 W
WThe Argiles d'Octeville is a geological formation in Normandy, France. It dates back to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic. It is equivalent to the Kimmeridge Clay in England and predominantly consists of claystone, with some limestone. It is well exposed in cliff section at Cap de la Hève
 W
WThe Calcaire de Caen or Calcaires de Caen Formation; French for Caen Limestone, is a geological formation in France. It dates back to the mid-Bathonian of the Jurassic. It was often quarried for building work and is referred to as Caen Stone.
 W
WCoelodus is an extinct genus of pycnodontiform fish from the Late Jurassic to early Paleocene (Danian). Fossils of the genus have been found in:JurassicGardies, FranceCretaceousYacoraite Formation, Argentina El Molino Formation, Bolivia Baharîje Formation, Egypt Ahlen and Bückeberg Formations, Germany Nimar Formation, India Alburni, Italy Damergou, Zinder, Niger Cochirleni Formation, Romania La Huérguina and Cabana Formations, Spain Pierre Shale, Kansas Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation, England Tucumcari Formation, New Mexico Twin Mountains and Paluxy Formations, TexasPaleoceneTremp Formation, Spain
 W
WCompsognathus is a genus of small, bipedal, carnivorous theropod dinosaur. Members of its single species Compsognathus longipes could grow to around the size of a turkey. They lived about 150 million years ago, during the Tithonian age of the late Jurassic period, in what is now Europe. Paleontologists have found two well-preserved fossils, one in Germany in the 1850s and the second in France more than a century later. Today, C. longipes is the only recognized species, although the larger specimen discovered in France in the 1970s was once thought to belong to a separate species and named C. corallestris.
 W
WDakosaurus is an extinct genus within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially. The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named Geosaurus maximus by Plieninger. Dakosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. The extent of its adaptation to a marine lifestyle means that it is most likely that it mated at sea, but since no eggs or nests have been discovered that have been referred to Dakosaurus, whether it gave birth to live young at sea like dolphins and ichthyosaurs or came ashore like turtles is not known. The name Dakosaurus means "biter lizard", and is derived from the Greek dakos ("biter") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard").
 W
WGeosaurus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform within the family Metriorhynchidae, that lived during the Late Jurassic and the Early Cretaceous. Geosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. No Geosaurus eggs or nests have been discovered, so little is known of the reptile's lifecycle, unlike other large marine reptiles of the Mesozoic, such as plesiosaurs or ichthyosaurs which are known to give birth to live young out at sea. Where Geosaurus mated, whether on land or at sea, is currently unknown. The name Geosaurus means "Mother of Giants lizard", and is derived from the Greek Ge- and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard"). The name Geosaurus was established by the French naturalist Georges Cuvier in 1824.
 W
WGyrodus is an extinct genus of pycnodontiform ray-finned fish that lived from the late Triassic (Rhaetian) to the middle Cretaceous (Cenomanian).
 W
WKuehneotherium is an early mammaliaform genus that lived during the late Triassic period and is characterized by reversed-triangle pattern of molar cusps. Although many fossils have been found, the fossils are limited to teeth, dental fragments, and mandible fragments. The genus includes Kuehneotherium praecursoris and all related species. It was first named and described by Doris M. Kermack, K. A. Kermack, and Frances Mussett in November 1967. The family Kuehneotheriidae and the genus Kuehneotherium were created to house the single species Kuehneotherium praecursoris. Modeling based upon a comparison of the Kuehneotherium jaw with other mammals indicates they were about the size of a modern-day shrew between 4 and 5.5 g at adulthood.
 W
WLeedsichthys is a giant member of the Pachycormidae, an extinct group of Mesozoic ray-finned fish that lived in the oceans of the Middle Jurassic period. It is the largest ray-finned fish known to have existed.
 W
WLexovisaurus is a genus of stegosaur from mid-to-Late Jurassic Europe, 164.7 mya. Fossils of limb bones and armor fragments have been found in middle to late Jurassic-aged strata of England and France.
 W
WLoricatosaurus is a dinosaur of family Stegosauridae from Callovian-age rocks of England and France.
 W
WThe Marnes de Dives is a geological formation in Normandy, France. It dates back to the upper part of the Callovian stage of the Middle Jurassic. And is partially equivalent to the Oxford Clay in England. It predominantly consists of ooidal marl, rich in pyrite and lignite, interbedded with thin limestone horizons. It is best exposed at the base of the Falaises des Vaches Noires as well as the foreshore at low tide. It is known for its fossils, notablity those of ammonites, marine crocodiles and fragmentary remains of dinosaurs, mostly theropods.
 W
WMicrocleidus is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Plesiosauroidea. It was about the size of a medium-sized dolphin, reaching a length of 3 metres (9.8 ft). The species has 40 neck vertebrae and a short tail of 28 vertebrae. Fossils of the genus have been found in France, the Posidonia Shale in Germany and the Alum Shale Formation of England.
 W
WThe Moon-Airel Formation is a geological formation in France. It dates back to the late Rhaetian and early Hettangian.
 W
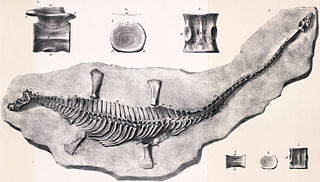
WNeosteneosaurus is a genus of machimosaurid, known form the Middle Jurassic Oxford Clay of the UK, and Marnes de Dives, France. The type species, N. edwardsi, was originally named as a species of Steneosaurus in 1868, but was moved to its own genus in 2020. Steneosaurus durobrivensis and Steneosaurus hulkei are considered a junior synonym.
 W
WOphthalmosaurus is an ichthyosaur of the Middle Jurassic period, named for its extremely large eyes. It had a graceful 6 m (19.5 ft) long dolphin-shaped body, and its almost toothless jaw was well adapted for catching squid. Major fossil finds of this genus have been recorded in Europe and North and South America.
 W
WPiveteausaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur known from a partial skull discovered in the Middle Jurassic Marnes de Dives formation of Calvados, in northern France and lived about 164.7-161.2 million years ago. In 2012 Thomas Holtz gave a possible length of 11 meters.
 W
WPoekilopleuron is a genus of megalosauroid dinosaur, which lived during the middle Bathonian of the Jurassic, about 168 to 166 million years ago. The genus has been used under many different spelling variants, although only one, Poekilopleuron, is valid. The type species is P. bucklandii, named after William Buckland, and many junior synonyms of it have also been erected. Few material is currently known, as the holotype was destroyed in World War II, although many casts of the material still exist.
 W
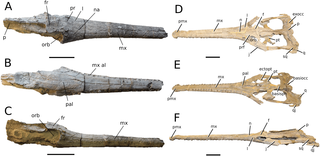
WProexochokefalos is an extinct genus of machimosaurid teleosauroid from the Jurassic of France
 W
WReineckeia is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the family Reineckeiidae.
 W
WStenopterygius is an extinct genus of thunnosaur ichthyosaur known from Europe. This genus of ichthyosaur grew to a maximum length of 4 meters.
 W
WStreptospondylus is a genus of tetanuran theropod dinosaur known from the Late Jurassic period of France, 161 million years ago. It was a medium-sized predator with an estimated length of 6 meters and a weight of 500 kg (1,100lbs).
 W
WTyrannoneustes is an extinct genus of geosaurine metriorhynchid crocodyliform from the Callovian stage Oxford Clay Formation of England and the Marnes de Dives of France. It contains a single species, Tyrannoneustes lythrodectikos, meaning "blood-biting tyrant swimmer". The genus was rediscovered after a century of storage in a museum basement after being unearthed by fossil hunter Alfred Nicholson Leeds between the years of 1907 and 1909. Its lower jaw measured about 26 inches long and its teeth were blade-like, likely built to attack prey as large or larger than itself, similar to the Late Jurassic Dakosaurus, Torvoneustes, and Plesiosuchus.