 W
WAigialosaurus is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous marine or semiaquatic lizard classified as part of the family Aigialosauridae within the Mosasauroidea. Exclusively found in deposits of Cenomanian age near Hvar, Croatia, the genus contain one valid species, A. dalmaticus. According to recent molecular and morphological data, Aigialosaurus is the oldest known member of the lineage leading to large Cretaceous marine reptiles called mosasaurs, a group most closely related to snakes among living squamates.
 W
WAnomalocaris is an extinct genus of radiodont (anomalocaridid), an order of animals thought to be closely related to ancestral arthropods. The first fossils of Anomalocaris were discovered in the Ogygopsis Shale by Joseph Frederick Whiteaves, with more examples found by Charles Doolittle Walcott in the Burgess Shale. Originally several fossilized parts discovered separately were thought to be three separate creatures, a misapprehension corrected by Harry B. Whittington and Derek Briggs in a 1985 journal article. Anomalocaris is thought to be one of the earliest examples of an apex predator, though others have been found in older Cambrian lagerstätten deposits.
 W
WAstraspis is an extinct genus of primitive jawless fish from the Ordovician of Central North America including the Harding Sandstone of Colorado and Bighorn Mountains of Wyoming. It is also known from Bolivia. It is related to other Ordovician fishes, such as the South American Sacabambaspis, and the Australian Arandaspis.
 W
WBorophagus is an extinct genus of the subfamily Borophaginae, a group of canids endemic to North America from the Middle Miocene epoch through the Late Pliocene epoch 12—2 Mya.
 W
WThe Chatham coot, also known as the Chatham Island coot, is an extinct bird in the rail family, Rallidae, that was endemic to the Chatham Islands of New Zealand. It was described from subfossil bones in 1892 by Scottish explorer, ornithologist and botanist Henry Forbes, who was director of the Canterbury Museum in Christchurch at the time.
 W
WThe Chatham raven is a prehistoric raven formerly native to the Chatham Islands. The closely related New Zealand raven, C. antipodum occurred in the North and South Islands of New Zealand. C. antipodum was formerly included in C. moriorum, and later considered a distinct species, however in 2017 genetic research determined that the two raven populations were subspecies rather than separate species, having only split 130,000 years ago.
 W
WCimolopteryx is a prehistoric bird genus from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is currently thought to contain only a single species, Cimolopteryx rara. The only specimen confidently attributed to C. rara was found in the Lance Formation of Wyoming, dating to the end of the Maastrichtian age, which ended about 66 million years ago. The dubious species "Cimolopteryx" maxima has been described from both the Lance Formation and the Hell Creek Formation of Montana. The humeral end of a left coracoid from the Frenchman Formation of southern Saskatchewan has also been attributed to the genus.
 W
WConiophis is an extinct genus of snakes from the late Cretaceous period. The type species, Coniophis precedes, was about 7 cm long and had snake-like teeth and body form, with a skull and a largely lizard-like bone structure. It probably ate small vertebrates. The fossil remains of Coniophis were first discovered at the end of the 19th century in the Lance Formation of the US state of Wyoming, and were described in 1892 by Othniel Charles Marsh. For the genus Coniophis, a number of other species have been described. Their affiliation is, however, poorly secured, mostly based on vertebrae descriptions from only a few fossils.
 W
WCryptoclidus is a genus of plesiosaur reptile from the Middle Jurassic period of England, France, and Cuba.
 W
WEczematolepis is an extinct genus of ptyctodontidan from the Milwaukee Formation of Wisconsin. Three species are known: E. fragilis, E. pustulosus and E. telleri. It was originally classified as the genus Acantholepis.
 W
WEdmontosaurus annectens is a species of flat-headed and duck-billed (hadrosaurid) dinosaur from the very end of the Cretaceous Period, in what is now North America. Remains of E. annectens have been preserved in the Frenchman, Hell Creek, and Lance Formations. All of these formations are dated to the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, representing the last three million years before the extinction of the dinosaurs. Also, E. annectens is also from the Laramie Formation, and magnetostratigraphy suggests an age of 69-68 Ma for the Laramie Formation. Edmontosaurus annectens is known from numerous specimens, including at least twenty partial to complete skulls, discovered in the U.S. states of Montana, South Dakota, North Dakota, Wyoming and Colorado and the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It was a large animal, up to approximately 12 metres (39 ft), potentially up to 15 m (49 ft) in length, with an extremely long and low skull. E. annectens exhibits one of the most striking examples of the "duckbill" snout common to hadrosaurs. It has a long taxonomic history, and specimens have at times been classified in the genera Diclonius, Trachodon, Hadrosaurus, Claosaurus, Thespesius, Anatosaurus and Anatotitan, before being grouped together in Edmontosaurus.
 W
WEunotosaurus is an extinct genus of reptile, possibly a close relative of turtles, from the late Middle Permian Karoo Supergroup of South Africa. The Eunotosaurus resided in the swamps of southern Africa. It is often considered as a possible "missing link" between turtles and their prehistoric ancestors. Its ribs were wide and flat, forming broad plates similar to a primitive turtle shell, and the vertebrae were nearly identical to those of some turtles. It is possible that these turtle-like features evolved independently of the same features in turtles, though some studies suggest Eunotosaurus is a genuine, primitive turtle relative. Other anatomical studies and phylogenetic analysis suggest that Eunotosaurus is a parareptile and not a basal turtle.
 W
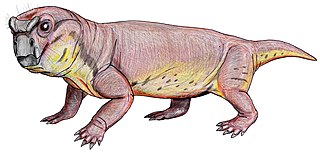
WGeikia is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsids from the late Permian. The abundance and diversity of dicynodonts during this period, combined with incomplete or inadequately prepared specimens, have led to challenges in determining relationships within this taxon. Only two species, Geikia locusticeps and Geikia elginensis have been assigned to this genus. While this is the currently accepted classification, fossil record limitations have led to repeated debate on the genus assignments of these species.
 W
WThe Hagerman horse, also called the Hagerman zebra or the American zebra, was a North American species of equid from the Pliocene epoch and the Pleistocene epoch. It was one of the oldest horses of the genus Equus and was discovered in 1928 in Hagerman, Idaho. It is the state fossil of Idaho.
 W
WHemipneustes is an extinct genus of sea urchins belonging to the family Holasteridae.
 W
WHemipneustes is an extinct genus of sea urchins belonging to the family Holasteridae.
 W
WHomo erectus is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago, and its specimens are among the first recognisable members of the genus Homo. H. erectus was the first human ancestor to spread throughout the Old World, having a distribution in Eurasia extending from the Iberian Peninsula to Java. African populations of H. erectus are likely to be the direct ancestors to several human species, such as H. heidelbergensis and H. antecessor, with the former generally considered to have been the direct ancestor to Neanderthals and Denisovans, and sometimes also modern humans. Asian populations of H. erectus may be ancestral to H. floresiensis and possibly to H. luzonensis. As a chronospecies, the time of the disappearance of H. erectus is a matter of contention. There are also several proposed subspecies with varying levels of recognition. The last known record of morphologically recognisable H. erectus are the Solo Man specimens from Java, around 117–108,000 years ago.
 W
WNautilus cookanum is an extinct species of nautilus. It lived during the Eocene epoch. N. cookanum placed within the genus Nautilus, together with extant species based on their shared shell characters. Fossils of the species from the Late Eocene Hoko River Formation are noted as one of the two oldest occurrences for the genus.
 W
WPicrocleidus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur. It is known only from the type species P. beloclis from the Middle Jurassic Oxford Clay Formation of the United Kingdom.
 W
WPontosaurus is a now extinct genus of pythonomorph from the Late Cretaceous period. It was originally named Hydrosaurus, but that name was preoccupied by an agamid lizard, so it was renamed. It is known from two species, both Cenomanian in age, the type P. lesinensis which is known from Hvar in Croatia, the other P. kornhuberi is known from the Sannine Formation in Lebanon.
 W
WPurussaurus is an extinct genus of giant caiman that lived in South America during the Miocene epoch, from the Colhuehuapian to the Montehermosan in the SALMA classification. It is known from skull material found in the Brazilian and Peruvian Amazon, Colombian Villavieja Formation, Panamanian Culebra Formation and the Urumaco and Socorro Formations of northern Venezuela.
 W
WRafinesquina is an extinct genus of large brachiopod that existed from the Darriwilian to the Ludlow epoch.