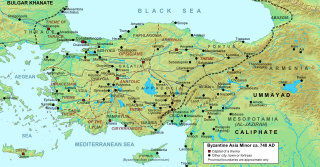
 W
WThe Battle of Akroinon was fought at Akroinon or Akroinos in Phrygia, on the western edge of the Anatolian plateau, in 740 between an Umayyad Arab army and the Byzantine forces. The Arabs had been conducting regular raids into Anatolia for the past century, and the 740 expedition was the largest in recent decades, consisting of three separate divisions. One division, 20,000 strong under Abdallah al-Battal and al-Malik ibn Shu'aib, was confronted at Akroinon by the Byzantines under the command of Emperor Leo III the Isaurian r. 717–741) and his son, the future Constantine V. The battle resulted in a decisive Byzantine victory. Coupled with the Umayyad Caliphate's troubles on other fronts and the internal instability before and after the Abbasid Revolt, this put an end to major Arab incursions into Anatolia for three decades.
 W
WThe Sack of Amorium by the Abbasid Caliphate in mid-August 838 was one of the major events in the long history of the Arab–Byzantine Wars. The Abbasid campaign was led personally by the Caliph al-Mu'tasim, in retaliation to a virtually unopposed expedition launched by the Byzantine emperor Theophilos into the Caliphate's borderlands the previous year. Mu'tasim targeted Amorium, a Byzantine city in western Asia Minor, because it was the birthplace of the ruling Byzantine dynasty and, at the time, one of Byzantium's largest and most important cities. The caliph gathered an exceptionally large army, which he divided in two parts, which invaded from the northeast and the south. The northeastern army defeated the Byzantine forces under Theophilos at Anzen, allowing the Abbasids to penetrate deep into Byzantine Asia Minor and converge upon Ancyra, which they found abandoned. After sacking the city, they turned south to Amorium, where they arrived on 1 August. Faced with intrigues at Constantinople and the rebellion of the large Khurramite contingent of his army, Theophilos was unable to aid the city.
 W
WThe Battle of Andrassos or Adrassos was an engagement fought on 8 November 960 in an unidentified mountain pass on the Taurus Mountains, between the Byzantines, led by Leo Phokas the Younger, and the forces of the Hamdanid Emirate of Aleppo under the emir Sayf al-Dawla.
 W
WThe Battle of Ankara or Angora was fought on 20 July 1402 at the Tchubuk plain near Angora between the forces of the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I (Bajazet) and Timur (Tamerlane), ruler of the Timurid Empire. The battle was a major victory for Timur, and it led to a period of crisis for the Ottoman Empire.
 W
WThe Battle of Anzen or Dazimon was fought on 22 July 838 at Anzen or Dazimon between the Byzantine Empire and the forces of the Abbasid Caliphate. The Abbasids had launched a huge expedition with two separate armies in retaliation for the Byzantine emperor Theophilos's successes the previous year, and aimed to sack Amorion, one of Byzantium's largest cities. Theophilos with his army confronted the smaller Muslim army, under the Iranian vassal prince Afshin, at Dazimon.
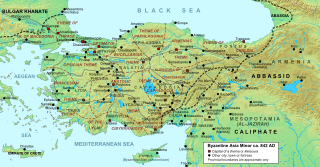 W
WThe Battle of Bathys Ryax was fought in 872 or 878 between the Byzantine Empire and the Paulicians. The Paulicians were a Christian sect which—persecuted by the Byzantine state—had established a separate principality at Tephrike on Byzantium's eastern border and collaborated with the Muslim emirates of the Thughur, the Abbasid Caliphate's borderlands, against the Empire. The battle was a decisive Byzantine victory, resulting in the rout of the Paulician army and the death of its leader, Chrysocheir. This event destroyed the power of the Paulician state and removed a major threat to Byzantium, heralding the fall of Tephrike itself and the annexation of the Paulician principality shortly after.
 W
WThe Battle of Ani was fought between the forces of the Kingdom of Armenia under Vahram Pahlavouni and the Byzantine Empire in 1042. The Byzantine Empire was soundly defeated, with up to 20,000 dead.
 W
WThe Battle of Pankaleia was a battle fought in 978 or 979 between the army loyal to the Byzantine emperor Basil II, commanded by Bardas Phokas the Younger, and the forces of the rebel general Bardas Skleros, which ultimately led to the defeat and exile of the latter. Sources are unclear in the succession and location of the events, so that while earlier scholars followed John Skylitzes in placing the Battle of Pankaleia in March 979 as the decisive victory for loyalist forces, today, following Leo the Deacon's account, it is placed in June 978 and regarded as a defeat for Phokas.
 W
WThe Battle of the Iron Bridge was fought between the Muslim Rashidun army and the Byzantine army in 637 AD. The battle took its name from a nearby nine-arch stone bridge spanning the Orontes River which had gates trimmed with iron. It was one of the last battles fought between the Byzantines and Rashidun Caliphate in the province of Syria. The aftermath of the battle marked the nearly complete annexation of the province into the Rashidun Caliphate with the fall of its capital.
 W
WThe siege of Kamacha by the Abbasid Caliphate took place in autumn 766, and involved the siege of the strategically important Byzantine fortress of Kamacha on the eastern bank of the Euphrates River, as well as a large-scale raid across eastern Cappadocia by a part of the Abbasid invasion army. Both enterprises failed, with the siege dragging on into winter before being abandoned and the raiding force being surrounded and heavily defeated by the Byzantines. The campaign was one of the first large-scale Abbasid operations against Byzantium, and is one of the few campaigns of the Arab–Byzantine wars for which detailed information survives, although it is barely mentioned in Arabic or in Byzantine sources.
 W
WThe Battle of Kopidnadon or Kopidnados took place in September 788 between the armies of the Abbasid Caliphate and the Byzantine Empire. The Abbasid army launched an invasion of Byzantine Asia Minor, and was confronted by a Byzantine force at Kopidnadon. The resulting battle was an Abbasid victory. Among the Byzantine losses was a certain Diogenes, who is identified by some scholars with the probable original source for the literary hero Digenes Akritas.
 W
WThe Battle of Köse Dağ was fought between the Sultanate of Rum ruled by the Seljuq dynasty and the Mongol Empire on June 26, 1243 at the defile of Köse Dağ, a location between Erzincan and Gümüşhane in modern northeastern Turkey. The Mongols achieved a decisive victory.
 W
WThe Battle of Krasos was a battle in the Arab–Byzantine Wars that took place in August 804, between the Byzantines under Emperor Nikephoros I and an Abbasid army under Ibrahim ibn Jibril. Nikephoros' accession in 802 resulted in a resumption of warfare between Byzantium and the Abbasid Caliphate. In late summer 804, the Abbasids had invaded Byzantine Asia Minor for one of their customary raids, and Nikephoros set out to meet them. He was surprised, however, at Krasos and heavily defeated, barely escaping with his own life. A truce and prisoner exchange were afterwards arranged. Despite his defeat, and a massive Abbasid invasion the next year, Nikephoros persevered until troubles in the eastern provinces of the Caliphate forced the Abbasids to conclude a peace.
 W
WThe Battle of Lalakaon, or Poson or Porson, was fought in 863 between the Byzantine Empire and an invading Arab army in Paphlagonia. The Byzantine army was led by Petronas, the uncle of Emperor Michael III, although Arab sources also mention the presence of Emperor Michael. The Arabs were led by the emir of Melitene (Malatya), Umar al-Aqta.
 W
WThe Battle of Manzikert was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia. The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and the capture of the Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes played an important role in undermining Byzantine authority in Anatolia and Armenia, and allowed for the gradual Turkification of Anatolia. Many of the Turks, who had been travelling westward during the 11th century, saw the victory at Manzikert as an entrance to Asia Minor.
 W
WThe Battle of Lalakaon, or Poson or Porson, was fought in 863 between the Byzantine Empire and an invading Arab army in Paphlagonia. The Byzantine army was led by Petronas, the uncle of Emperor Michael III, although Arab sources also mention the presence of Emperor Michael. The Arabs were led by the emir of Melitene (Malatya), Umar al-Aqta.
 W
WThe Battle of Mauropotamos was fought in 844, between the armies of the Byzantine Empire and the Abbasid Caliphate, at Mauropotamos. After a failed Byzantine attempt to recover the Emirate of Crete in the previous year, the Abbasids launched a raid into Asia Minor. The Byzantine regent, Theoktistos, headed the army that went to meet the invasion but was heavily defeated, and many of his officers defected to the Arabs. Internal unrest prevented the Abbasids from exploiting their victory, however. A truce and a prisoner exchange were consequently agreed in 845, followed by a six-year cessation of hostilities, as both powers focused their attention elsewhere.
 W
WThe Siege of Nicaea of 727 was an unsuccessful attempt by the Umayyad Caliphate to capture the Byzantine city of Nicaea, the capital of the Opsician Theme. Ever since its failure to capture the Byzantine Empire's capital, Constantinople, in 717–718, the Caliphate had launched a series of raids into Byzantine Asia Minor. In 727, the Arab army, led by one of the Caliph's sons, penetrated deep into Asia Minor, sacked two Byzantine fortresses and in late July arrived before Nicaea. Despite constant attacks for 40 days, the city held firm and the Arabs withdrew and returned to the Caliphate. The successful repulsion of the attack was a major boost for Byzantine emperor Leo III the Isaurian's recently initiated campaign to abolish the veneration of icons in the Empire; Leo claimed it as evidence of divine favour for his policy. The siege of Nicaea marks also the high point of the Umayyad raids, as new threats and defeats on their far-flung frontiers decreased Umayyad strength elsewhere, while Byzantine power strengthened afterwards.
 W
WThe Battle of Pelekanon, also known by its Latinised form Battle of Pelecanum, occurred on June 10–11, 1329 between an expeditionary force by the Byzantines led by Andronicus III and an Ottoman army led by Orhan I. The Byzantine army was defeated, with no further attempt made at relieving the cities in Anatolia under Ottoman siege.
 W
WThe Battle of Poimanenon or Poemanenum was fought in early 1224 between the forces of the two main successor states of the Byzantine Empire; the Latin Empire and the Byzantine Greek Empire of Nicaea. The opposing forces met at Poimanenon, south of Cyzicus in Mysia, near Lake Kuş.
 W
WThe Battle of the Rhyndacus was fought on 15 October 1211 between the forces of two of the main successor states of the Byzantine Empire, the Latin Empire and the Byzantine Greek Empire of Nicaea, established following the dissolution of the Byzantine state after the Fourth Crusade.
 W
WThe Siege of Sinope in 1214 was a successful siege and capture of Sinope by the Seljuq Turks under their Sultan, Kaykaus I. Sinope was an important port city on the Black Sea coast of modern Turkey, at the time held by the Empire of Trebizond, one of the Byzantine Greek successor states formed after the Fourth Crusade. The siege is described in some detail by the near-contemporary Seljuq chronicler Ibn Bibi. The Trapezuntine emperor Alexios I led an army to break the siege, but he was defeated and captured, and the city surrendered on 1 November.
 W
WThe Siege of Smyrna was fought between the Knights of Rhodes, who held the harbour and sea-castle of Smyrna in western Anatolia, and the army of the Turco-Mongol emir Timur. The Turco-Mongols blockaded the harbour and attacked the fortifications with stone-throwing siege engines, while the defenders, numbering only about 200 knights, countered with arrows and incendiary projectiles. After two weeks of strong resistance against a far superior adversary, the outer wall was destroyed by mining and breached. Some of the garrison managed to escape by sea, but the inhabitants and the city itself were destroyed.
 W
WThe Siege of Trebizond in April 1282 was an unsuccessful siege of Trebizond, the capital of the namesake empire, by the Georgian king David I of Imereti. Little is known about the attack, but it may have relied on support within the Trapezuntine aristocracy, which opposed the rapprochement of Emperor John II of Trebizond with the Palaiologan Byzantine court at Constantinople. Though King David failed to take the city, the Georgians occupied several provinces, including theme of Lazia.
 W
WThe Siege of Tyana was carried out by the Umayyad Caliphate in 707–708 or 708–709 in retaliation for a heavy defeat of an Umayyad army under Maimun the Mardaite by the Byzantine Empire in c. 706. The Arab army invaded Byzantine territory and laid siege to the city in summer 707 or 708. The date is uncertain, as virtually each of the extant Greek, Arabic, and Syriac parallel sources has in this respect a different date. Tyana initially withstood the siege with success, and the Arab army faced great hardship during the ensuing winter and was on the point of abandoning the siege in spring, when a relief army sent by Emperor Justinian II arrived. Quarrels among the Byzantine generals, as well as the inexperience of a large part of their army, contributed to a crushing Umayyad victory. Thereupon the inhabitants of the city were forced to surrender. Despite the agreement of terms, the city was plundered and largely destroyed, and according to Byzantine sources its people were made captive and deported, leaving the city deserted.