 W
WAcanthodes is an extinct genus of spiny shark. Fossils have been found in Europe, North America, and Australia.
 W
WAcheloma is an extinct genus of temnospondyl that lived during the Early Permian. The type species is A. cumminsi.
 W
WAmynilyspes is an extinct genus of pill millipedes characterized by fourteen tergites, large eyes, and prominent spines. Individuals measure up to 30 mm (1.2 in) in length.
 W
WArchidesmus is an extinct millipede genus from the Lower Devonian Old Red Sandstone of the United Kingdom. It is the only member of the taxonomic family Archidesmidae. Individuals were up to 5 cm (2.0 in) long, and had 60 to 80 body segments decorated with tubercles (bumps) on the upper surface, and most segments possessed wing-like keels (paranota) extending to the side. The type species Archidesmus macnicoli was described by British paleontologist Benjamin Peach in 1882. A second species, A. loganensis was also described by Peach but its status as a valid species- or even a myriapod- is debated.
 W
WArchipolypoda is an extinct group of millipedes known from fossils in Europe and North America and containing the earliest known land animals. The Archipolypoda was erected by Scudder (1882) but redefined in 2005 with the description of several new species from Scotland. Distinguishing characteristics include relatively large eyes with densely packed ocelli, and modified leg pairs on the 8th body ring. Some species had prominent spines while others had a flattened appearance.
 W
WDiacodexis is an extinct genus of small herbivore mammals belonging to the family Dichobunidae which lived in North America, Europe and Asia from 55.4 mya to 46.2 mya and existing for approximately 9.2 million years .
 W
WEchinognathus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Classified as part of the family Megalograptidae, the genus contains one only species, E. clevelandi, whose fossils have been found in deposits from the Katian age of the Late Ordovician period of New York. The name of the species, clevelandi, honors William N. Cleveland, who found the specimens that were used for the description of Echinognathus.
 W
WEdaphosaurus is a genus of extinct edaphosaurid synapsids that lived in what is now North America and Europe around 303.4 to 272.5 million years ago, during the late Carboniferous to early Permian periods. American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope first described Edaphosaurus in 1882, naming it for the "dental pavement" on both the upper and lower jaws, from the Greek edaphos έδαφος and σαῦρος ("lizard").
 W
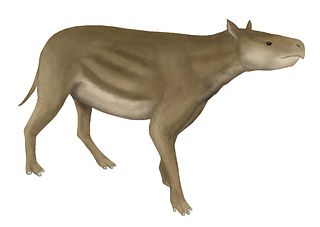
WHeptodon is an extinct genus of tapir-type herbivore of the family Helaletidae endemic to North America during the Early Eocene. It lived from 50.3—48.6 mya, existing for approximately 1.7 million years .
 W
WMeniscoessus is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. It lived toward the end of the "age of the dinosaurs" and was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It lies within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Cimolomyidae.
 W
WNeusticosaurus, is an extinct genus of marine reptile belonging to the nothosaur order, from Italy, Switzerland and Germany. At 18 cm (8 in) long, it was one of the smallest nothosaurs. Neusticosaurus probably fed on small fish.
 W
WPalmoxylon is an extinct genus of palm named from petrified wood found around the world.
 W
WPantolambda is an extinct genus of Paleocene pantodont mammal. Pantolambda lived during the middle Paleocene, and has been found both in Asia and North America.
 W
WParaceratites subnodosus is an extinct species of ammonite cephalopods in the family Ceratitidae.
 W
WPlioplatecarpus is a genus of mosasaur lizard. Like all mosasaurs, it lived in the late Cretaceous period, about 73-68 million years ago.
 W
WPolysternon is a genus of turtles in the extinct family Bothremydidae. It was described by Portis in 1882, and contains the species P. provinciale, which existed during the Cretaceous of what is now France; P. atlanticum, which existed during the Cretaceous at Laño in what is now Spain, and a new species, P. isonae, from the Late Maastrichtian of Spain.
 W
WProtypotherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals native to South America during the Miocene epoch. A number of closely related animals date back further, to the Paleocene. Fossils of Protypotherium have been found in the Deseadan Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay, Muyu Huasi Formation of Bolivia, Cura-Mallín and Río Frías Formations of Chile, and Santa Cruz, Salicas, Ituzaingó, Cerro Bandera, Chichinales, Sarmiento and Collón Curá Formations of Argentina.
 W
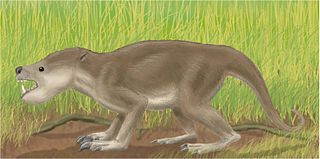
WPsittacotherium is an extinct genus of taeniodont from the Paleocene of North America. With a weight of about 50 kg and a length over 1.1 m (3.5 ft), it had the size of a large dog.
 W
WThecospondylus is a dubious genus of dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of England. Scientists are unsure as to whether Thecospondylus was a saurischian or an ornithischian.