 W
WA lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself that rises and falls.
 W
WA naviduct is a special class of navigable aqueduct, in which the waterway also includes a lock. One example of a naviduct has been built at Enkhuizen on the Houtribdijk in the Netherlands on the instructions of the Rijkswaterstaat. This cost over €55 million and was completed in 2003. It is big enough to simultaneously transfer two large Rhine river-barges from the Markermeer to the IJsselmeer or vice versa. The structure was chosen because a busy waterway crosses a dam carrying a busy road, but the space available for separate aqueduct and lock facilities was restricted.
 W
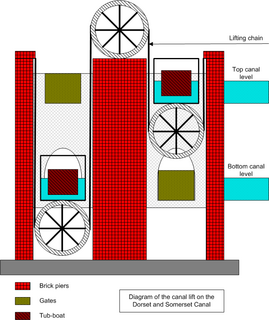
WThe balance lock was a type of boat lift designed by James Fussell (1748-1832 to transport boats up and down a hillside on a canal. An experimental balance lock was built as part of the Dorset and Somerset Canal and work was started for four more, but the project failed for financial reasons and they were not completed.
 W
WA caisson is a form of lock gate. It consists of a large floating iron or steel box. This can be flooded to seat the caisson in the opening of the dock to close it, or pumped dry to float it and allow it to be towed clear of the dock.
 W
WThe caisson lock is a type of canal lock in which a narrowboat is floated into a sealed watertight box and raised or lowered between two different canal water levels. It was invented in the late 18th century as a solution to the problem posed by the excessive demand for water when conventional locks were used to raise and lower canal boats through large height differences. Such locks, each of which would only raise and lower boats through small height differences of a few feet, would not suffice when large height differences had to be tackled nor when water was in short supply. The caisson was thought to be one solution, although it transpired that the technology of the day was not capable of achieving this type of construction economically.
 W
WA canal pound, reach, or level, is the stretch of level water impounded between two canal locks. Canal pounds can vary in length from the non-existent, where two or more immediately adjacent locks form a lock staircase, to many miles.
 W
WThe Classification of European Inland Waterways is a set of standards for interoperability of large navigable waterways forming part of the Trans-European Inland Waterway network within Continental Europe and Russia. It was created by the European Conference of Ministers of Transport in 1992, hence the range of dimensions are also referred to as CEMT Class I–VII.
 W
WEarly locks were designed with a single gate, known as a flash lock or staunch lock. The earliest European references to what were clearly flash locks were in Roman times.
 W
WA caisson is a form of lock gate. It consists of a large floating iron or steel box. This can be flooded to seat the caisson in the opening of the dock to close it, or pumped dry to float it and allow it to be towed clear of the dock.
 W
WThe Freycinet gauge is a standard governing the dimensions of the locks of some canals, put in place as a result of a law passed during the tenure of Charles de Freycinet as minister of public works of France, dating from 5 August 1879. The law required the size of lock chambers to be increased to a length of 39 metres (128 ft), a width of 5.2 metres (17 ft) and a minimum water depth of 2.2 metres, thus allowing 300 to 350 tonne barges to pass through.
 W
WA guillotine lock is a type of canal lock. The lock itself operates on the same principle as any normal pound lock, but is unusual in that each gate is a single piece, usually of steel, that slides vertically upwards when opened to allow a boat to traverse underneath. The resemblance to the French guillotine is obvious.
 W
WThe Inner Harbor Navigation Canal Lock—commonly known as Industrial Canal Lock or simply Industrial Lock—is a navigation lock in New Orleans. It connects the Lower Mississippi River to the Industrial Canal and other sea-level waterways. Because it is shorter and narrower than most modern locks on the Mississippi River System, the 1920s vintage lock has become a bottleneck between the nation's two highest-tonnage waterways—the Mississippi and the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway.
 W
WA lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself that rises and falls.
 W
WA lock keeper, lock tender, or lock operator looks after a canal or river lock, operating it and if necessary maintaining it or organizing its maintenance. Traditionally, lock keepers lived on-site, often in small purpose-built cottages. A lock keeper may also be the operator for the lock's Weir and, in many cases lock keepers play an important role in moderating and controlling water levels in response to drought and heavy rain. With the decline in commercial traffic the occupation is dying out on inland waterways, at least in Britain. Many previously manned locks are now unmanned.
 W
WMarala Headworks is a headworks situated on the Chenab River near the city of Sialkot in Punjab, Pakistan. A weir was first built during 1906–1912 in British India to feed the Upper Chenab Canal, as part of the 'Triple Canals Project'. A new Marala Barrage was constructed in 1968 to feed the Marala–Ravi Link Canal in addition to the original Upper Chenab Canal.
 W
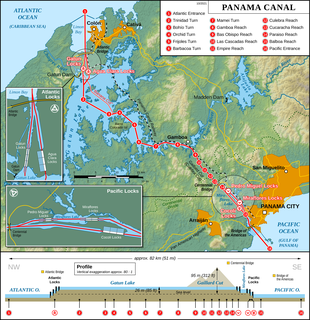
WThe Panama Canal locks are a lock system that lifts ships up 85 feet to the main elevation of the Panama Canal and down again. The original canal had a total of six steps for a ship's passage. The total length of the lock structures, including the approach walls, is over 1.9 miles (3 km). The locks were one of the greatest engineering works ever to be undertaken when they opened in 1914. No other concrete construction of comparable size was undertaken until the Hoover Dam, in the 1930s.
 W
WA caisson is a form of lock gate. It consists of a large floating iron or steel box. This can be flooded to seat the caisson in the opening of the dock to close it, or pumped dry to float it and allow it to be towed clear of the dock.
 W
WA caisson is a form of lock gate. It consists of a large floating iron or steel box. This can be flooded to seat the caisson in the opening of the dock to close it, or pumped dry to float it and allow it to be towed clear of the dock.
 W
WA caisson is a form of lock gate. It consists of a large floating iron or steel box. This can be flooded to seat the caisson in the opening of the dock to close it, or pumped dry to float it and allow it to be towed clear of the dock.
 W
WTaunsa Barrage is a barrage on the River Indus in Taunsa Tehsil of Dera Ghazi Khan District, Punjab province of Pakistan. It is situated 20 kilometres southeast of Taunsa Sharif and 16 kilometres from Kot Addu. This barrage controls water flow in the River Indus for irrigation and flood control purposes. Taunsa Barrage was designated a Ramsar site on 22 March 1996.
 W
WA weigh lock is a specialized canal lock designed to determine the weight of barges in order to assess toll payments based upon the weight and value of the cargo carried. This requires that the unladen weight of the barge be known.
 W
W