 W
WThe Amazon biome contains the Amazon rainforest, an area of tropical rainforest, and other ecoregions that cover most of the Amazon basin and some adjacent areas to the north and east. The biome contains blackwater and whitewater flooded forest, lowland and montane terra firme forest, bamboo and palm forest, savanna, sandy heath and alpine tundra. Some areas are threatened by deforestation for timber and to make way for pasture or soybean plantations.
 W
WAccording to IBGE (2004), Brazil has its territory occupied by six terrestrial biomes and one marine biome.
 W
WDeserts and xeric shrublands are a biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Deserts and xeric shrublands form the largest terrestrial biome, covering 19% of Earth's land surface area. Ecoregions in this habitat type vary greatly in the amount of annual rainfall they receive, usually less than 250 millimetres (10 in) annually except in the margins. Generally evaporation exceeds rainfall in these ecoregions. Temperature variability is also diverse in these lands. Many deserts, such as the Sahara, are hot year-round, but others, such as East Asia's Gobi, become quite cold in winter.
 W
WFlooded grasslands and savannas is a terrestrial biome of the WWF biogeographical system, consisting of large expanses or complexes of flooded grasslands. These areas support numerous plants and animals adapted to the unique hydrologic regimes and soil conditions. Large congregations of migratory and resident waterbirds may be found in these regions. However, the relative importance of these habitat types for these birds as well as more vagile taxa typically varies as the availability of water and productivity annually and seasonally shifts among complexes of smaller and larger wetlands throughout a region.
 W
WA mangrove is a shrub or small tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics, mainly between latitudes 25° N and 25° S. The total mangrove forest area of the world in 2000 was 137,800 square kilometres (53,200 sq mi), spanning 118 countries and territories.
 W
WMediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub is a biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is generally characterized by dry summers and rainy winters, although in some areas rainfall may be uniform. Summers are typically hot in low-lying inland locations but can be cool near colder seas. Winters are typically mild to cool in low-lying locations but can be cold in inland and higher locations. All these ecoregions are highly distinctive, collectively harboring 10% of the Earth's plant species.
 W
WMontane grasslands and shrublands is a biome defined by the World Wildlife Fund. The biome includes high altitude grasslands and shrublands around the world. The term "montane" in the name of the biome refers to "high altitude", rather than the ecological term which denotes the region below treeline.
 W
WA riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on fauna and aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, or even non-vegetative areas. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word riparian is derived from Latin ripa, meaning "river bank".
 W
WSeasonal tropical forest, also known as moist deciduous, semi-evergreen seasonal, tropical mixed or monsoon forests, typically contain a range of tree species: only some of which drop some or all of their leaves during the dry season. This tropical forest is classified under the Walter system as (ii) tropical climate with high overall rainfall concentrated in the summer wet season and cooler “winter” dry season: representing a range of habitats influenced by monsoon (Am) or tropical wet savannah (Aw) climates. Drier forests in the Aw climate zone are typically deciduous and placed in the Tropical dry forest biome: with further transitional zones (ecotones) of savannah woodland then tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands.
 W
WTaiga, generally referred to in North America as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches.
 W
WTemperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.
 W
WTemperate coniferous forest is a terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Temperate coniferous forests are found predominantly in areas with warm summers and cool winters, and vary in their kinds of plant life. In some, needleleaf trees dominate, while others are home primarily to broadleaf evergreen trees or a mix of both tree types. A separate habitat type, the tropical coniferous forests, occurs in more tropical climates.
 W
WTemperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The predominant vegetation in this biome consists of grass and/or shrubs. The climate is temperate and ranges from semi-arid to semi-humid. The habitat type differs from tropical grasslands in the annual temperature regime as well as the types of species found here.
 W
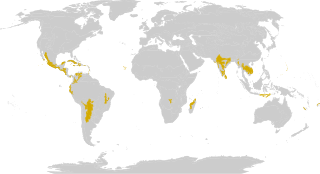
WTropical and subtropical coniferous forests are a tropical forest habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. These forests are found predominantly in North and Central America and experience low levels of precipitation and moderate variability in temperature. Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests are characterized by diverse species of conifers, whose needles are adapted to deal with the variable climatic conditions. Most tropical and subtropical coniferous forest ecoregions are found in the Nearctic and Neotropical realms, from the Mid-Atlantic states to Nicaragua and on the Greater Antilles, Bahamas, and Bermuda. Other tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregions occur in Asia. Mexico harbors the world's richest and most complex subtropical coniferous forests. The conifer forests of the Greater Antilles contain many endemics and relictual taxa.
 W
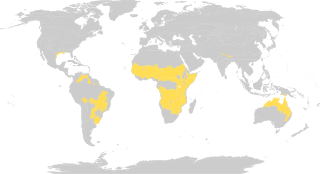
WThe tropical and subtropical dry forest is a habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature and is located at tropical and subtropical latitudes. Though these forests occur in climates that are warm year-round, and may receive several hundred centimeters of rain per year, they have long dry seasons which last several months and vary with geographic location. These seasonal droughts have great impact on all living things in the forest.
 W
WTropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is dominated by grass and/or shrubs located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and tropical latitudes.
 W
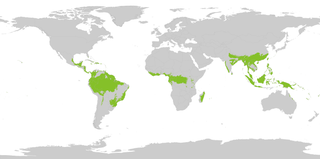
WTropical and subtropical moist forest (TSMF), also known as tropical moist forest, is a tropical and subtropical forest habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The habitat type is sometimes known as jungle.
 W
WSalt ponds are a natural feature of both temperate and tropical coastlines. These ponds form a vital buffer zone between terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Contaminants such as sediment, nitrates and phosphates are filtered out by salt ponds before they can reach the ocean. The depth, salinity and overall chemistry of these dynamic salt ponds fluctuate depending on temperature, rainfall, and anthropogenic influences such as nutrient runoff. The flora and fauna of tropical salt ponds differ markedly from those of temperate ponds. Mangrove trees are the dominant vegetation of tropical salt pond ecosystems, which also serve as vital feeding and breeding grounds for shore birds.
 W
WIn physical geography, tundra is a type of biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sámi word тӯндар meaning "uplands", "treeless mountain tract". Tundra vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, sedges and grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra regions. The ecotone between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline. The tundra soil is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus.
 W
WA wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded by water, either permanently or seasonally, where oxygen-free processes prevail. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from other land forms or water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique hydric soil. Wetlands play a number of functions, including water purification, water storage, processing of carbon and other nutrients, stabilization of shorelines, and support of plants and animals. Wetlands are also considered the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of plant and animal life. Whether any individual wetland performs these functions, and the degree to which it performs them, depends on characteristics of that wetland and the lands and waters near it. Methods for rapidly assessing these functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed in many regions and have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions and the ecosystem services some wetlands provide.