 W
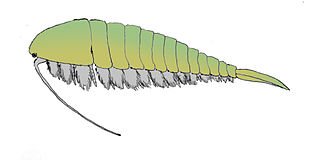
WAlalcomenaeus is one of the most widespread and longest-surviving arthropod genera of the Early and Middle Cambrian. Known from over 300 specimens in the Burgess Shale, and the Chengjiang, it bears great similarity to the opabiniids.
 W
WBarbourofelis is an extinct genus of large, predatory, feliform carnivoran mammals of the family Barbourofelidae. The genus was endemic to North America and Eurasia during the Miocene until its extinction during the Pliocene, living from as early as 17 until 7.3 Ma.
 W
WBuxolestes is an extinct genus of semi-aquatic, non-placental eutherian mammals belonging to the family Pantolestidae. Species in this genus were part of the first placental evolutionary radiation during the Middle Eocene and found in the Bracklesham Group and Wittering Formation of England, at the Messel Pit in Germany and in Bouxwiller, France.
 W
WColombitherium is an extinct mammal from Late Eocene Colombia. It has originally been assigned to the order Pyrotheria and the family Colombitheriidae, although a later detailed analysis of the fossil questions that classification. A fossil jawbone of approximately 9 centimetres (3.5 in) length of Colombitherium has been found by Texas Petroleum in 1945, in the Upper Eocene strata of the middle Gualanday Group in the department of Tolima, Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
 W
WDaspletosaurus is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in western North America between about 77 and 74 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period. The genus Daspletosaurus contains two species. Fossils of the earlier type species, D. torosus, have been found in Alberta, while fossils of the later second species, D. horneri, have been found only in Montana. A possible third species, also from Alberta, awaits formal identification and another possible species D. degrootorum, also exists, but it may belong to the separate genus Thanatotheristes instead. Daspletosaurus is closely related to the much larger and more recent tyrannosaurid Tyrannosaurus rex. Like most tyrannosaurids, Daspletosaurus was a multi-tonne bipedal predator equipped with dozens of large, sharp teeth. Daspletosaurus had the small forelimbs typical of tyrannosaurids, although they were proportionately longer than in other genera.
 W
WDeinocheirus is a genus of large ornithomimosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous around 70 million years ago. In 1965, a pair of large arms, shoulder girdles, and a few other bones of a new dinosaur were first discovered in the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia. In 1970, this specimen became the holotype of the only species within the genus, Deinocheirus mirificus; the genus name is Greek for "horrible hand". No further remains were discovered for almost fifty years, and its nature remained a mystery. Two more complete specimens were described in 2014, which shed light on many aspects of the animal. Parts of these new specimens had been looted from Mongolia some years before, but were repatriated in 2014.
 W
WDilophosaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now North America during the Early Jurassic, about 193 million years ago. Three skeletons were discovered in northern Arizona in 1940, and the two best preserved were collected in 1942. The most complete specimen became the holotype of a new species in the genus Megalosaurus, named M. wetherilli by Samuel P. Welles in 1954. Welles found a larger skeleton belonging to the same species in 1964. Realizing it bore crests on its skull, he assigned the species to the new genus Dilophosaurus in 1970, as Dilophosaurus wetherilli. The genus name means "two-crested lizard", and the species name honors John Wetherill, a Navajo councilor. Further specimens have since been found, including an infant. Footprints have also been attributed to the animal, including resting traces. Another species, Dilophosaurus sinensis from China, was named in 1993, but was later found to belong to the genus Sinosaurus. It was designated as the state dinosaur of Connecticut based on tracks found there.
 W
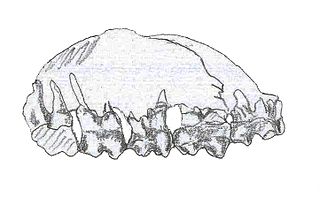
WEmuella is a genus of trilobites of the family Emuellidae. Its fossils have been found in South Australia. It can be recognised by touching glabella and frontal border, and the sub-pentagonal head, as compared to, a short field between the front of the axis in the head or glabella and the border ridge, and a semi-circular headsheald in the sister-genus Balcoracania. Both emuellid genera share eye ridges that are positioned parallel to the frontal and lateral border of the head, prominent genal spines that are a smooth continuation of the lateral margin of the head, a prothorax of 6 segments, with the 5th and 6th merged and carrying large trailing spines. Both genera have in adulthood a highly variable but large number of segments of the opistothorax, although the largest number found in B. dailyi with 97 is much larger than in Emuella (52).
 W
WEocyclotosaurus is an extinct genus of mastodonsauroid temnospondyl from the Middle Triassic (Anisian). It measured over 1 metre and had a 22 cm skull.
 W
WIndopithecus giganteus is an extinct species of large ape that lived in the late Miocene of the Siwalik Hills in northern India. Although frequently assigned to the more well-known genus Gigantopithecus, recent authors consider it to be a distinct genus in its own right.
 W
WHippohyini was an extinct tribe of Suinae which existed in Asia during the Pliocene.
 W
WLongisquama is a genus of extinct reptile. There is only one species, Longisquama insignis, known from a poorly preserved skeleton and several incomplete fossil impressions from the Middle to Late Triassic Madygen Formation in Kyrgyzstan. It is known from a type fossil specimen, slab and counterslab and five referred specimens of possible integumentary appendages. All specimens are in the collection of the Paleontological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow.
 W
WMicrovenator is a genus of dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Cloverly Formation in what is now south central Montana. Microvenator was an oviraptorosaurian theropod. The holotype fossil is an incomplete skeleton, most likely a juvenile, with a living length of about 1.2 m. The adult size of Microvenator is estimated to be closer to 3 m long. Microvenator celer is primitive and may be the "sister taxon to all other oviraptorosaurs."
 W
WMirocetus is a genus of archaic odontocete from the late Oligocene (Chattian) of Azerbaijan. Like many other primitive odontocetes, its classification has been fluid since its description.
 W
WPatriomanis is an extinct genus of pangolin from the Eocene of North America. It currently represents the only pholidotan known from the Western Hemisphere. The genus contains one species, P. americana, which is known from six specimens, mostly from the Chadronian White River Formation of Montana. It had long digits and a prehensile tail, suggesting that it was arboreal, and its jaw was capable of opening wider than modern pangolins. Its ears and the hair between its scales were also longer than modern pangolins.
 W
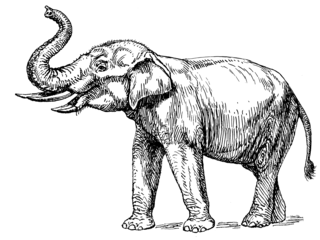
WPrimelephas is a genus of Elephantinae that existed during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. The name of the genus suggests 'first elephant'. These primitive elephantids are thought to be the common ancestor of Mammuthus, the mammoths, and the closely allied genera Elephas and Loxodonta, the Asian and African elephants, diverging some 4-6 million years ago. It had four tusks, which is unusual for an elephant. The type species, Primelephas gomphotheroides, was described by Vincent Maglio in 1970, with the specific epithet indicating the fossil specimens were gomphothere-like. Primelephas korotorensis is the only other species to be assigned to the genus.
 W
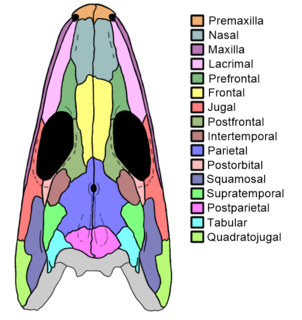
WProbainognathus meaning “progressive jaw” is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived around 235 to 221.5 million years ago, during the Late Triassic in what is now South America. Probainognathus is a member of the family Probainognathidae, and is a close relative of the family Chiniquodontidae. The various similarities to Chiniquodontidae led Alfred Romer to initially suggest Probainognathus be placed within that family, but it was subsequently decided that the differences were enough to warrant its placement within Probainognathidae.
 W
WProterogyrinus was an extinct genus of early tetrapods from the order Embolomeri. Fossil remains of Proterogyrinus have been found in Scotland, UK, and West Virginia, United States, and date back to the Serpukhovian, which is from about 331 to 323 million years ago. The genus was originally named by renowned vertebrate paleontologist Alfred Sherwood Romer in 1970. A comprehensive redescription was later published by Canadian paleontologist Robert Holmes in 1984. The generic name "Proterogyrinus" is Greek for "earlier wanderer" or "earlier tadpole". This name was chosen by Romer in keeping with a trend of naming long-bodied early tetrapods with the suffix "-gyrinus".
 W
WRabidosaurus is an extinct genus of large herbivorous dicynodont of the family Kannemeyeriidae from the Anisian Donguz Formation, Russia.
 W
WSauropelta is a genus of nodosaurid dinosaur that existed in the Early Cretaceous Period of North America. One species has been named although others may have existed. Anatomically, Sauropelta is one of the most well-understood nodosaurids, with fossilized remains recovered in the U.S. states of Wyoming, Montana, and possibly Utah. It is also the earliest known genus of nodosaurid; most of its remains are found in a section of the Cloverly Formation dated to 108.5 million years ago.
 W
WStaurikosaurus is a genus of herrerasaurid dinosaur from the Late Triassic of Brazil, found in the Santa Maria Formation.
 W
WTenontosaurus is a genus of medium- to large-sized ornithopod dinosaur. The genus is known from the late Aptian to Albian ages of the middle Cretaceous period sediments of western North America, dating between 115 and 108 million years ago.
 W
WUgandax is an extinct genus of bovines in the subtribe Bubalina that lived from the Miocene to the Pleistocene of Africa. Cladistic analyses suggest Ugandax represents an ancestral form of the African buffalo, Synceros, and teeth assigned to Ugandax represent the earliest appearance of bovines in Africa.
 W
WWadiasaurus is an extinct genus of dicynodont, the remains of which were found in Yerrapalli Formation, India.