 W
WAllyl isothiocyanate (AITC) is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH2CHCH2NCS. This colorless oil is responsible for the pungent taste of mustard, radish, horseradish, and wasabi. This pungency and the lachrymatory effect of AITC are mediated through the TRPA1 and TRPV1 ion channels. It is slightly soluble in water, but more soluble in most organic solvents.
 W
WAmoscanate (INN), also known as nithiocyamine, is an experimental anthelmintic agent of the arylisothiocyanate class which was found to be highly effective in animals against the four major species of schistosomes which infect humans, and is also highly active against hookworm infection. However, significant liver toxicity was seen in lab animals at higher doses. The ether analogue of amoscanate, nitroscanate, is used in veterinary medicine as an anthelmintic.
 W
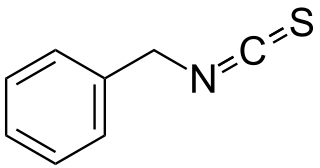
WBenzyl isothiocyanate (BITC) is an isothiocyanate found in plants of the mustard family.
 W
WBitoscanate is an organic chemical compound used in the treatment of hookworms. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
 W
W4,4'-Diisothiocyano-2,2'-stilbenedisulfonic acid (DIDS) is an anion exchange inhibitor, blocking reversibly, and later irreversibly, exchangers such as chloride-bicarbonate exchanger.
 W
WFluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is a derivative of fluorescein used in wide-ranging applications including flow cytometry. First described in 1942, FITC is the original fluorescein molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate reactive group (-N=C=S), replacing a hydrogen atom on the bottom ring of the structure. It is typically available as a mixture of isomers, fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate (5-FITC) and fluorescein 6-isothiocyanate (6-FITC). FITC is reactive towards nucleophiles including amine and sulfhydryl groups on proteins. It was synthesized by Robert Seiwald and Joseph Burckhalter in 1958.
 W
WFourphit (4-isothiocyanato-1-[1-phenylcyclohexyl]piperidine) is a covalent binding NMDA antagonist, dopaminergic and sigma receptor agonist.
 W
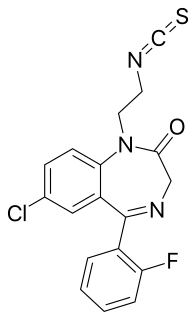
WIrazepine is a benzodiazepine derivative containing isothiocyanate functional group. It is a non-competitive benzodiazepine binding site antagonist. Irazepine and other alkylating benzodiazepine, kenazepine, bind to brain benzodiazepine receptors in a non-competitive (covalent) fashion in vitro, and may exert a long-lasting anticonvulsant effect.
 W
WIsothiocyanate is the chemical group –N=C=S, formed by substituting the oxygen in the isocyanate group with a sulfur. Many natural isothiocyanates from plants are produced by enzymatic conversion of metabolites called glucosinolates. These natural isothiocyanates, such as allyl isothiocyanate, are also known as mustard oils. An artificial isothiocyanate, phenyl isothiocyanate, is used for amino acid sequencing in the Edman degradation.
 W
W(R)-p-Isothiocyanatobenzoylecgonine methyl ester (p-ISOCOC) is a cocaine analogue and irreversible (covalent) binding inhibitor of the cocaine receptor, as well as irreversible blocker of dopamine uptake by DAT. p-Isococ also blocks the high-affinity cocaine site in preference to the low-affinity site.
 W
WMetaphit is a research chemical that acts as an acylator of NMDARAn, sigma and DAT binding sites in the CNS. It is the m-isothiocyanate derivative of phencyclidine (PCP) and binds irreversibly to the PCP binding site on the NMDA receptor complex. However, later studies suggest the functionality of metaphit is mediated by sites not involved in PCP-induced passive avoidance deficit, and not related to the NMDA receptor complex. Metaphit was also shown to prevent d-amphetamine induced hyperactivity, while significantly depleting dopamine content in the nucleus accumbens. Metaphit was the first acylating ligand used to study the cocaine receptor. It is a structural isomer of the similar research compound fourphit, as it and metaphit both are isothiocyanate substituted derivatives of an analogous scaffold shared with PCP.
 W
WMethyl isothiocyanate is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH3N=C=S. This low melting colorless solid is a powerful lachrymator. As a precursor to a variety of valuable bioactive compounds, it is the most important organic isothiocyanate in industry.
 W
W6-(Methylsulfinyl)hexyl isothiocyanate is a compound within the isothiocyanate group of organosulfur compounds. 6-MITC is obtained from cruciferous vegetables, chiefly wasabi. Like other isothiocyanates, it is produced when the enzyme myrosinase transforms the associated glucosinolate into 6-MITC upon cell injury.
 W
W1-Naphthyl isothiocyanate is a chemical compound which is an isothiocyanate derivative of naphthalene.
 W
WNitroscanate is an anthelmintic drug used in veterinary medicine to treat Toxocara canis, Toxascaris leonina, Ancylostoma caninum, Uncinaria stenocephala, Taenia, and Dipylidium caninum.
 W
WPhenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) is a naturally occurring isothiocyanate whose precursor, gluconasturtiin is found in some cruciferous vegetables, especially watercress.
 W
WPhenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) is a reagent used in reversed phase HPLC. PITC is less sensitive than o-phthaldehyde (OPA) and cannot be fully automated. PITC can be used for analysing secondary amines, unlike OPA.
 W
WSulforaphane is a compound within the isothiocyanate group of organosulfur compounds. It is obtained from cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cabbages. It is produced when the enzyme myrosinase transforms glucoraphanin, a glucosinolate, into sulforaphane upon damage to the plant, which allows the two compounds to mix and react. Young sprouts of broccoli and cauliflower are particularly rich in glucoraphanin.