 W
WBis(triethoxysilylpropyl)tetrasulfide is an organosulfur compound with the formula S4[C3H6Si(OEt)3]2 (Et = C2H5). The molecule consists of two trialkoxysilyl propyl groups linked with a polysulfide. It is often sold as a mixture with the trisulfide. The compound is a colorless viscous liquid that is soluble in ordinary organic solvents such as toluene. Commercial samples often are yellowish. The compound is added to rubber compositions that contain silica filler.
 W
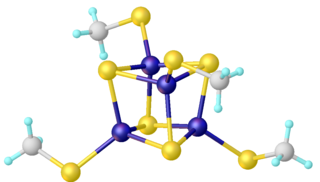
WIn biochemistry, dinitrosyl iron complexes (DNIC's) are coordination complexes with the formula [Fe(NO)2(SR)2]−. Together with Roussin esters (Fe2(NO)4(SR)2), they result from the degradation of iron-sulfur proteins by nitric oxide. Commonly the thiolate ligands are cysteinyl residues or glutathione. These metal nitrosyl complexes have attracted much attention because they serve as biochemical signals in response to oxidative stress, manifested in the formation of NO. The anions are tetrahedral.
 W
WDisulfur dinitride is the chemical compound S2N2 with a cyclic square planar structure.
 W
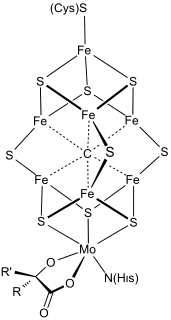
WFeMoco (FeMo cofactor) is the primary cofactor of nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen molecules N2 into ammonia (NH3) through the process known as nitrogen fixation. Containing iron and molybdenum, the cofactor is called FeMoco. Its stoichiometry is Fe7MoS9C.
 W
WHeptasulfur imide is the inorganic compound with the formula S7NH. It is a pale yellow solid that is, like elemental sulfur, highly soluble in carbon disulfide. The compound, which is only of academic interest, is representative of a family of sulfur imides Sx(NH)y.
 W
WIron–sulfur clusters are molecular ensembles of iron and sulfide. They are most often discussed in the context of the biological role for iron–sulfur proteins, which are pervasive. Many Fe–S clusters are known in the area of organometallic chemistry and as precursors to synthetic analogues of the biological clusters.
 W
WS-Nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP) is the chemical compound with the formula ONSC(CH3)2CH(NHAc)CO2H. SNAP is an S-nitrosothiol and is used as a model for the general class of S-nitrosothiols which have received much attention in biochemistry because nitric oxide and some organic nitroso derivatives serve as signaling molecules in living systems, especially related to vasodilation. SNAP is derived from the amino acid penicillamine. S-Nitrosoglutathione is a related agent.
 W
WS-Nitrosothiols, also known as thionitrites, are organic compounds or functional groups containing a nitroso group attached to the sulfur atom of a thiol. S-Nitrosothiols have the general formula RSNO, where R denotes an organic group. Originally suggested by Ignarro to serve as intermediates in the action of organic nitrates, endogenous S-nitrosothiols were discovered by Stamler and colleagues and shown to represent a main source of NO bioactivity in vivo. More recently, S-nitrosothiols have been implicated as primary mediators of protein S-nitrosylation, the oxidative modification of Cys thiol that provides ubiquitous regulation of protein function.
 W
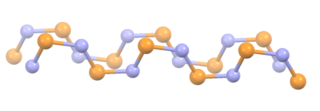
WPolysulfides are a class of chemical compounds containing chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: anions and organic polysulfides. Anions have the general formula S2−n. These anions are the conjugate bases of the hydrogen polysulfides H2Sn. Organic polysulfides generally have the formulae RSnR, where R = alkyl or aryl.
 W
WPolythiazyl, (SN)x, is an electrically conductive, gold- or bronze-colored polymer with metallic luster. It was the first conductive inorganic polymer discovered and was also found to be a superconductor at very low temperatures. It is a fibrous solid, described as "lustrous golden on the faces and dark blue-black", depending on the orientation of the sample. It is air stable and insoluble in all solvents.
 W
WPolythionates are oxoanions with the formula Sn(SO3)22- (n≥0). They occur naturally and are the products of redox reactions of thiosulfate. Polythionates are readily isolable, unlike the parent polythionic acids.
 W
WPolythionic acid is an oxoacid which has a straight chain of sulfur atoms and has the chemical formula Sn(SO3H)2 (n > 2). Trithionic acid (H2S3O6), tetrathionic acid (H2S4O6) are simple examples. They are the conjugate acids of polythionates. The compounds of n < 80 are expected to exist, and those of n < 20 have already been synthesized. Dithionic acid (H2S2O6) does not belong to the polythionic acids due to strongly different properties.
 W
WRezvilutamide is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which is under development by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine for the treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer. It is a selective androgen receptor antagonist with reduced brain distribution compared to the structurally related nonsteroidal antiandrogen enzalutamide. As of October 2020, rezvilutamide is in phase 3 clinical trials for prostate cancer. Other structural analogues of rezvilutamide besides enzalutamide include apalutamide and proxalutamide.
 W
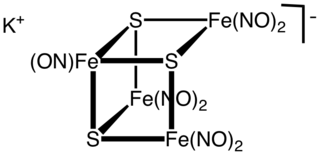
WRoussin's black salt is a chemical compound with the formula KFe4S3(NO)7. It consists of the potassium salt of the [Fe4S3(NO)7]− anion, metal nitrosyl compound. First described by Zacharie Roussin in 1858, it is one of the first synthetic iron-sulfur clusters along with the red salt also bearing his name.
 W
WRoussin’s Red Salt is the inorganic compound with the formula K2[Fe2S2(NO)4]. This metal nitrosyl was first described by Zacharie Roussin in 1858, making it one of the first synthetic iron-sulfur clusters.
 W
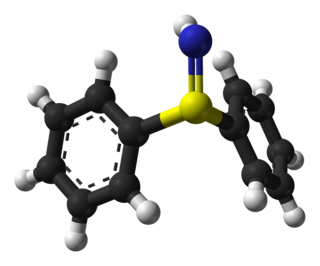
WA sulfilimine (or sulfimide) is a type of chemical compound containing a sulfur-to-nitrogen double bond. The parent compound is sulfilimine H2S=NH, which is mainly of theoretical interest.
 W
WThe sulfur oxoacids are chemical compounds that contain sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen. The best known and most important industrially used is sulfuric acid. Sulfur has several oxoacids; however, some of these are known only from their salts. The acids that have been characterised contain a variety of structural features, for example:tetrahedral sulfur when coordinated to oxygen terminal and bridging oxygen atoms terminal peroxo groups terminal S=S chains of (−S−)n
 W
WSulfur tetrachloride is an inorganic compound with chemical formula SCl4. It has only been obtained as an unstable pale yellow solid. The corresponding SF4 is a stable, useful reagent.
 W
WTetrasulfur tetranitride is an inorganic compound with the formula S4N4. This gold-poppy coloured solid is the most important binary sulfur nitride, which are compounds that contain only the elements sulfur and nitrogen. It is a precursor to many S-N compounds and has attracted wide interest for its unusual structure and bonding.
 W
WA thiosulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfur to sulfur double bond of the type RR'S=S with R and R' both alkyl or aryl residues. The thiosulfoxide has a molecular shape known as trigonal pyramidal. Its coordination is also trigonal pyramidal. The point group of the thiosulfoxide is Cs. A 1982 review concluded that there was as yet no definitive evidence for the existence of stable thiosulfoxides which can be attributed to the double bond rule which states that elements of period 3 and beyond do not form multiple bonds. The related sulfoxides of the type RR'S=O are very common. Many compounds containing a sulfur-sulfur double bond have been reported in the past although only a few verified classes of actually stable compounds exist, closely related to thiosulfoxides.