 W
WAethiocarenus is an extinct genus of insects which has a single species Aethiocarenus burmanicus described from a 98.79 ±0.62 million year old fossil found in Burmese amber from the Hukawng Valley of Myanmar. The insect is unusual due to the vertex of the triangular head being attached to the pronotum as opposed to the hypotenuse. When first described Aethiocarenus was placed as the sole member of the family Aethiocarenidae and order Aethiocarenodea. However, Aethiocarenus was later considered to be a nymph of Alienopterus. Vršanský et al. (2018) considered Aethiocarenus to be an alienopterid nymph, but considered it distinct from other members of this group and deserving a separate genus rank.
 W
WAfrasia djijidae is a fossil primate that lived in Myanmar approximately 37 million years ago, during the late middle Eocene. The only species in the genus Afrasia, it was a small primate, estimated to weigh around 100 grams (3.5 oz). Despite the significant geographic distance between them, Afrasia is thought to be closely related to Afrotarsius, an enigmatic fossil found in Libya and Egypt that dates to 38–39 million years ago. If this relationship is correct, it suggests that early simians dispersed from Asia to Africa during the middle Eocene and would add further support to the hypothesis that the first simians evolved in Asia, not Africa. Neither Afrasia nor Afrotarsius, which together form the family Afrotarsiidae, is considered ancestral to living simians, but they are part of a side branch or stem group known as eosimiiforms. Because they did not give rise to the stem simians that are known from the same deposits in Africa, early Asian simians are thought to have dispersed from Asia to Africa more than once prior to the late middle Eocene. Such dispersals from Asia to Africa also were seen around the same time in other mammalian groups, including hystricognathous rodents and anthracotheres.
 W
WAmphipithecus mogaungensis was a primate that lived in Late Eocene Myanmar. Along with another primate Pondaungia cotteri, both are difficult to categorise within the order Primates. What little is known suggests that they are neither adapiform nor omomyid primates, two of the earliest primate groups to appear in the fossil record. Deep mandibles and mandibular molars with low, broad crowns suggest they are both simians, a group that includes monkeys, apes, and humans, though more material is needed for further comparison. The teeth also suggest that these were frugivore primates, with a body mass of 6–10 kg (13–22 lb).
 W
WAptenoperissus is a genus of extinct wasp with eight described species, placed into the monotypic family Aptenoperissidae. The type species Aptenoperissus burmanicus resembles a mix between a grasshopper, an ant, and a wasp. It was described by a group of researchers from Oregon State University in a paper released online in October 2016. The piece of 100 million year old Burmese amber that it was preserved in was found in the Hukawng Valley of Myanmar in Southern Asia. A new family, Aptenoperissidae, was described to accommodate this insect. Aptenoperissus had a strong stinger for defense against predators and to stab grubs for its food. The creature had long legs making it perfect for jumping higher than most insects. Subsequently additional species were described from the Myanmar amber: A. amabilis, A. delicatus, A. formosus, A. etius, A. magnifemoris, A. pusillus and A. zonalis.
 W
WAstreptolabis is an extinct genus of earwig in the Dermaptera family Pygidicranidae known from a group of Cretaceous fossils found in Myanmar. The genus contains two described species, Astreptolabis ethirosomatia and Astreptolabis laevis and is the sole member of the subfamily Astreptolabidinae.
 W
WAtrypa is a genus of brachiopod with shells round to short egg-shaped, covered with many fine radial ridges, that split further out and growthlines perpendicular to the costae and 2-3 times wider spaced. The pedunculate valve is a little convex, but tends to level out or even become slightly concave toward the anterior margin. The brachial valve is highly convex. There is no interarea in either valve. Atrypa was a cosmopolitan and occurred from the late Lower Silurian (Telychian) to the early Upper Devonian (Frasnian). Other sources expand the range from the Late Ordovician to Carboniferous, approximately from 449 to 336 Ma. A proposed new species, A. harrisi, was found in the trilobite-rich Floresta Formation in Boyacá, Colombia.
 W
WBarbaturex is an extinct genus of giant herbivorous iguanian lizards from the Eocene of Myanmar. It is represented by a single species, Barbaturex morrisoni, which is known from several partial dentaries and a fused pair of frontals, two bones that form part of the top of the skull. Based on the size of these bones, Barbaturex morrisoni is estimated to have been about 1 metre (3.3 ft) from snout to vent, and possibly up to 6 feet (1.8 m) including the tail. Barbaturex morrisoni was named after The Doors frontman Jim Morrison, a play on his epithet "The Lizard King". The genus's name is a portmanteau of the Latin words Barbatus and rex, meaning "bearded king", in reference to ridges along the mandible and the lizard's large size.
 W
WBurmomyrma is an extinct genus of ant-mimic wasp in the extinct family Falsiformicidae. The genus contains a single described species, Burmomyrma rossi. Burmomyrma is known from a single Middle Cretaceous fossil which was found in Asia.
 W
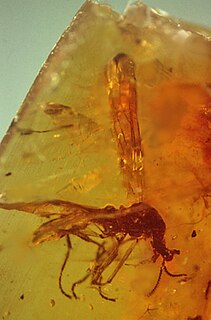
WCamelomecia is an extinct genus of stem-group ants not placed into any Formicidae subfamily. Fossils of the single known species, Camelomecia janovitzi, are known from the Middle Cretaceous of Asia. The genus is one of several ants described from Middle Cretaceous ambers of Myanmar.
 W
WCascoplecia insolitis, commonly known as the unicorn fly, is an extinct dipteran that lived in the Early Cretaceous. The type specimen was found in Burmese amber. George Poinar, Jr., who described this fossil, coined a new family name for it – Cascopleciidae. One of the defining characteristics of Cascoplecia is the presence of three ocelli raised on an extended, horn-like protuberance. Its distinctiveness has been questioned by other authors, who suggest that the taxon is simply an aberrant member of the Bibionidae.
 W
WChimerarachne is a genus of extinct arachnids containing a single species Chimerarachne yingi. Fossils of Chimerarachne were discovered in Burmese amber from Myanmar which dates to the mid-Cretaceous, about 100 million years ago. Its classification is disputed, either belonging to Uraraneida a group otherwise known from the Devonian to Permian, or a separate clade closer to spiders. Since the earliest spider fossils are from the Carboniferous, either answer results in an at least a 170 myr ghost lineage with no fossil record, making it a Lazarus taxon. The size of the animal is quite small, being only 2.5 mm in body length, with the tail being about 3mm in length. These fossils resemble spiders in having two of their key defining features: spinnerets for spinning silk, and a modified male organ on the pedipalp for transferring sperm. At the same time they retain a whip-like tail, rather like that of a whip scorpion and uraraneids. Chimerarachne is not ancestral to spiders, being much younger than the oldest spiders which are known from the Carboniferous, but it appears to be a late survivor of an extinct group which was probably very close to the origins of spiders. It suggests that there used to be spider-like animals with tails which lived alongside true spiders for at least 200 million years.
 W
WCretaceogekko is an extinct monotypic genus of gecko known from a single partial specimen preserved in Burmese amber from the Cenomanian of Myanmar. The specimen was found in the Hukawng Valley in 2001 and the genus and species were named by E. Nicholas Arnold and George Poinar in 2008. The specimen includes a foot and partial tail. Cretaceogekko is the oldest known gecko, predating the Late Cretaceous gecko Gobekko and the Paleogene gecko Yanatarogecko, which has also been preserved in amber.
 W
WCretoperipatus burmiticus is an extinct species of velvet worm that is known from Cretaceous Burmese amber approximately 100 million years old. It was found in Kachin state, Myanmar.
 W
WElectrorana is an extinct genus of frog that lived in what is now Myanmar in the Cenomanian forests, 99 million years ago. The type and only species is E. limoae.
 W
WLeptaena is an extinct genus of mid-sized brachiopod that existes from the Dariwilian epoch to the Emsian epoch, though some specimens have been found in strata as late in age as the Tournasian epoch. Like some other Strophomenids, Lepteana were epifaunal, meaning they lived on top of the seafloor, not buried within it, and were suspension feeders.
 W
WManipulator modificaputis is an extinct predatory cockroach which lived during the Upper Cretaceous period. The holotype specimen is fossilized in a 100-million-year-old piece of Burmese amber, which was found in a quarry of volcanoclastic mudstone at Noije Bum in the Hukawng Valley in Myanmar. The insect has been described by Peter Vršanský, of the Geological Institute SAS of Bratislava, and by Günter Bechly, of the Staatliches Museum für Naturkunde in Stuttgart.
 W
WMelittosphex burmensis is one of the two oldest-known species of bees. The species was described from an amber inclusion in Burmese Amber in the year 2006 by George Poinar, Jr., a zoologist at Oregon State University. The fossil was found in a mine in the Hukawng Valley of northern Myanmar and is believed to date from the Cretaceous Period, 100 million years ago.
 W
WMyanmymar is an extinct genus of fairyfly preserved in Burmese amber from Myanmar. It has only one species, Myanmymar aresconoides. It is dated to the earliest part of the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, around 99 million years old. As of 2011, it is the oldest known fossil mymarid.
 W
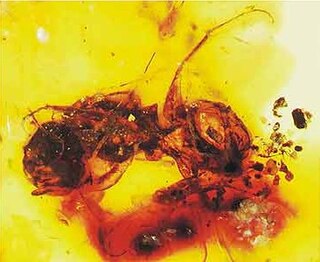
WMyanmyrma is an extinct genus of ants not placed into any Formicidae subfamily. Fossils of the single known species, Myanmyrma gracilis, are known from the Middle Cretaceous of Asia. The genus is one of several ants described from Middle Cretaceous ambers of Myanmar.
 W
WNanoraphidia is an extinct genus of snakefly in the family Mesoraphidiidae containing the species Nanoraphidia electroburmica and Nanoraphidia lithographica.
 W
WPalaeoagaracites is an extinct monotypic genus of gilled fungus in the order Agaricales. It contains the single species Palaeoagaracites antiquus.
 W
WPaleoophiocordyceps coccophagus is an extinct parasitic fungus in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae from Cretaceous-aged Burmese amber. P. coccophagus' morphology is very similar to the species of Ophiocordyceps. The only known specimen consists of two whip-like fruiting bodies emerging from the head of a male scale insect of an undescribed species very similar to the extinct species Albicoccus dimai.
 W
WTytthodiplatys is an extinct genus of earwig in the family Diplatyidae known from a Cretaceous fossil found in Myanmar. The genus contains a single described species, Tytthodiplatys mecynocercus.
 W
WZigrasimecia is an extinct genus of ants which existed in the Cretaceous period approximately 98 million years ago. The first specimens were collected from Burmese amber in Kachin State, 100 kilometres (62 mi) west of Myitkyina town in Myanmar. In 2013, palaeoentomologists Phillip Barden and David Grimaldi published a paper describing and naming Zigrasimecia tonsora. They described a dealate female with unusual features, notably the highly specialized mandibles. Other features include large ocelli, short scapes, 12 antennomeres, small eyes, and a clypeal margin that has a row of peg-like denticles. The genus Zigrasimecia was originally incertae sedis within Formicidae until a second species, Zigrasimecia ferox, was described in 2014, confirming its placement in the subfamily Sphecomyrminae.