude of this earthquake was put at Mw 7.6. According to some sources the depth was 35 km, and according to a study of Phyo M. M. the depth was 5 to 30 km.
 W
WThe 1946 Sagaing earthquakes struck central Burma at 15:17 local time on September 12. The first earthquake registered a magnitude of 8.0 and was followed-up by an M7.8 main shock. Both events remain some of the largest in the country since the 1762 Arakan Earthquake.
 W
WThe 1956 Sagaing earthquake occurred on July 16, 1956, at 15:07 UTC. The earthquake was located near Sagaing, Burma. This earthquake had a magnitude of Mw 7.1.
 W
WThe 1975 Bagan earthquake occurred on July 8 at 6:34 pm local time in Bagan, Myanmar. Many important stupas and temples were destroyed. The strongest intensity was felt in the towns of Nyaung-U, Pakokku, and Yesagyo, and in the Myaing townships on the confluence of the Ayeyawady River. Damages were also reported in Chauk and Natmauk townships. It had a magnitude of Mw 7.0.
 W
WOn November 6, 1988, an earthquake struck Lancang County, Yunnan, near the border with Shan State, Burma (Myanmar) with a moment magnitude of Mw 7.7. It is the largest earthquake to affect both Yunnan Province and Shan State since 1970 and 1912, respectively. In January 1970, a Mw 7.1 struck Tonghai County, resulting in over 15,000 deaths, and in May 1912, Shan State was hit with a Mw 7.7 that caused serious damage in the region.
 W
WThe 1988 Myanmar-India earthquake struck the Sagaing Region of Myanmar, about 30 km from the border with India on 6 August at 7:06 am MMT with a moment magnitude of 7.3. It was the largest earthquake in the world that year, after a Mw 7.8 in the Gulf of Alaska. Twelve people were killed, and 30 were injured as a result. Serious damage were reported in India and Bangladesh. The earthquake was reportedly felt in the Soviet Union.
 W
WThe 1997 Chittagong earthquake occurred on 21 November at 11:23 UTC in the Bangladesh-India-Myanmar border region. It had a magnitude of Mw 6.1. The epicenter was located in southern Mizoram, India. No fatalities were reported there, but 23 people were killed in Chittagong when a five-story building collapsed in Bangladesh. The shaking could also be felt in Dhaka.
 W
WThe 2003 Taungdwingyi earthquake struck central Myanmar at midnight, on 21 September with a magnitude of Mwb 6.6.
 W
WThe 2011 Burma earthquake occurred with a magnitude 6.9 Mw on 24 March. It had an epicenter in the eastern part of Shan State in Burma (Myanmar) with a hypocenter 10 km deep. It had two aftershocks, one of magnitude 4.8, another at magnitude 5.4, and two subsequent shocks at magnitude 5.0 and 6.2. The quake's epicentre was 70 miles (110 km) from the northern Thai city of Chiang Rai, north of Mae Sai and southeast of Kentung.
 W
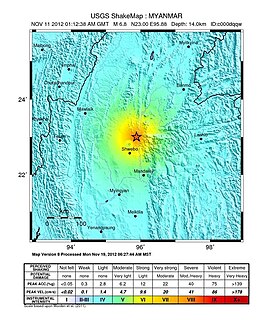
WThe 2012 Shwebo earthquake occurred at 07:42 local time on 11 November in Myanmar. It had a magnitude of 6.8 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The epicenter was near the town of Male, 52 km NNE of the city of Shwebo, 64 km west of Mogok and 120 km north of Mandalay. Significant damage and possible casualties have been reported from near the epicenter, with up to 26 people dead and many more injured. Part of a bridge under construction fell into the Irrawaddy River near Shwebo and a gold mine collapsed at Sintku. An aftershock with a magnitude of 5.8 followed at 17:24 local time.
 W
WA magnitude 6.9 earthquake struck Myanmar 135 km (84 mi) north-west of Mandalay on April 13 with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong). It struck at 8:25 pm local time, and was centered in an isolated area. The estimated depth was 134 km. It lasted for around one minute according to Xinhua reporters.
 W
WA magnitude 6.8 earthquake struck Myanmar 25 km (16 mi) west of Chauk on 24 August 2016 with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong). It struck at 5:04 pm local time, and was centered in an isolated area. The estimated depth was 84.1 km. Tremors from the earthquake were felt in Yangon, in the eastern cities of Patna, Guwahati, and Kolkata in India, in Bangkok in Thailand and in Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh. According to reports, several temples in the nearby ancient city of Bagan were damaged and four people were reported dead.
 W
WThe November 2011 Myanmar earthquake was a magnitude 5.9 (Mw) moderate earthquake epicentered at Myanmar, about 130 km east of Manipur capital Imphal, India, on 21 November 2011 at 09:45 local time. The tremor was also felt in Indian states of Assam, Nagaland, Kolkata and some areas of north Bengal and in Bangladesh.