 W
WPhospholipids (PL) are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group, and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine.
 W
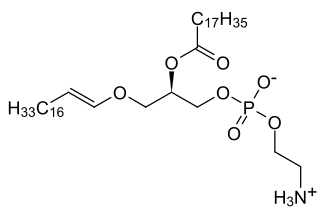
WPlasmalogens are a subclass of ether phospholipids that are commonly found in cell membranes in the nervous, immune and cardiovascular systems. There are two types of ether phospholipids, plasmanyl and plasmenyl. Plasmenyl-phospholipids, which include plasmalogen, and have an ether bond in position SN1 to an alkenyl group. Plasmanyl-phospholipids, in distinction, have an ether bond in position SN1 to an alkyl group.
 W
W2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholines are a class of phospholipids that are intermediates in the metabolism of lipids. Because they result from the hydrolysis of an acyl group from the sn-1 position of phosphatidylcholine, they are also called 1-lysophosphatidylcholine. The synthesis of phosphatidylcholines with specific fatty acids occurs through the synthesis of 1-lysoPC. The formation of various other lipids generates 1-lysoPC as a by-product.
 W
WDinogunellins are unusual toxic phospholipids found in the roe of some fishes, and is one of the best studied ichthyotoxin. These phospholipids could be found as a complex with non-toxic proteins like in the cabezon toxin or in the lipostichaerin.
 W
WDipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) is a phospholipid (and a lecithin) consisting of two C16 palmitic acid groups attached to a phosphatidylcholine head-group.
 W
WDolichyl β-d-glucosyl phosphate is a molecule involved in glycosylation. It is a polyprenyl glycosyl phosphate having dolichol as the polyprenyl component and β-d-glucose as the glycosyl component.
 W
WEgg lecithin is a type of lecithin, a group of compounds primarily containing phospholipids, that is derived from eggs.
 W
WThe presence of ethanol can lead to the formations of non-lamellar phases also known as non-bilayer phases. Ethanol has been recognized as being an excellent solvent in an aqueous solution for inducing non-lamellar phases in phospholipids. The formation of non-lamellar phases in phospholipids is not completely understood, but it is significant that this amphiphilic molecule is capable of doing so. The formation of non-lamellar phases is significant in biomedical studies which include drug delivery, the transport of polar and non-polar ions using solvents capable of penetrating the biomembrane, increasing the elasticity of the biomembrane when it is being disrupted by unwanted substances and functioning as a channel or transporter of biomaterial.
 W
WGlycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes.
 W
WHydroxylated lecithin is chemically modified lecithin. It is made by treating lecithin with hydrogen peroxide and an organic acid such as acetic or lactic acid. In the process, some of the organic acid becomes peroxy acid. The peroxy acid reacts with olefins in the fatty acid side chains creating intermediate epoxides. The epoxides react further with water, organic acid, or peroxy acid, to ultimately form vicinal diols. Because the natural fatty acid olefins have (Z)-configurations, the resulting vicinal diols have anti stereochemical configurations.
 W
WLecithin is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances, and are used for smoothing food textures, emulsifying, homogenizing liquid mixtures, and repelling sticking materials.
 W
WLysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a phospholipid derivative that can act as a signaling molecule.
 W
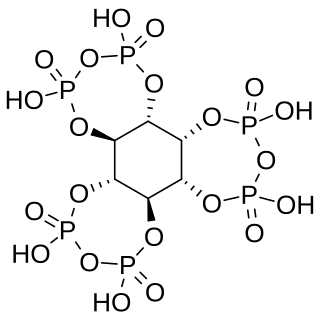
WMyo-inositol trispyrophosphate (ITPP) is an inositol phosphate, a pyrophosphate, a drug candidate, and a putative performance-enhancing substance, which exerts its biological effects by increasing tissue oxygenation.
 W
WPerifosine is a drug candidate being developed for a variety of cancer indications. It is an alkyl-phospholipid structurally related to miltefosine. It acts as an Akt inhibitor and a PI3K inhibitor. It was being developed by Keryx Biopharmaceuticals who have licensed it from Æterna Zentaris Inc.
 W
WPhosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup. They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybeans, from which they are mechanically or chemically extracted using hexane. They are also a member of the lecithin group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues. Dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine is a major component of pulmonary surfactant and is often used in the L/S ratio to calculate fetal lung maturity. While phosphatidylcholines are found in all plant and animal cells, they are absent in the membranes of most bacteria, including Escherichia coli. Purified phosphatidylcholine is produced commercially.
 W
WPhosphatidylethanols (PEth) are a group of phospholipids formed only in the presence of ethanol via the action of phospholipase D (PLD). The lipid accumulates in the brain and competes at agonists sites of lipid-gated ion channels contributing to alcohol intoxication. The chemical similarity of PEth to phosphatidic acid (PA) and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) suggest a likely broad perturbation to lipid signaling, the exact role of PEth as a competitive lipid ligand has not been studied extensively.
 W
WPhosphatidylethanolamines are a class of phospholipids found in biological membranes. They are synthesized by the addition of cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine to diglycerides, releasing cytidine monophosphate. S-Adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidylethanolamines to yield phosphatidylcholines. It can mainly be found in the inner (cytoplasmic) leaflet of the lipid bilayer.
 W
WPhosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant and in the plasma membrane where it directly activates lipid-gated ion channels.
 W
WPhosphatidylinositol consists of a family of lipids as illustrated on the right, where red is x, blue is y, and black is z, in the context of independent variation, a class of the phosphatidylglycerides. In such molecules the isomer of the inositol group is assumed to be the myo- conformer unless otherwise stated. Typically phosphatidylinositols form a minor component on the cytosolic side of eukaryotic cell membranes. The phosphate group gives the molecules a negative charge at physiological pH.
 W
WPhosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3), abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI 3-kinases) phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2). It is a phospholipid that resides on the plasma membrane.
 W
WPhosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns3P) is a phospholipid found in cell membranes that helps to recruit a range of proteins, many of which are involved in protein trafficking, to the membranes. It is the product of both the class II and III phosphoinositide 3-kinases activity on phosphatidylinositol.
 W
WPhosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes, yet an important second messenger. The generation of PtdIns(3,4)P2 at the plasma membrane activates a number of important cell signaling pathways.
 W
WPhosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)P2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins.
 W
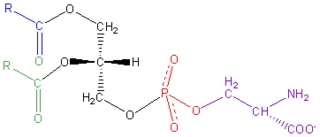
WPhosphatidylserine is a phospholipid and is a component of the cell membrane. It plays a key role in cell cycle signaling, specifically in relation to apoptosis. It is a key pathway for viruses to enter cells via apoptotic mimicry.
 W
WSphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphocholine and ceramide, or a phosphoethanolamine head group; therefore, sphingomyelins can also be classified as sphingophospholipids. In humans, SPH represents ~85% of all sphingolipids, and typically make up 10–20 mol % of plasma membrane lipids.